8th Grade Position and Direction Worksheets
What Does Position and Direction Cover in 8th Grade Math?
Position and direction in 8th grade focuses on transformations in the coordinate plane, including reflections, rotations, translations, and their combinations. Students analyze how figures change position while preserving size and shape, developing understanding of congruence through transformation. This connects directly to Common Core Standard 8.G.A, which requires students to understand and apply properties of rotations, reflections, and translations.
Students lose points on assessments when they confuse the direction of rotations or apply reflections across the wrong axis. Teachers notice that students perform better when they physically trace transformations on graph paper before attempting abstract problems. The symmetry work in these worksheets builds the foundation for understanding reflection as a specific type of transformation with predictable properties.
What Should 8th Graders Know About Symmetry and Transformations?
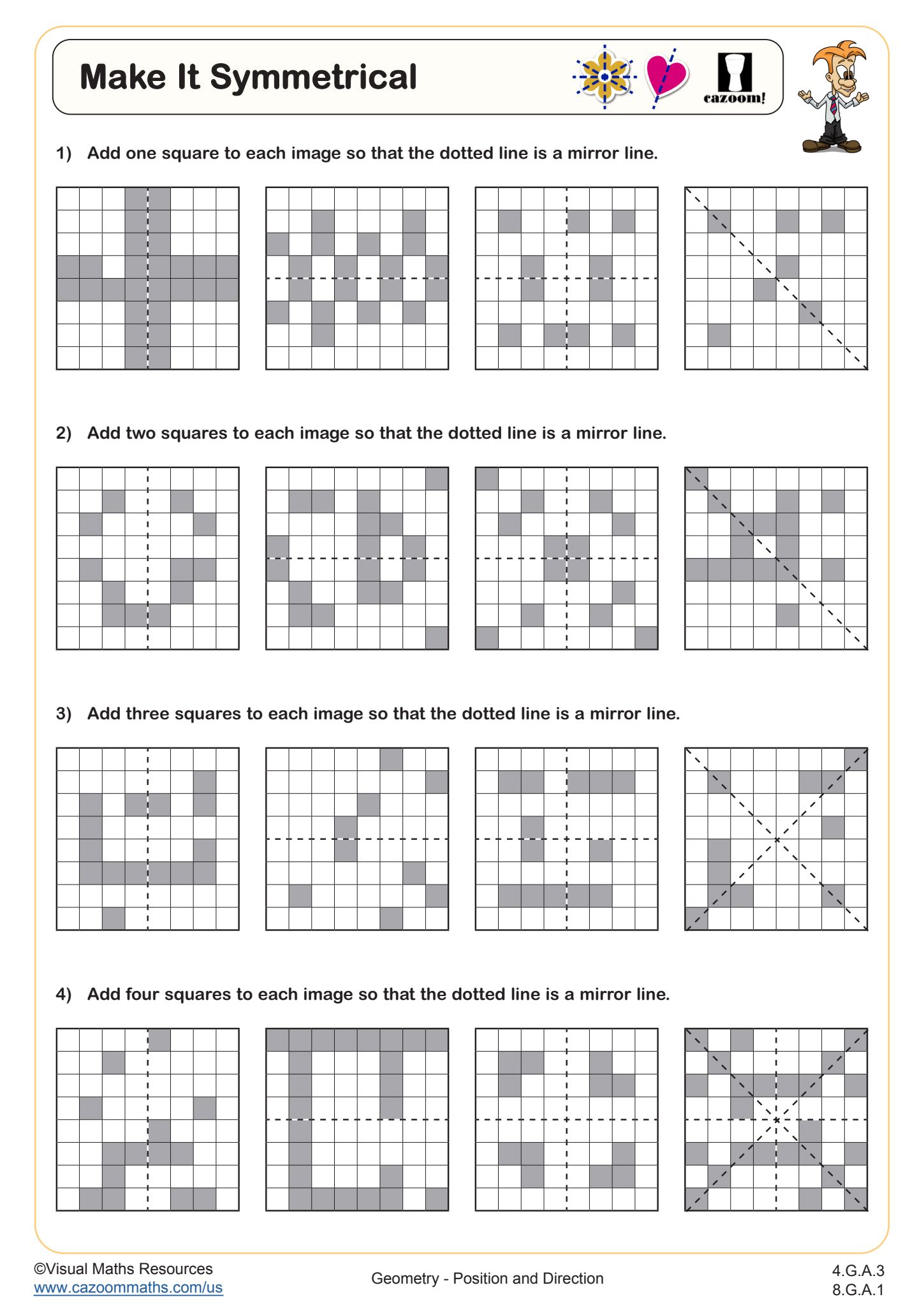
By 8th grade, students should recognize multiple lines of symmetry in geometric figures and complete symmetric patterns accurately on coordinate grids. They need to understand that symmetry represents a special case of reflection where a figure maps onto itself. Students at this level should describe transformations using precise mathematical language and identify corresponding points across lines of symmetry, maintaining equal perpendicular distances from the reflection line.
This builds directly on 7th grade work with scale drawings and proportional relationships, while preparing students for high school geometry's formal study of rigid transformations and congruence proofs. Students who master symmetry concepts in middle school transition more smoothly to understanding function transformations in Algebra II and analyzing geometric relationships in advanced mathematics courses.
How Does Line Symmetry Work on Coordinate Grids?
Line symmetry on coordinate grids requires students to reflect points across a specified axis or line, creating mirror images with equal distances from the line of reflection. When reflecting across the y-axis, the x-coordinate changes sign while the y-coordinate remains constant. Horizontal and vertical lines of symmetry are most common, though students also encounter diagonal lines like y = x, which swap coordinate values. Students confidently tackle symmetry problems once they recognize that each point and its reflection sit equidistant from the symmetry line.
Symmetry appears throughout STEM fields, from engineering designs that must balance structural loads to computer graphics algorithms that generate reflections in video games and animation software. Architects use symmetry principles when designing building facades, while chemists analyze molecular symmetry to predict chemical properties and reactions. Understanding coordinate-based symmetry prepares students for CAD software and digital design tools used across technical careers.
How Can Teachers Use These Position and Direction Worksheets?
These worksheets provide structured practice with completing symmetric figures on coordinate grids, allowing students to visualize reflection properties through hands-on grid work. The format helps students develop accuracy in counting units and maintaining equal distances from lines of symmetry. Answer keys enable quick checking of student work, making it easy to identify whether errors stem from miscounting, directional confusion, or misunderstanding the reflection concept itself.
Teachers use these worksheets effectively as warm-up activities before introducing more complex transformation sequences, or as targeted intervention for students who struggle with spatial visualization. The grid-based format works well for paired activities where one student creates a partial symmetric figure and their partner completes it. These materials also serve as homework assignments that reinforce classroom instruction without requiring extensive setup, and they provide valuable review before geometry units on rigid transformations or state assessment preparation sessions.