Manipulating Equations WORKSHEET
Create equations and inequalities in one variable and use them to solve problems. Include equations arising from linear and quadratic functions, and simple rational and exponential functions.
Manipulating Equations WORKSHEET DESCRIPTION
This resource is designed to improve students’ algebraic thinking by guiding them through the step-by-step manipulation of equations, an essential skill in solving algebra problems.
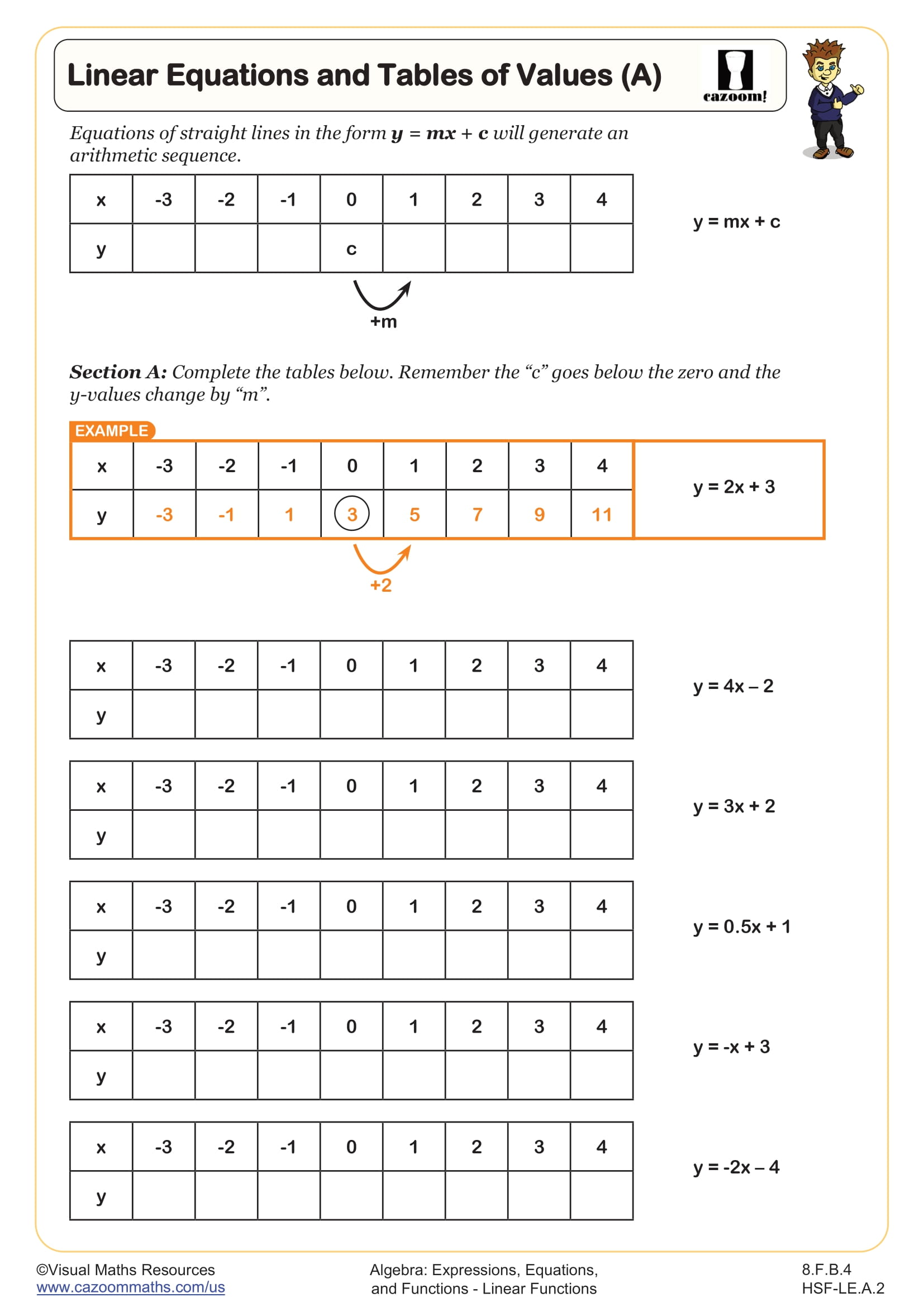
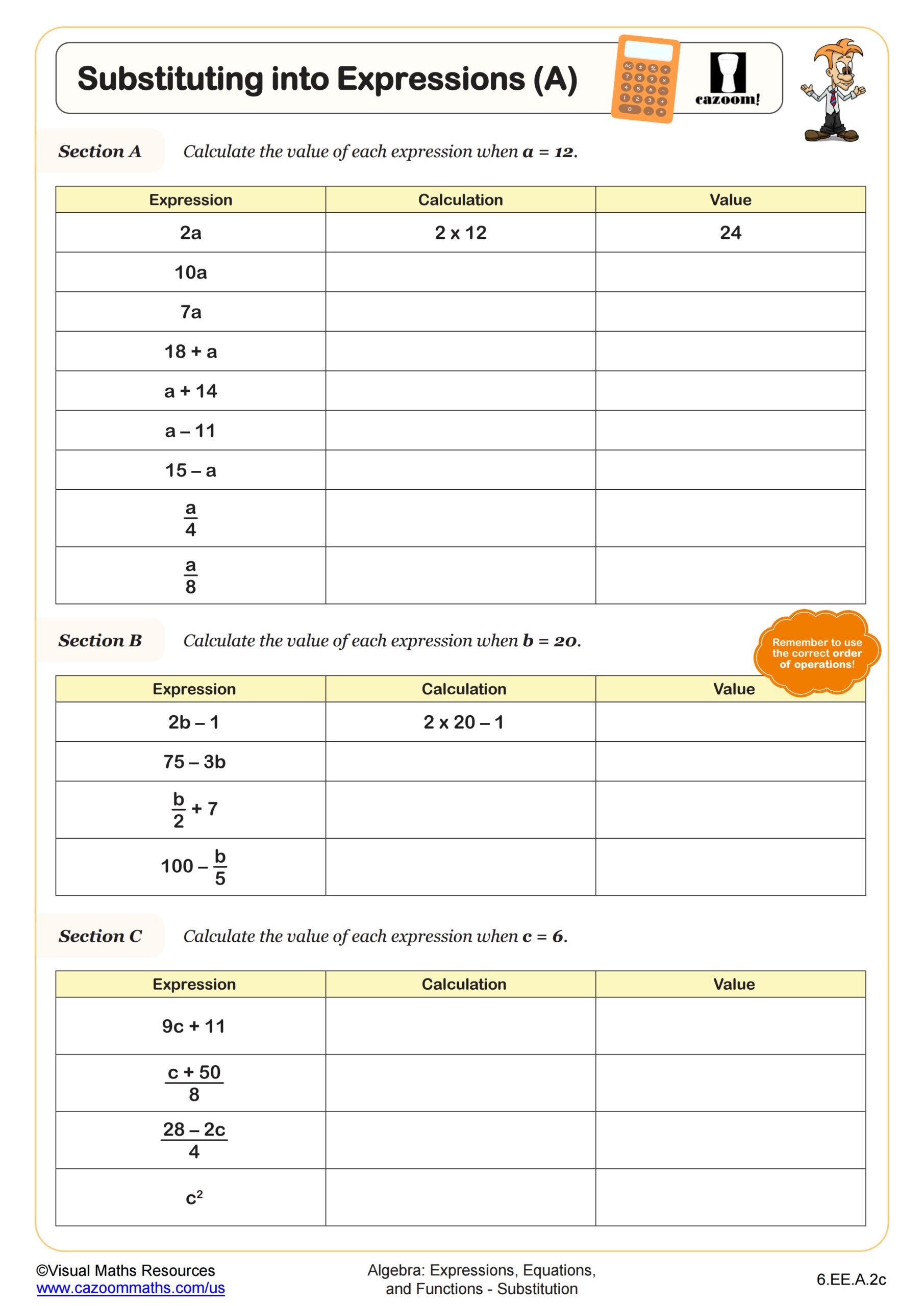
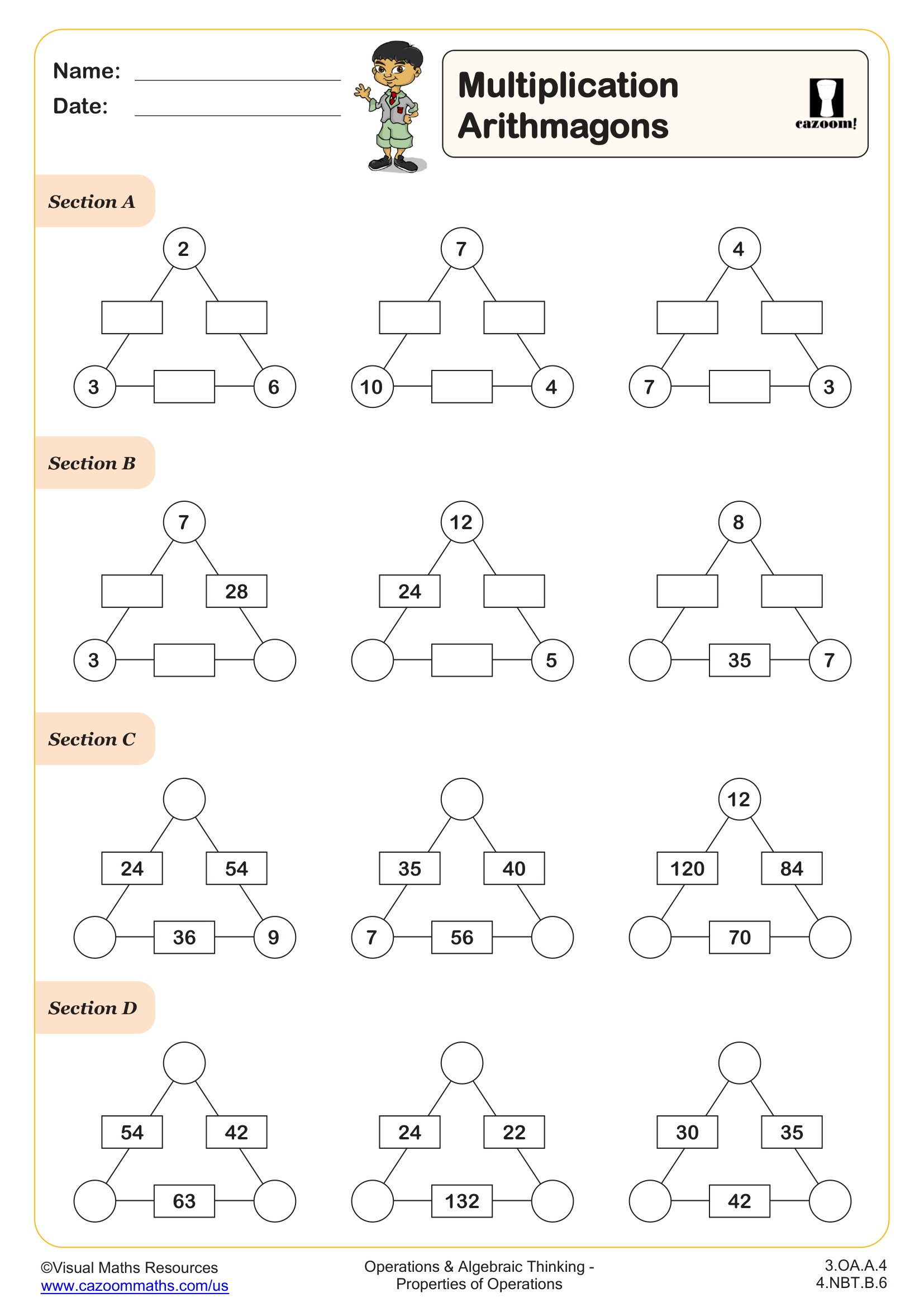
In this worksheet, learners begin with simple operations, applying addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division to both sides of an equation; it requires students to rewrite the equation after performing the specified operation, helping them understand how different operations impact both sides of the equation.
By practicing these varied examples, students will develop the skills necessary to confidently manipulate and solve equations. This makes it an excellent resource for mastering algebraic manipulation.
All worksheets are created by the team of experienced teachers at Cazoom Math.

RELATED TO Manipulating Equations WORKSHEET
Frequently Asked Questions
This manipulating equations worksheet is designed for students in 6th Grade and aligns with Common Core State Standards.