Finding the Difference - Directed Numbers WORKSHEET
Finding the Difference - Directed Numbers WORKSHEET DESCRIPTION
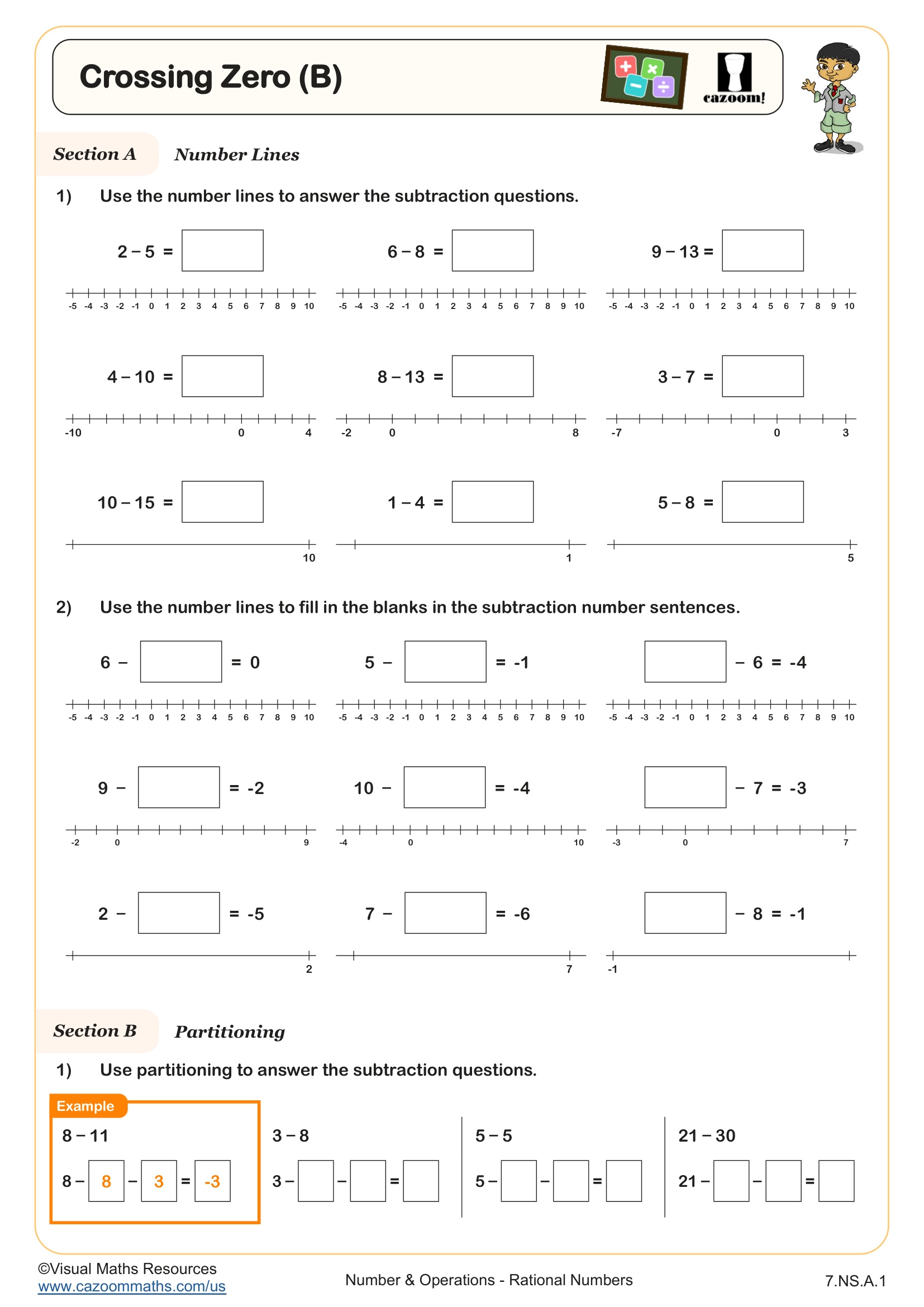
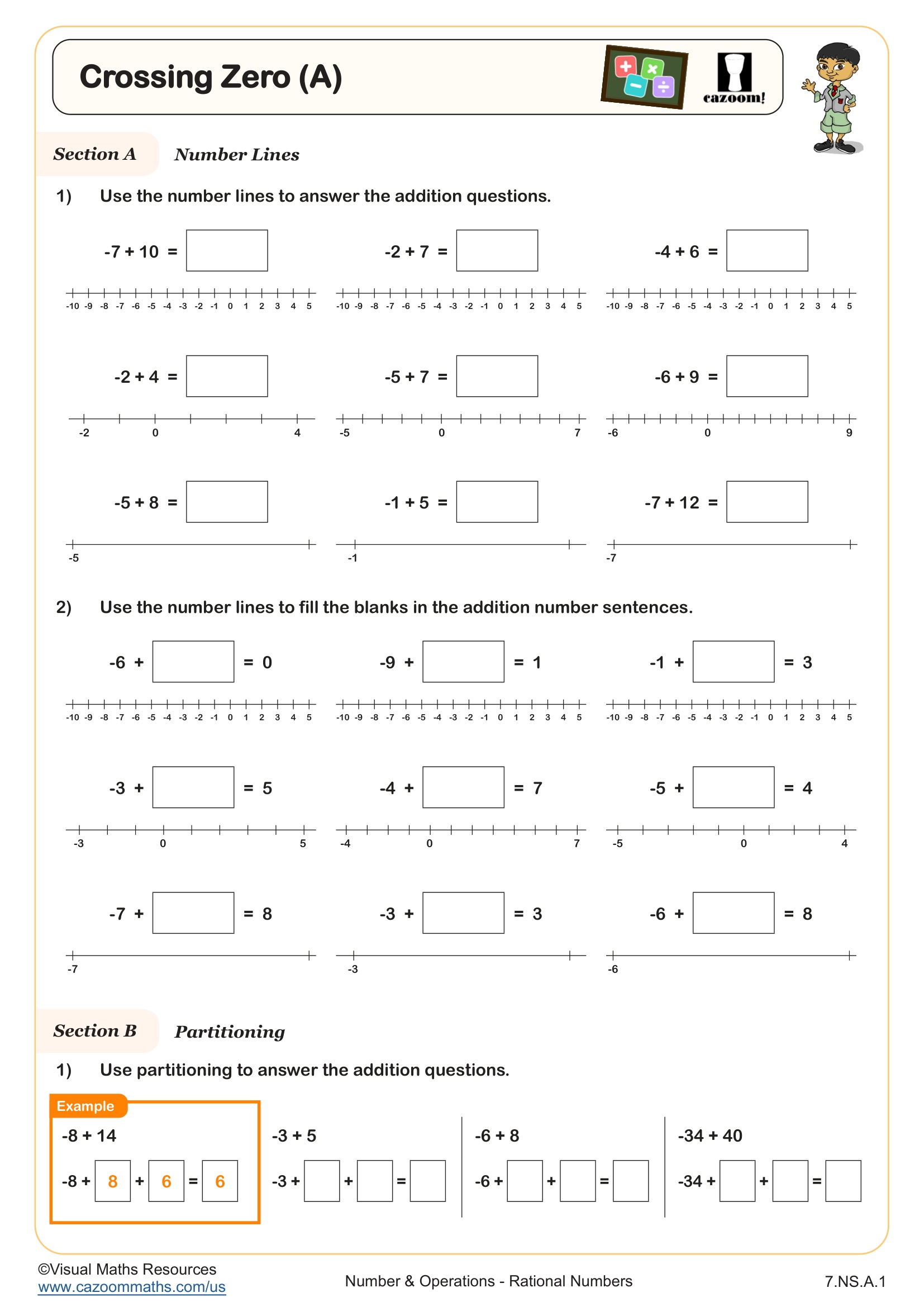
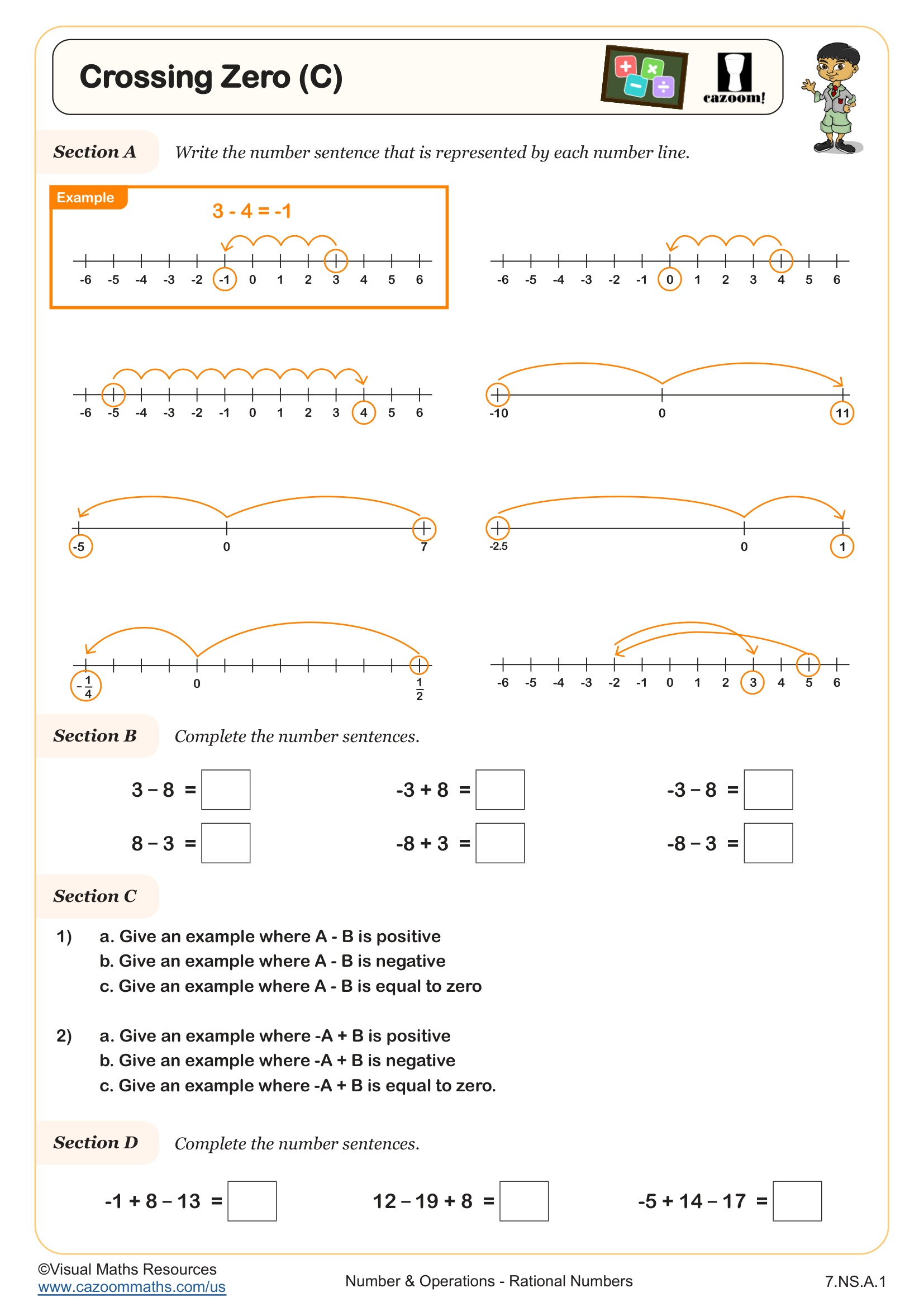
Teaching students to find the difference between numbers as the distance between them on the number line, reinforces the idea that subtraction is about finding how far apart two values are and will aid your learners in taking the next steps towards addition and subtraction of positive and negative numbers.
The worksheet begins with a reminder of what it means to find the difference between pairs of positive numbers.
Section B utilises number lines to aid students to find the difference between a positive and negative number and leads on to make links to the equality of the expressions x - (-y) and x + y.
In section C, students will use what they learned as they find the difference between pairs of positive and negative numbers.
Learners will calculate with fractions and as such should be able to add and subtract fractions with different denominators.
All worksheets are created by the team of experienced teachers at Cazoom Math.

RELATED TO Finding the Difference - Directed Numbers WORKSHEET
Frequently Asked Questions
This finding the difference - directed numbers worksheet is designed for students in 7th Grade and aligns with Common Core State Standards.