Evaluating Exponential Expressions (A) WORKSHEET
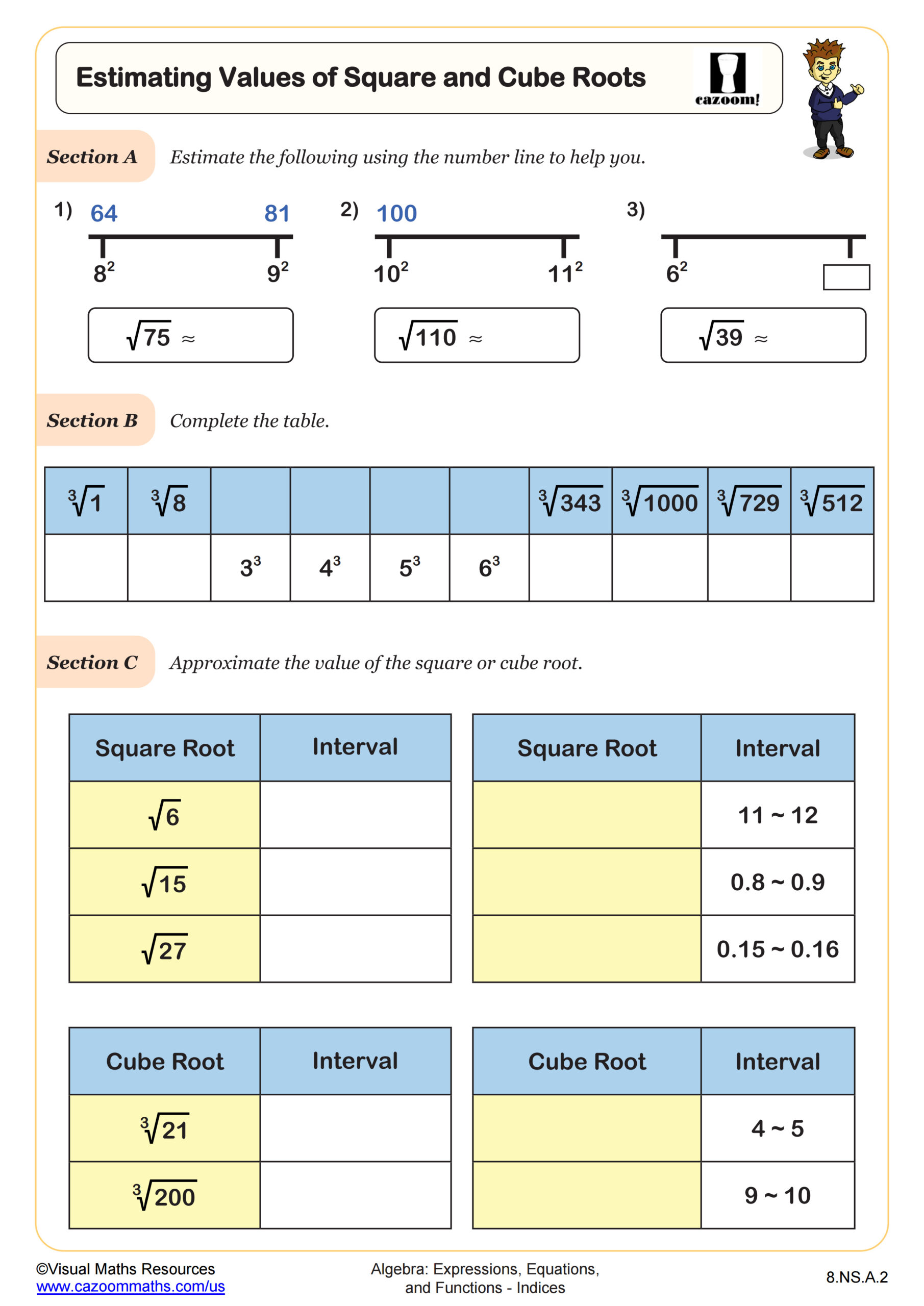
Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x2 = p and x3 = p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Know that √2 is irrational.
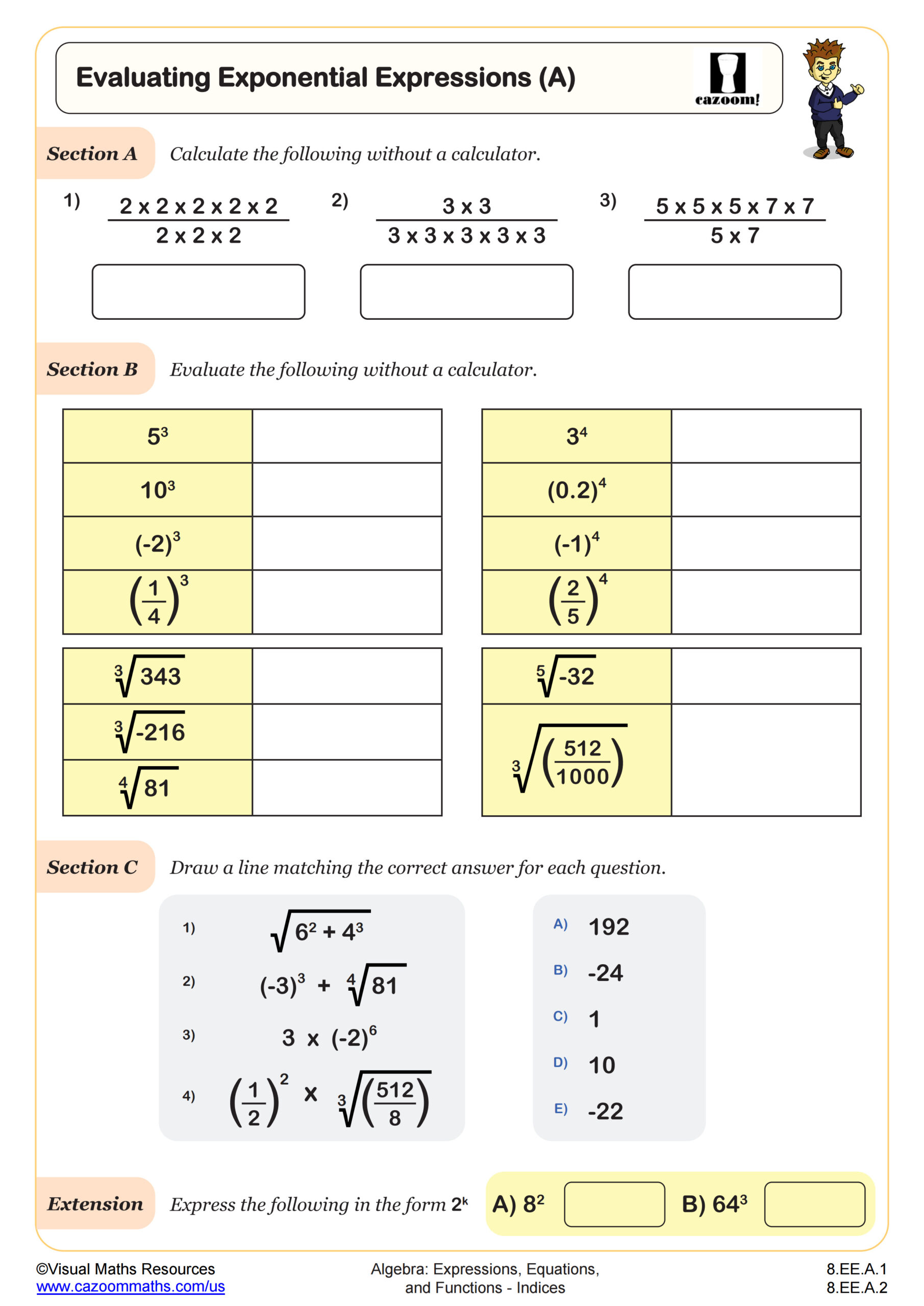
Evaluating Exponential Expressions (A) WORKSHEET DESCRIPTION
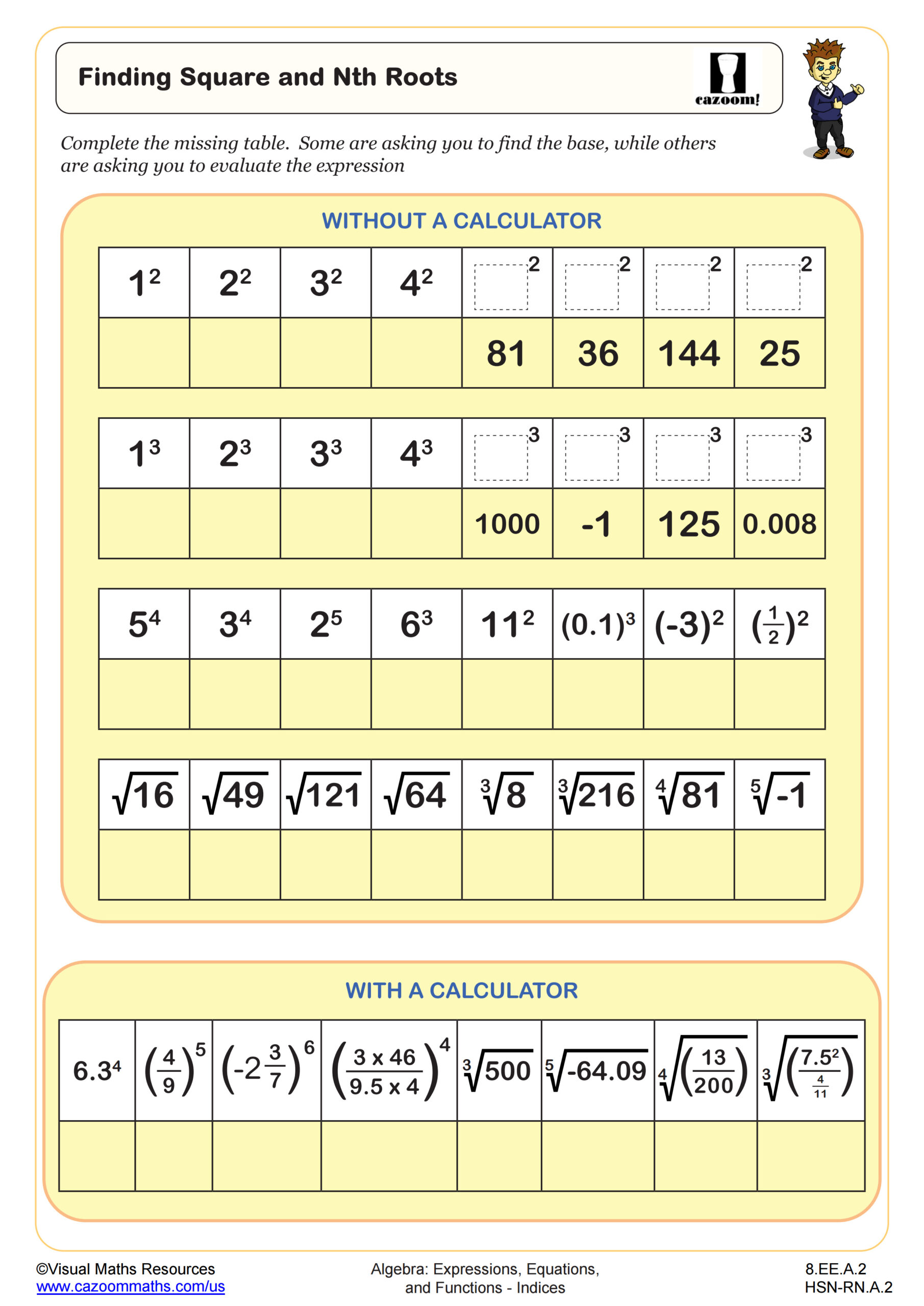
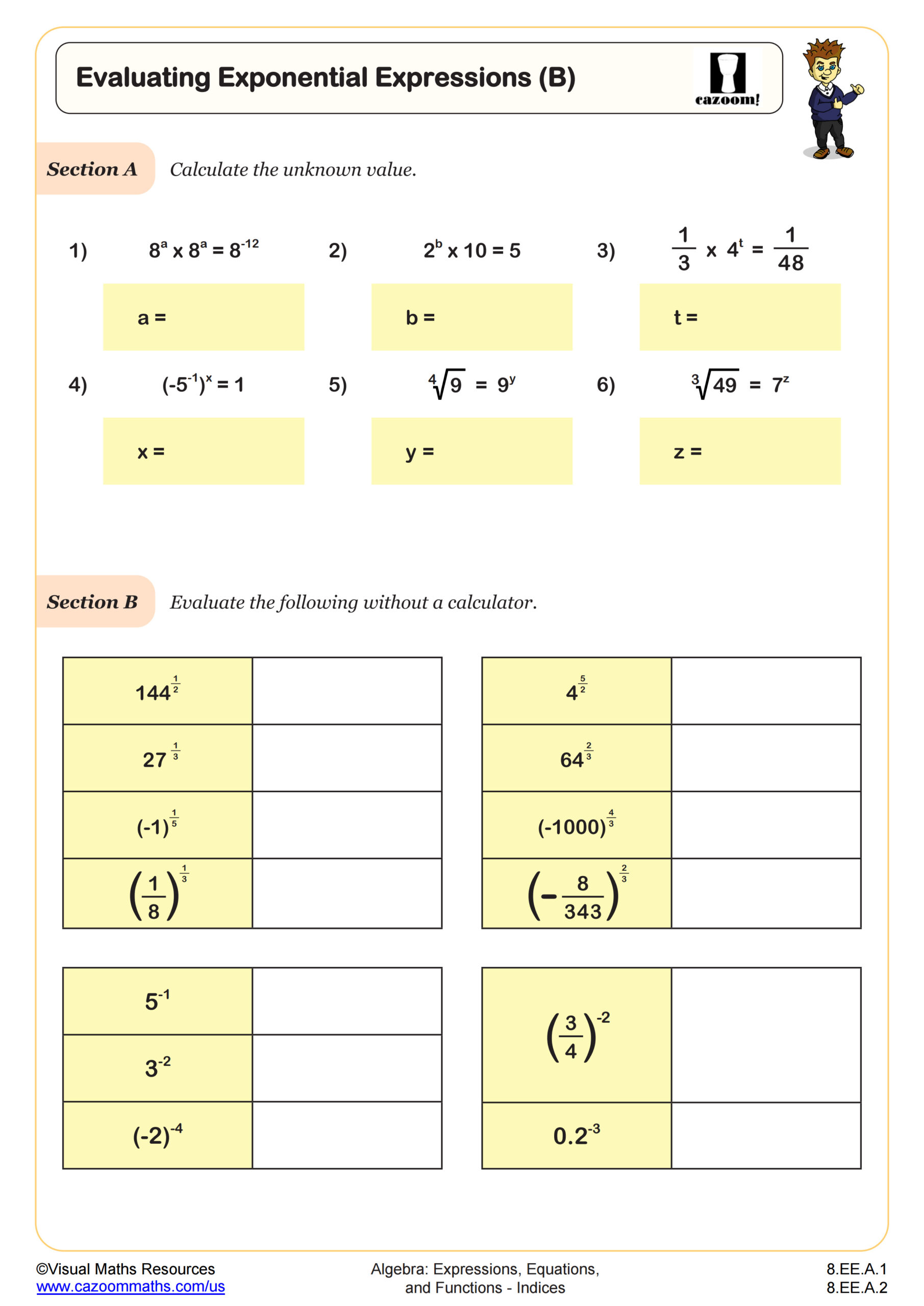
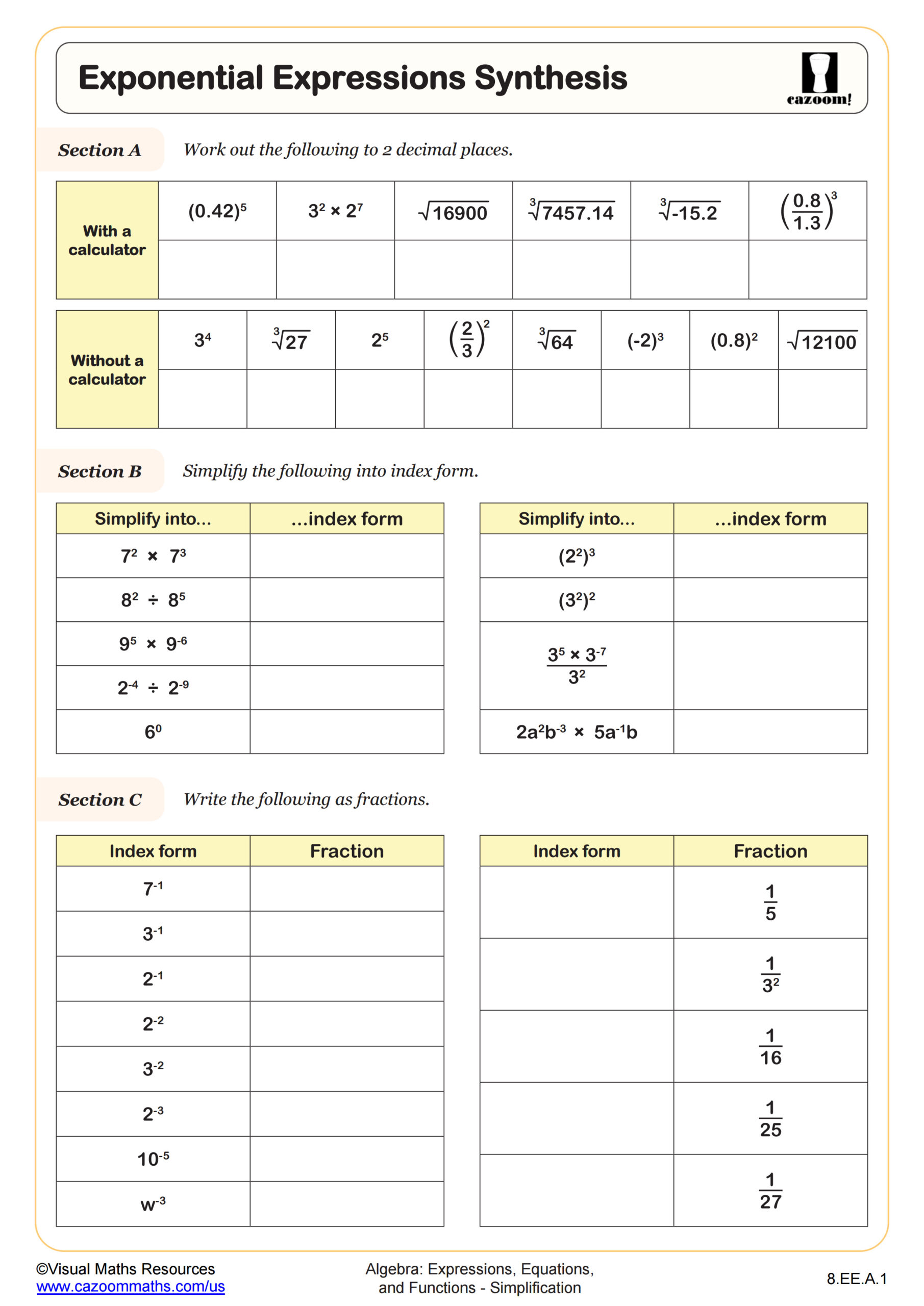
Following on from Finding Square and Nth Roots, this worksheet asks learners to consolidate their knowledge of powers and roots by simplifying some calculations and applying them to integers and fractions. Section A begins the worksheet with a few calculations of fractions to simplify and evaluate. Section B then requires learner to recall some powers of 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 applying powers and roots to integers, fractions, and decimals. Section C presents a matching task with some more complicated exponent problems. A final extension problem asks learners to change the base of some numbers in exponential form.
RELATED TO Evaluating Exponential Expressions (A) WORKSHEET
Frequently Asked Questions
This evaluating exponential expressions (a) worksheet is designed for students in 8th Grade and aligns with Common Core State Standards.