Substitution Builder (B) WORKSHEET
Apply properties of operations as strategies to add, subtract, factor, and expand linear expressions with rational coefficients.
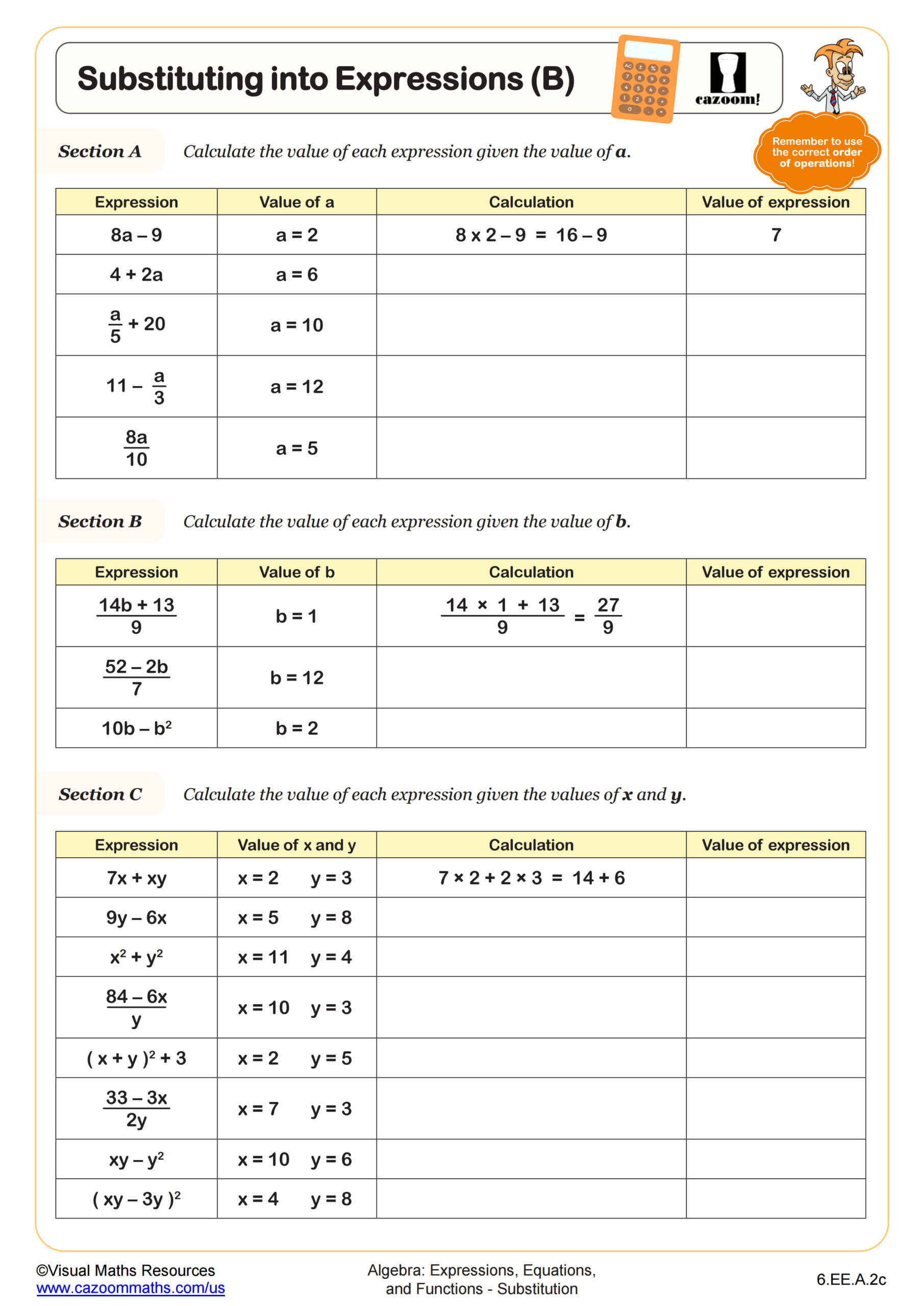
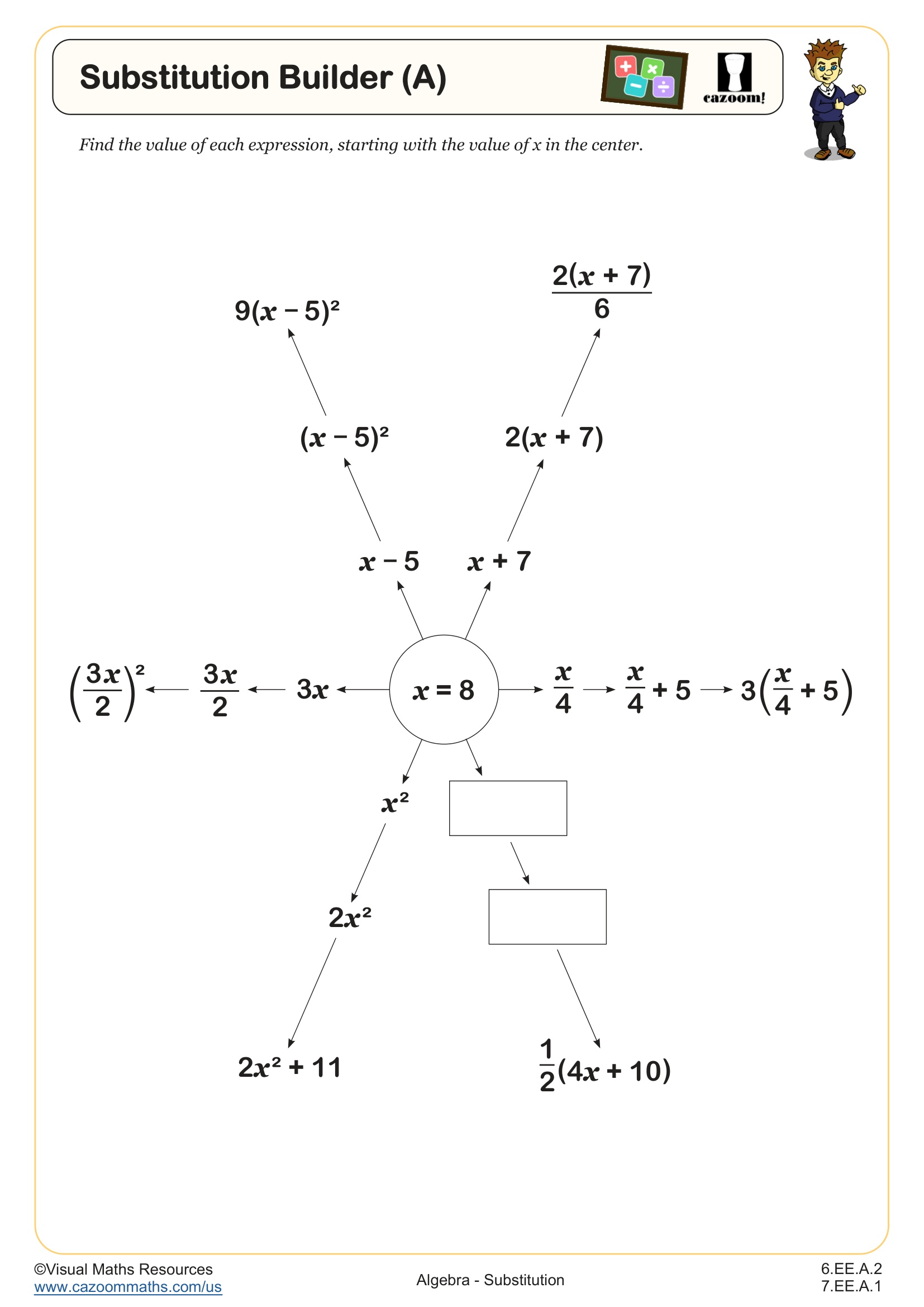
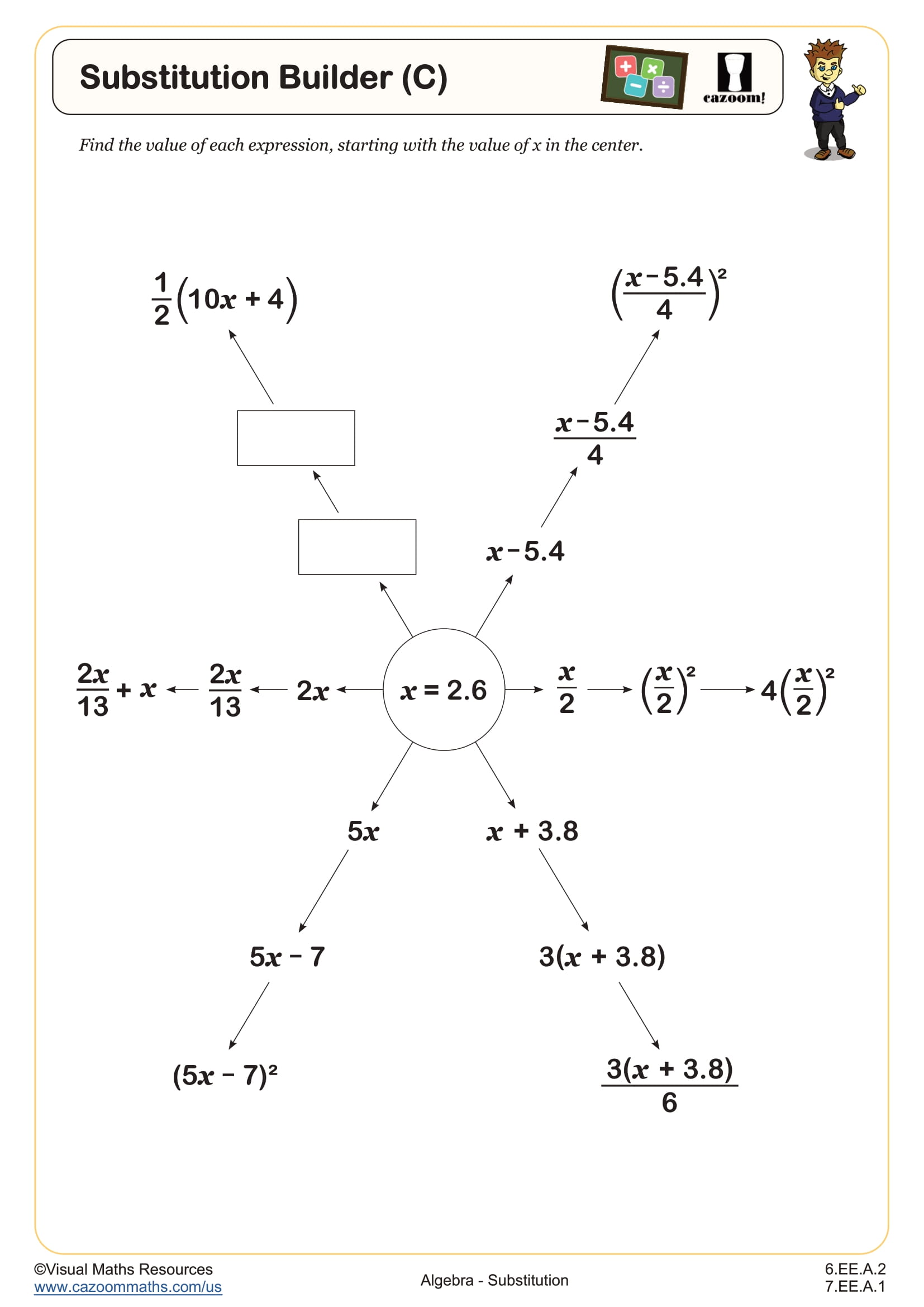
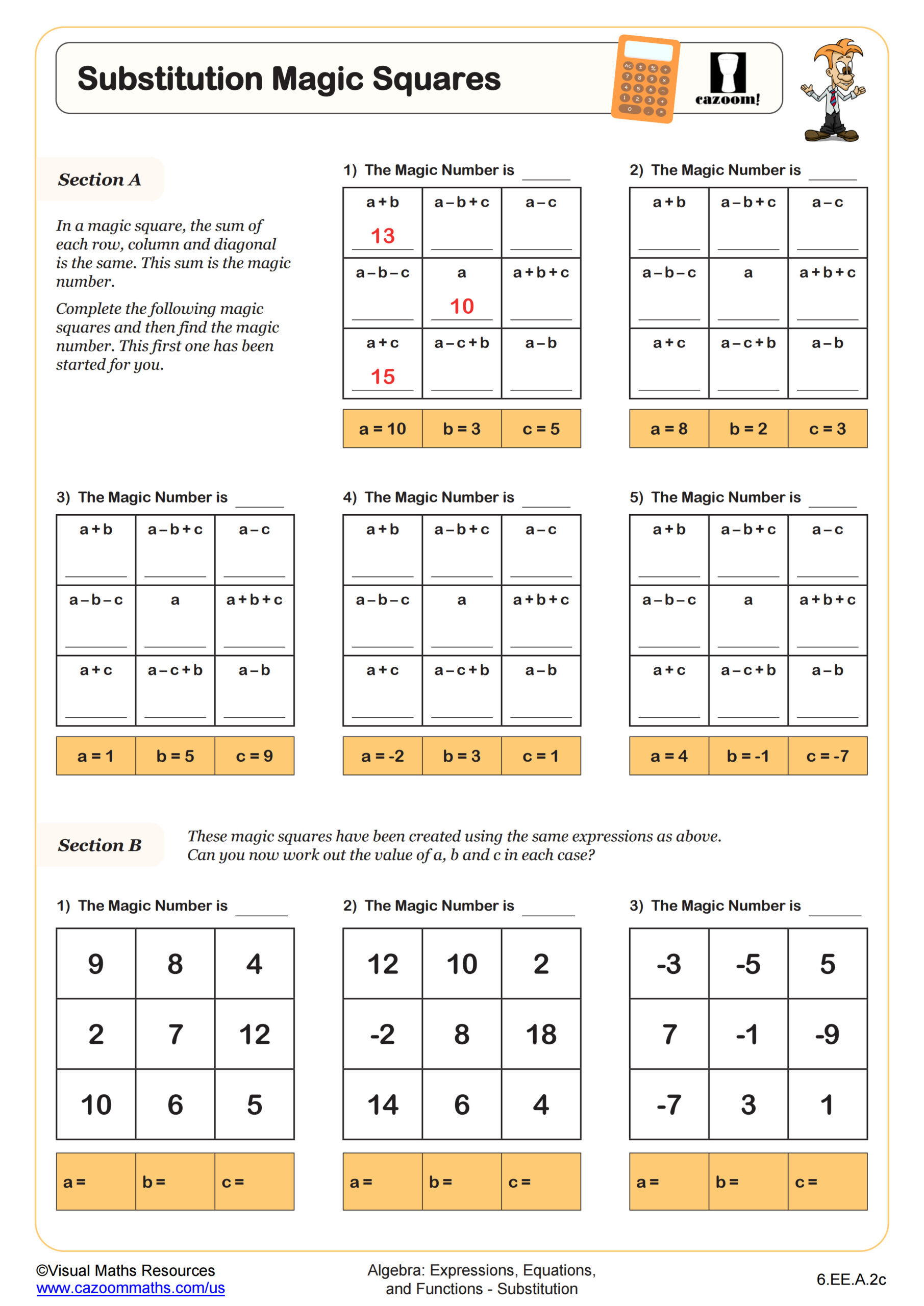
Substitution Builder (B) WORKSHEET DESCRIPTION
These ‘Substitution Builders’ are designed to help students understand the importance of correctly applying the order of operations when substituting values into complex expressions. In Substitution Builder (B), learners will substitute the value -9 into multiple expressions beginning with one operation and building to expressions with three operations, providing them with a clear demonstration of how the order of operations influences the final result. Students will work with fractions as division, brackets and indices throughout. There are another two worksheets in this series where the value of x is either a positive integer or a decimal number.
All worksheets are created by the team of experienced teachers at Cazoom Math.
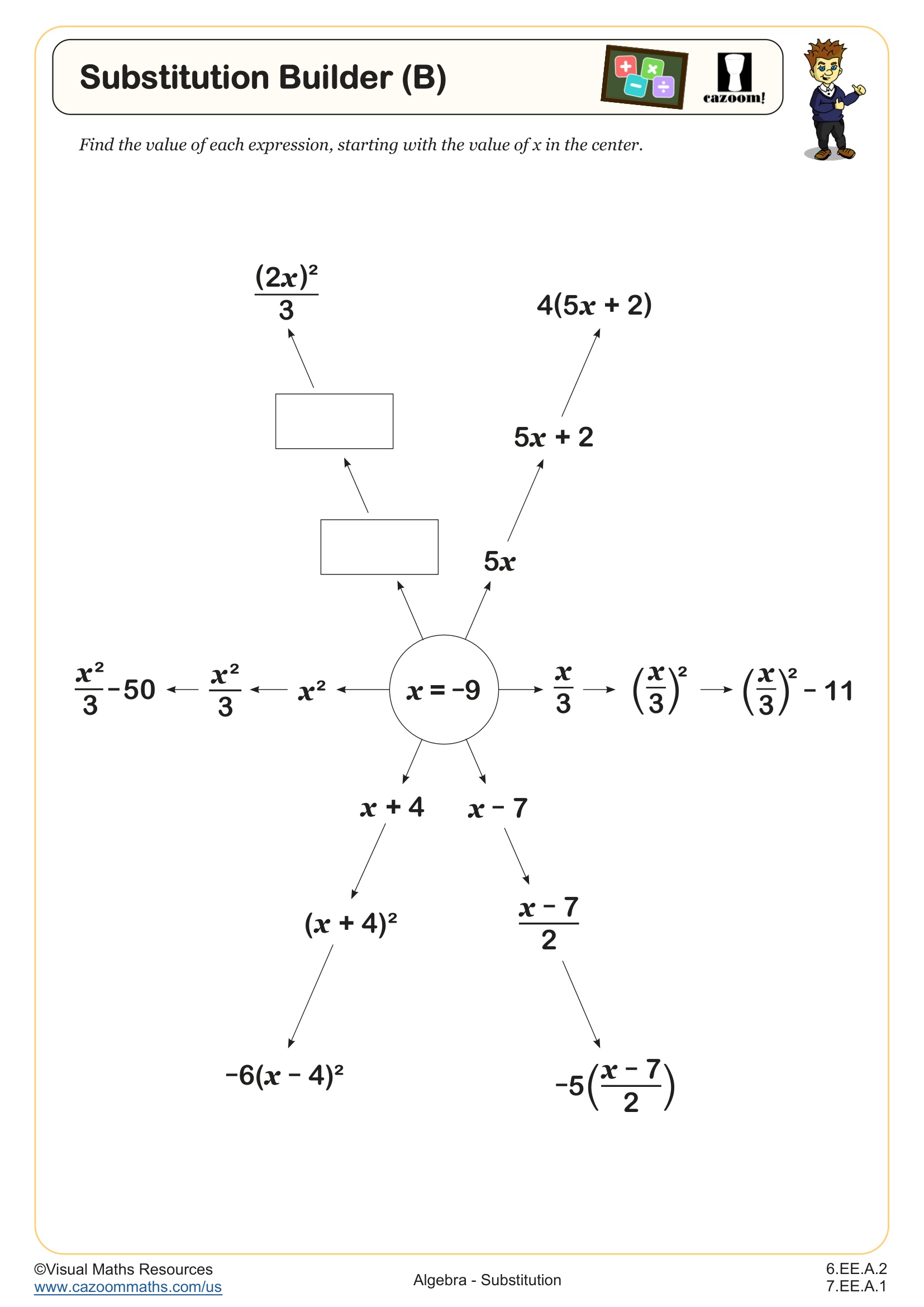
RELATED TO Substitution Builder (B) WORKSHEET
Frequently Asked Questions
This substitution builder (b) worksheet is designed for students in 6th Grade and 7th Grade and aligns with Common Core State Standards.