Adding Integers - Number Search WORKSHEET
Adding Integers - Number Search WORKSHEET DESCRIPTION
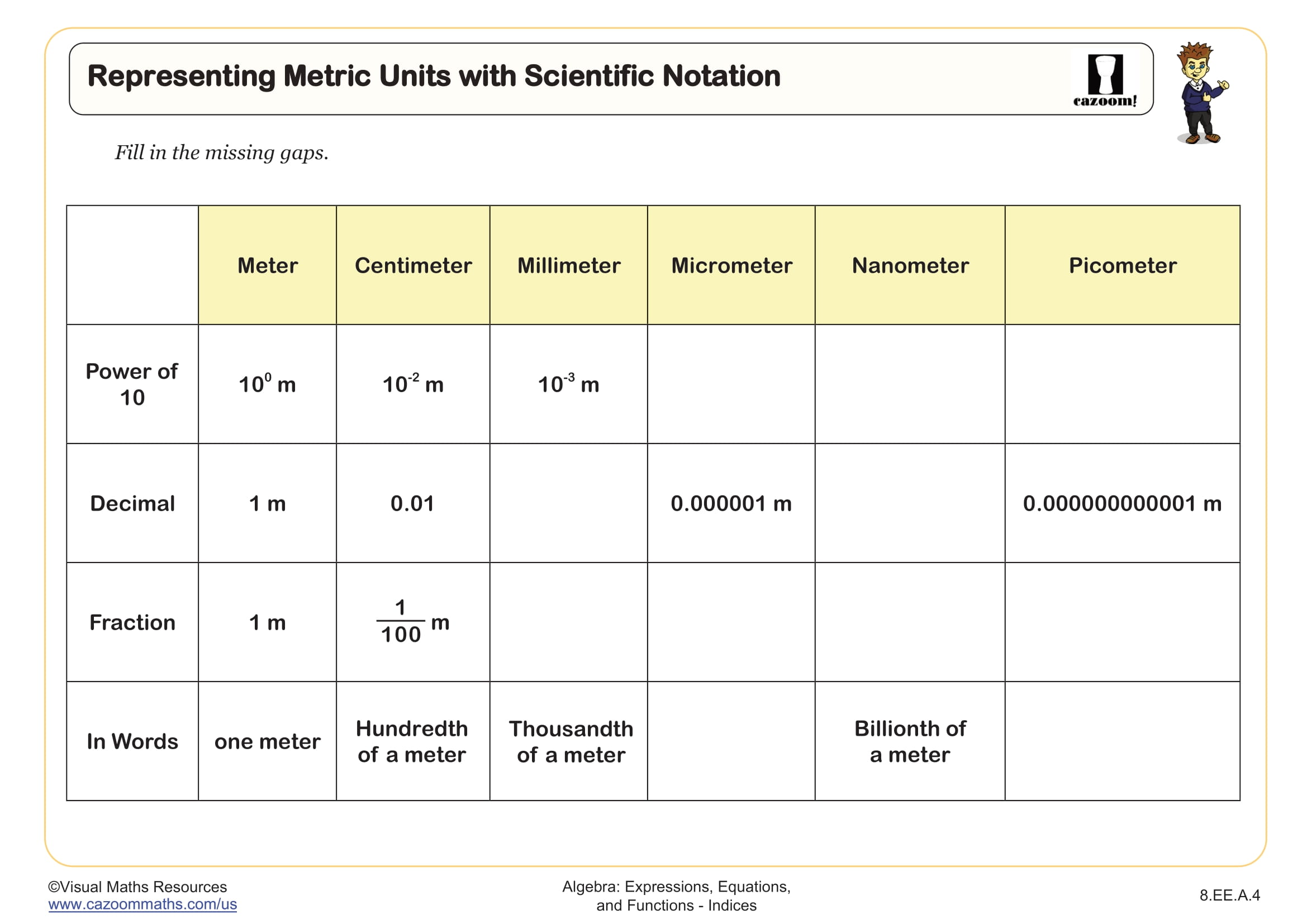
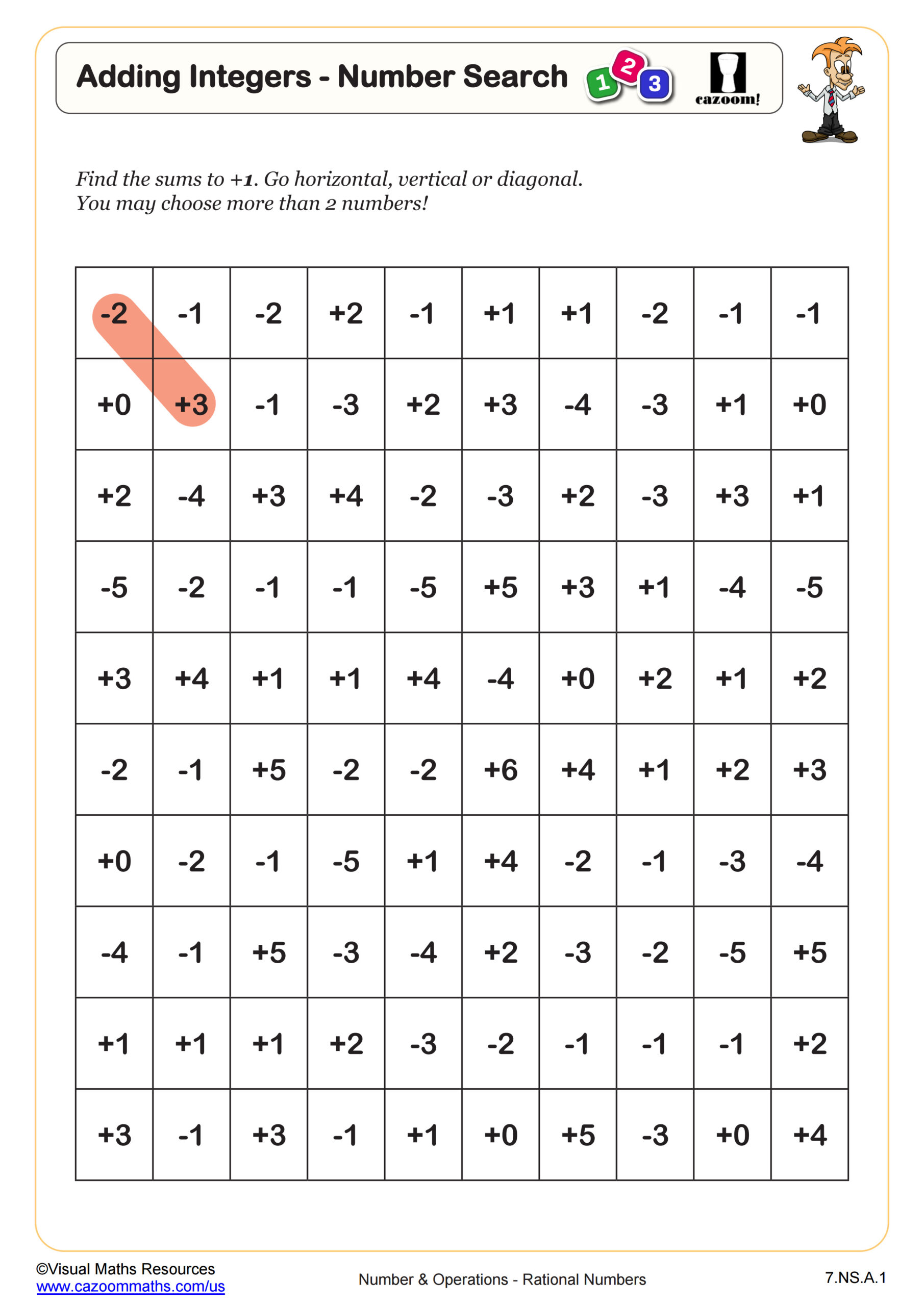
This fun number search involves students finding sets numbers that sum to 1 and is perfect for students getting used to addition that crosses zero, the commutativity of addition, and addition involving negative and positive numbers.
Numbers can be combined horizontally, vertically, and diagonally, and may contain up to four numbers. Our answers show numbers being used more than once, but teachers and parents can make up their own minds on this rule. Why not add a competitive edge: who will find the most? Who will be the first to find 30 sets of numbers that sum to 1?
All worksheets are created by the team of experienced teachers at Cazoom Math.
RELATED TO Adding Integers - Number Search WORKSHEET
Frequently Asked Questions
This adding integers - number search worksheet is designed for students in 7th Grade and aligns with Common Core State Standards.