Dividing a Number by 1 and Itself WORKSHEET
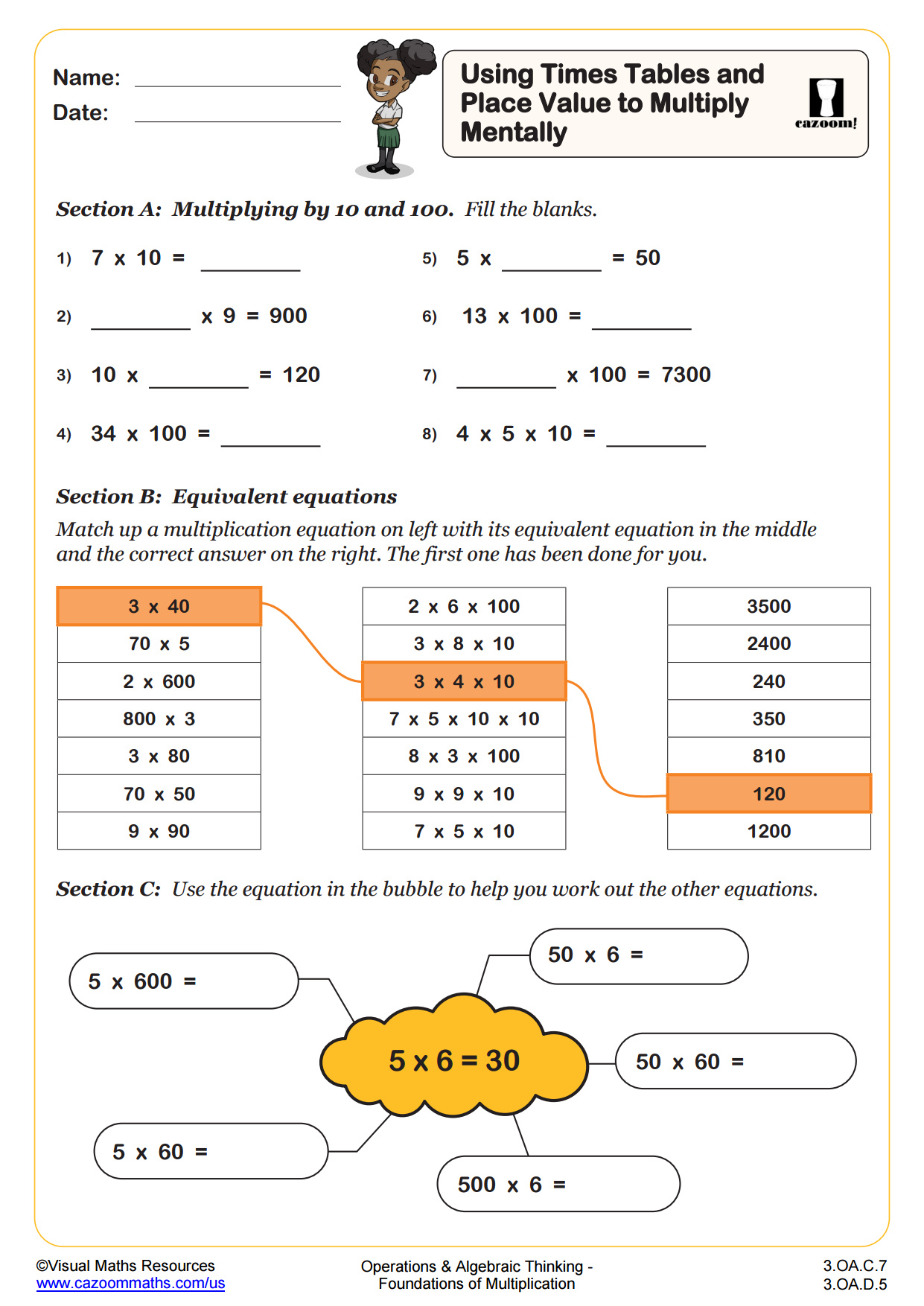
Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide.2 Examples: If 6 × 4 = 24 is known, then 4 × 6 = 24 is also known. (Commutative property of multiplication.) 3 × 5 × 2 can be found by 3 × 5 = 15, then 15 × 2 = 30, or by 5 × 2 = 10, then 3 × 10 = 30. (Associative property of multiplication.) Knowing that 8 × 5 = 40 and 8 × 2 = 16, one can find 8 × 7 as 8 × (5 + 2) = (8 × 5) + (8 × 2) = 40 + 16 = 56. (Distributive property.)
Dividing a Number by 1 and Itself WORKSHEET DESCRIPTION
The worksheet mixes theory, practical exercises, and a fun puzzle to enhance understanding.
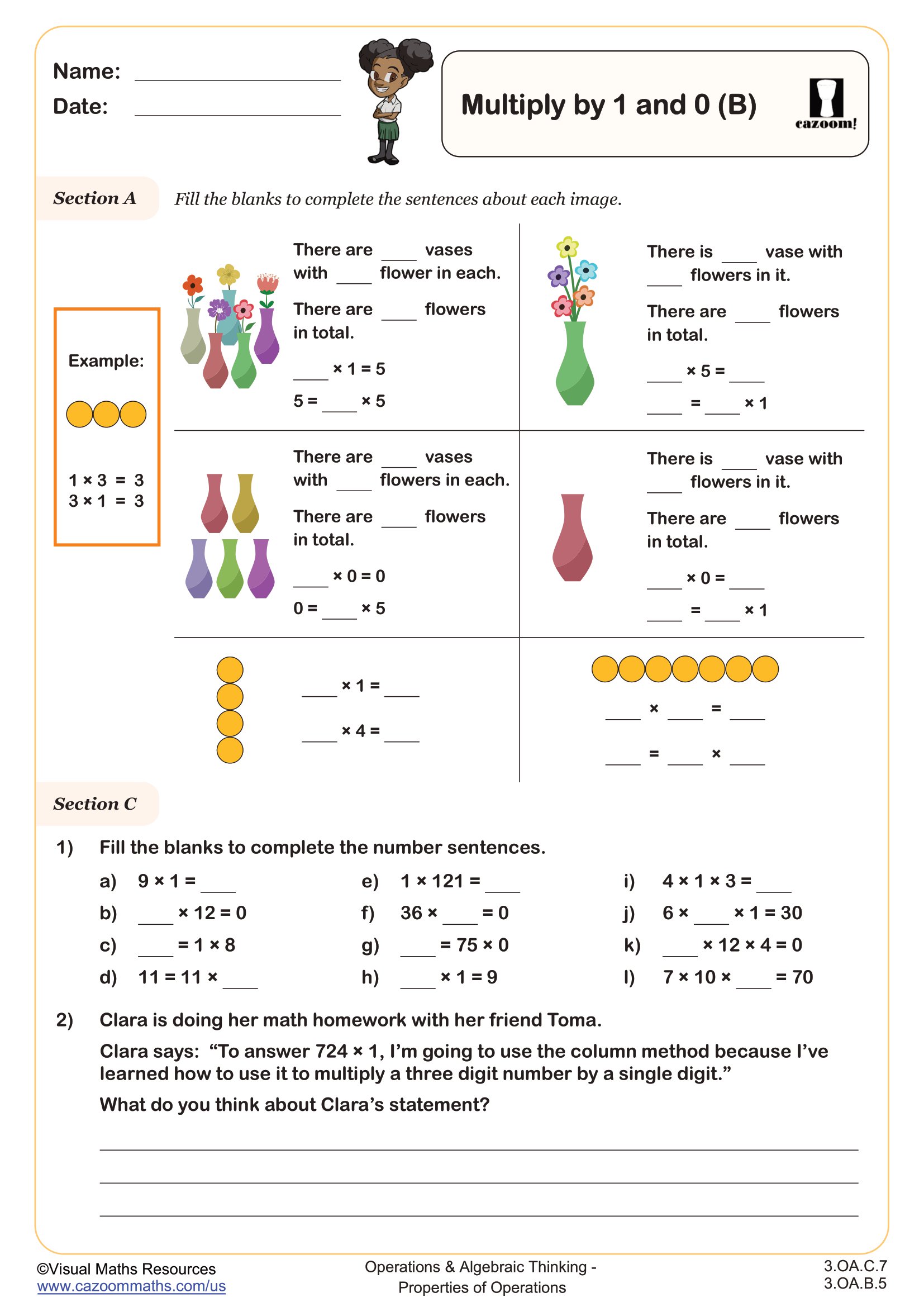
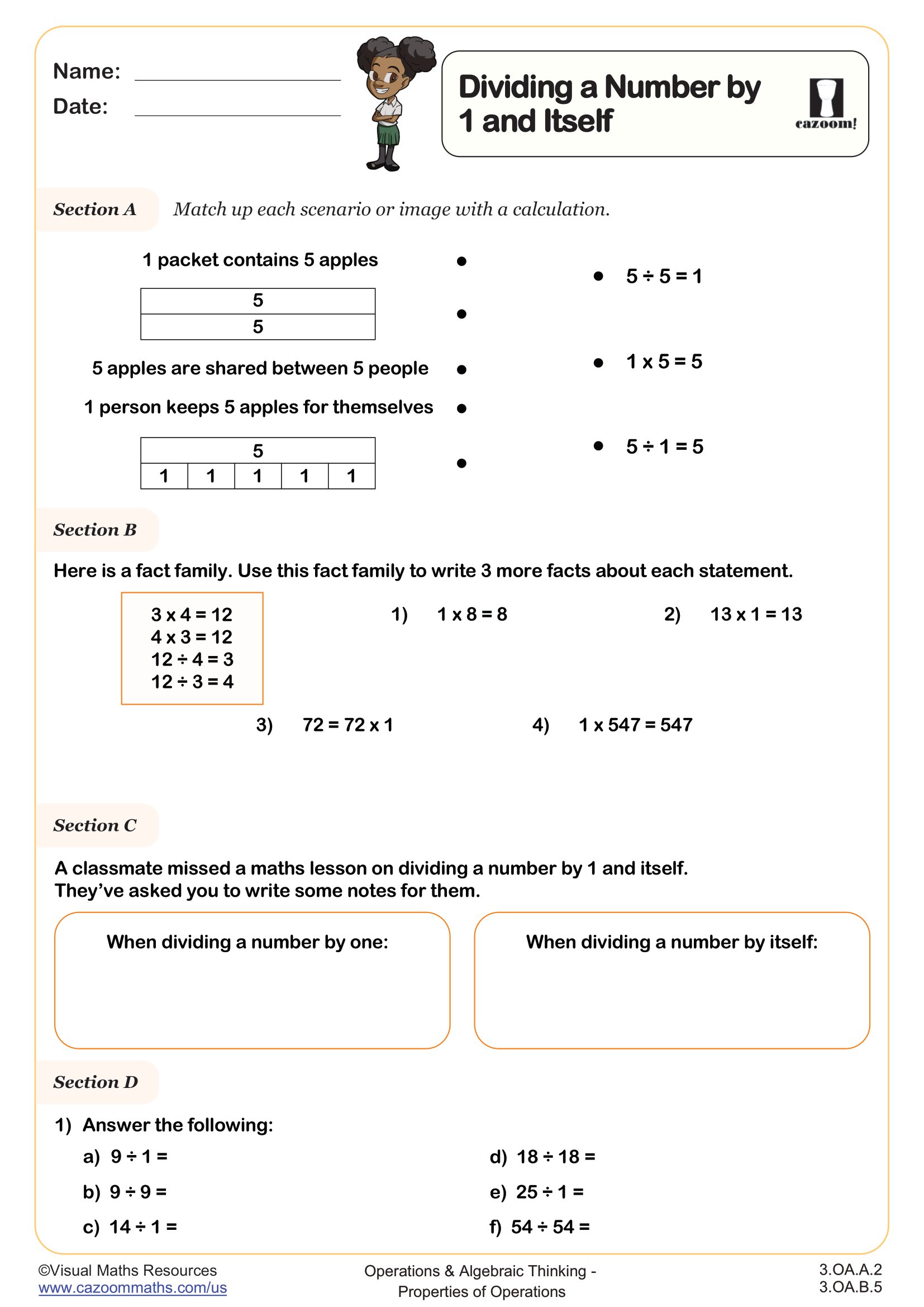
Section A provides scenarios or images for students to match with appropriate calculations.
Next in section B students write multiplication and division fact families, all of which involve multiplying by 1 and therefore dividing by 1 and the number itself.
Learners have a chance to articulate what they notice in section C as they are asked to write notes for a classmate who missed a lesson on dividing a number by 1 and itself.
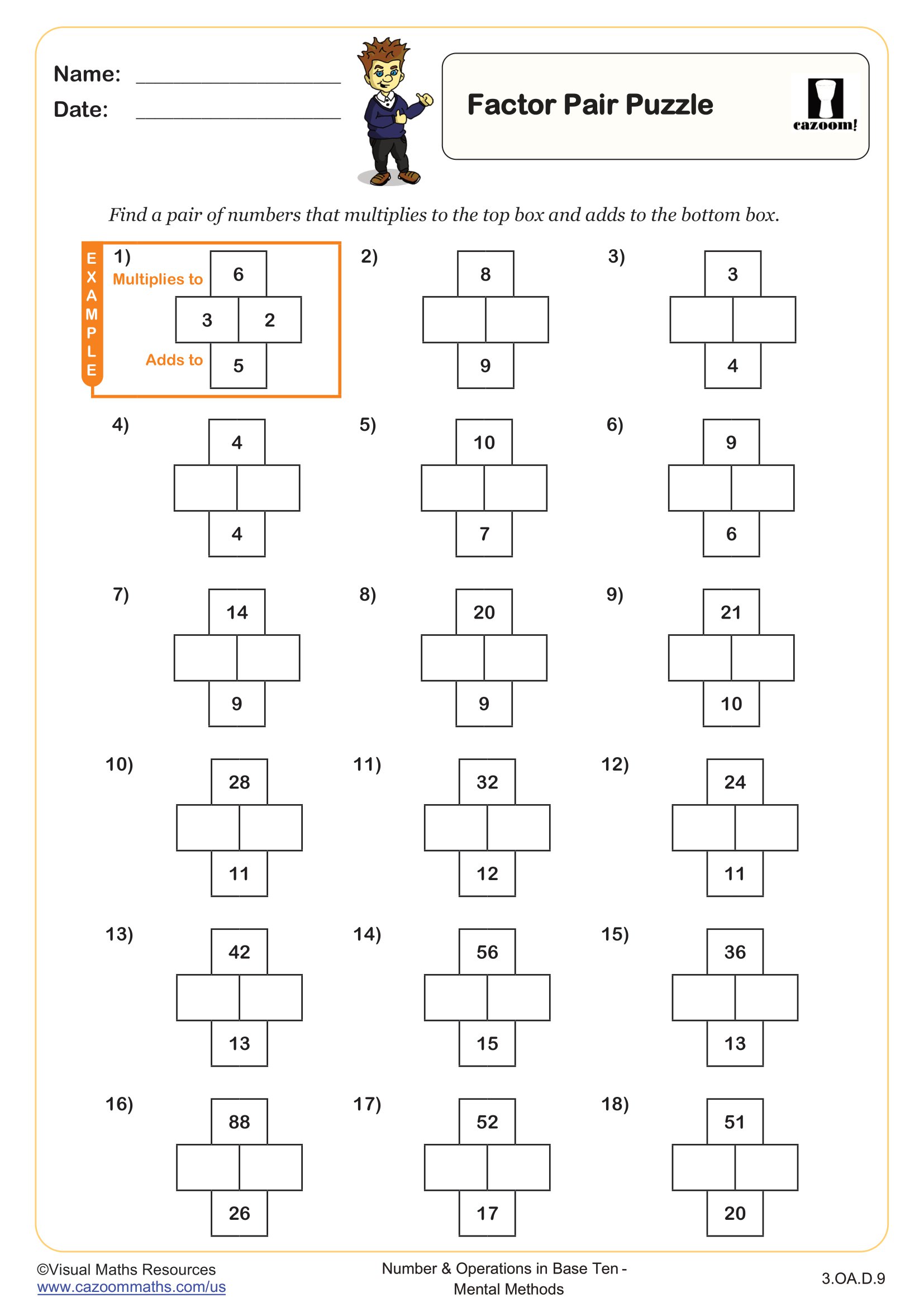
Section D contains various exercises like filling in blanks, identifying the odd one out from a set of division and multiplication statements, deciding whether statements are true or false and a code breaker.
All worksheets are created by the team of experienced teachers at Cazoom Math.
RELATED TO Dividing a Number by 1 and Itself WORKSHEET
Frequently Asked Questions
This dividing a number by 1 and itself worksheet is designed for students in 3rd Grade and aligns with Common Core State Standards.