7th Grade PEMDAS Worksheets
What Does PEMDAS Stand For and Why Do 7th Graders Need It?
PEMDAS is a mnemonic device representing the order of operations: Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division (left to right), Addition and Subtraction (left to right). Seventh graders need mastery of PEMDAS because it governs how they evaluate algebraic expressions, solve multi-step equations, and work with formulas across all STEM subjects. This skill appears extensively in Common Core State Standards for grade 7 and directly impacts success in algebra courses.
A common misconception is that multiplication always comes before division or addition before subtraction. Students often evaluate 8 ÷ 2 × 4 as 8 ÷ 8 = 1 instead of working left to right to get 16. Teachers notice this error disappears when students recognize that operations at the same level are performed in the order they appear, not based on the acronym's letter order.
Are These Worksheets Right for 7th Grade Students?
These worksheets are specifically designed for 7th grade students in middle school, aligning with curriculum standards that expect fluency with complex order of operations problems. At this level, students move beyond basic PEMDAS introduced in 6th grade to work with negative numbers, fractions as division, and expressions requiring multiple applications of the rules.
In 6th grade, students typically encounter simpler order of operations with whole numbers and basic parentheses. By 7th grade, the complexity increases to prepare students for 8th grade algebra, where they'll apply PEMDAS to evaluate expressions with variables, simplify algebraic terms, and solve equations. This progression ensures students can handle expressions like 3(2x + 5) - 4² without computational errors that derail algebraic reasoning.
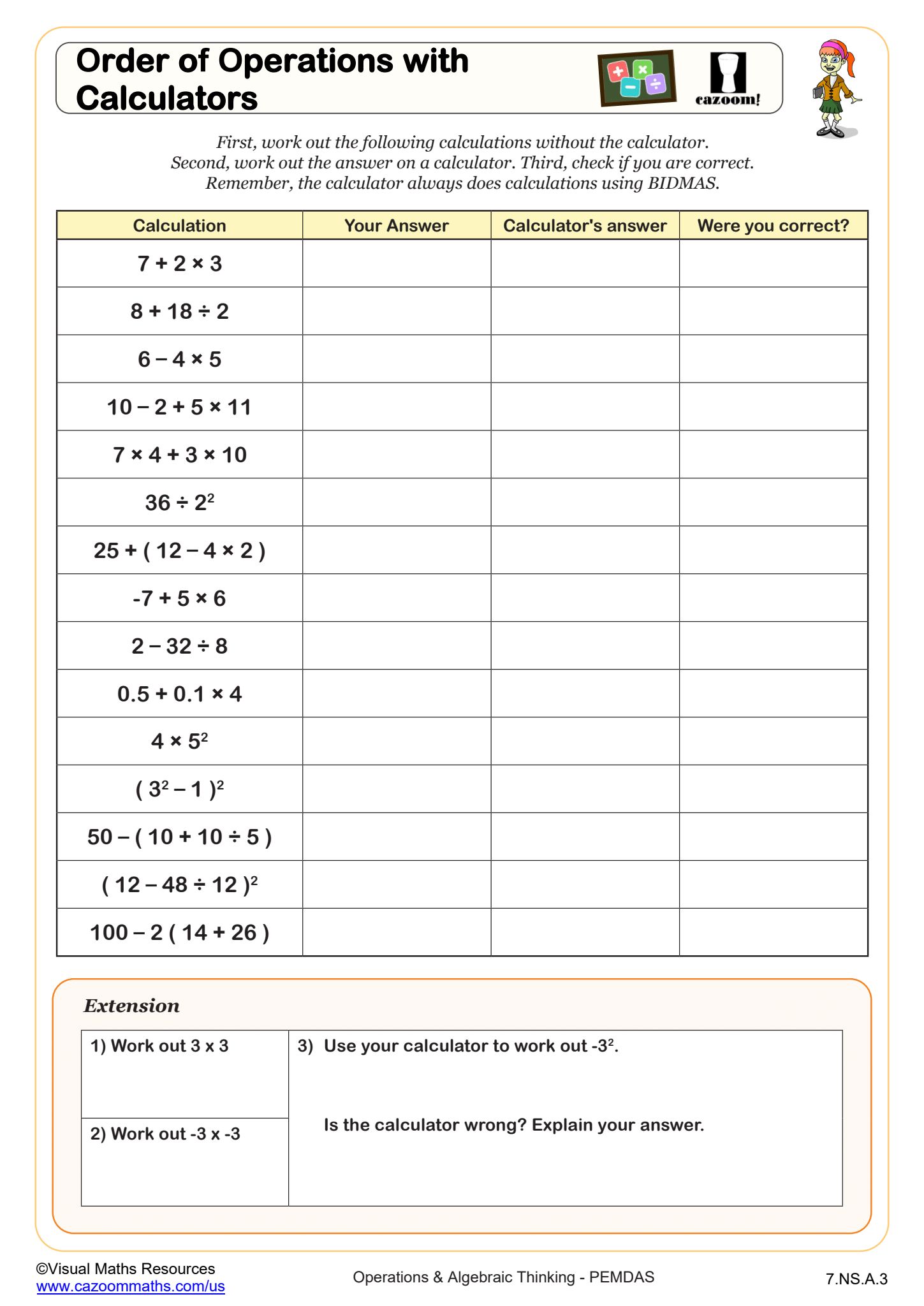
How Do Students Practice Adding Parentheses to Change Expression Values?
Adding parentheses strategically changes which operations are performed first, altering an expression's final value. Students work with problems like 5 + 3 × 2 = 11, then explore how (5 + 3) × 2 = 16 produces a different result. This skill develops algebraic thinking and helps students understand why grouping symbols matter in mathematical communication and formula construction.
This concept connects directly to computer programming and engineering, where parentheses in code determine calculation order. In spreadsheet formulas, financial calculations, and CAD software, incorrect parentheses placement produces wrong results. Students who master this skill recognize that writing =(A1+B1)*C1 versus =A1+B1*C1 in Excel yields different values, making this practice relevant for data science, accounting, and any STEM field requiring precise computational instructions.
How Can Teachers Use These PEMDAS Worksheets Effectively?
The worksheets scaffold learning by separating skills into focused practice areas. Students might start with basic four-operation problems, progress to expressions with parentheses and exponents, then tackle fractions as division and calculator use. The templates allow students to create their own PEMDAS problems, which deepens understanding as they consider what makes a problem challenging or what operation order creates specific answers.
Teachers use these worksheets for targeted intervention when grading reveals consistent order of operations errors, as warm-ups before introducing algebraic expressions, or as homework to reinforce classroom instruction. The answer keys make them valuable for student self-checking during independent practice or math centers. Many teachers assign different subtopics to small groups, then have students teach their section to peers, which builds both mastery and mathematical communication skills required for middle school assessments.