KS1 Arrays Worksheets
What are arrays in primary maths?
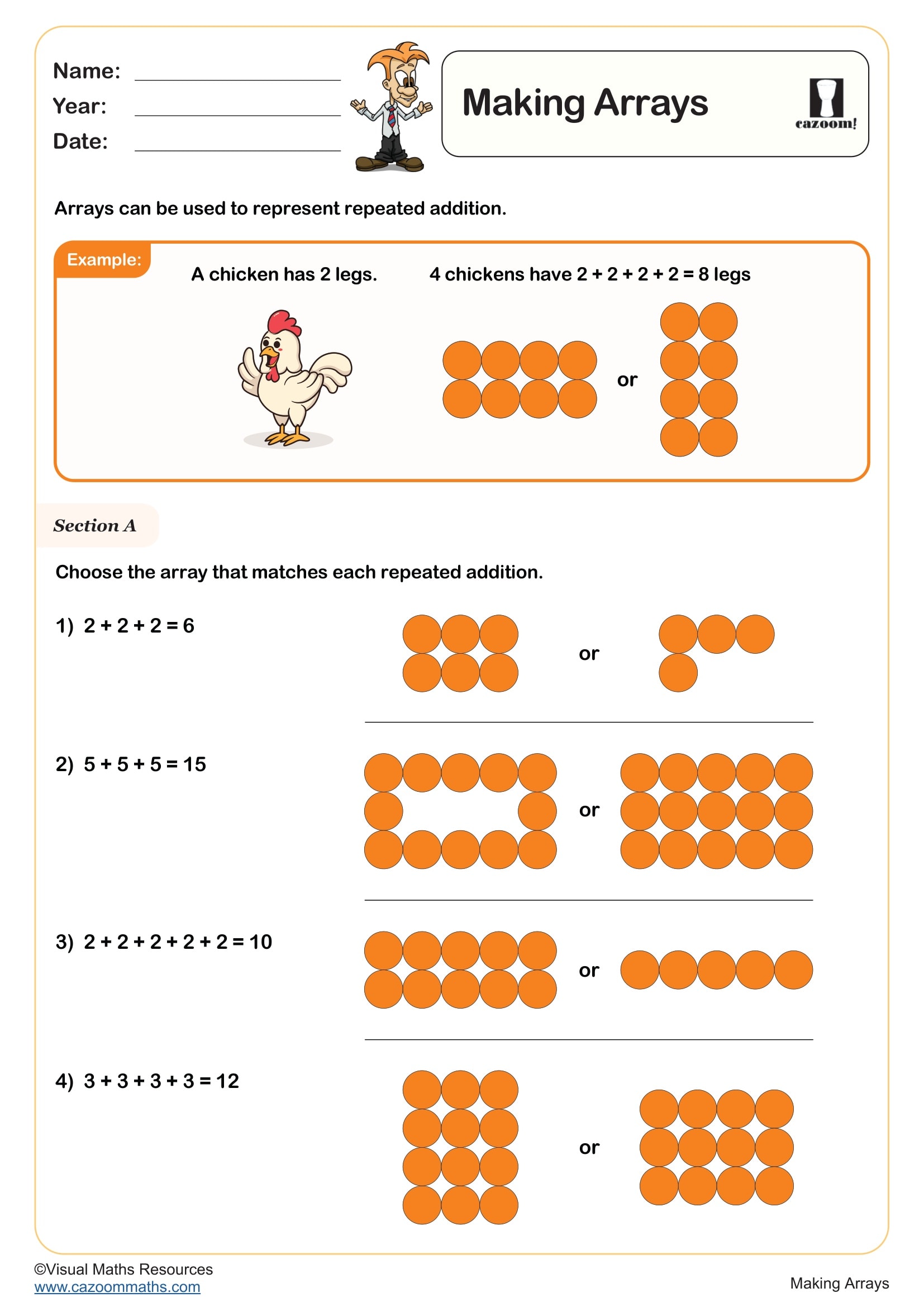
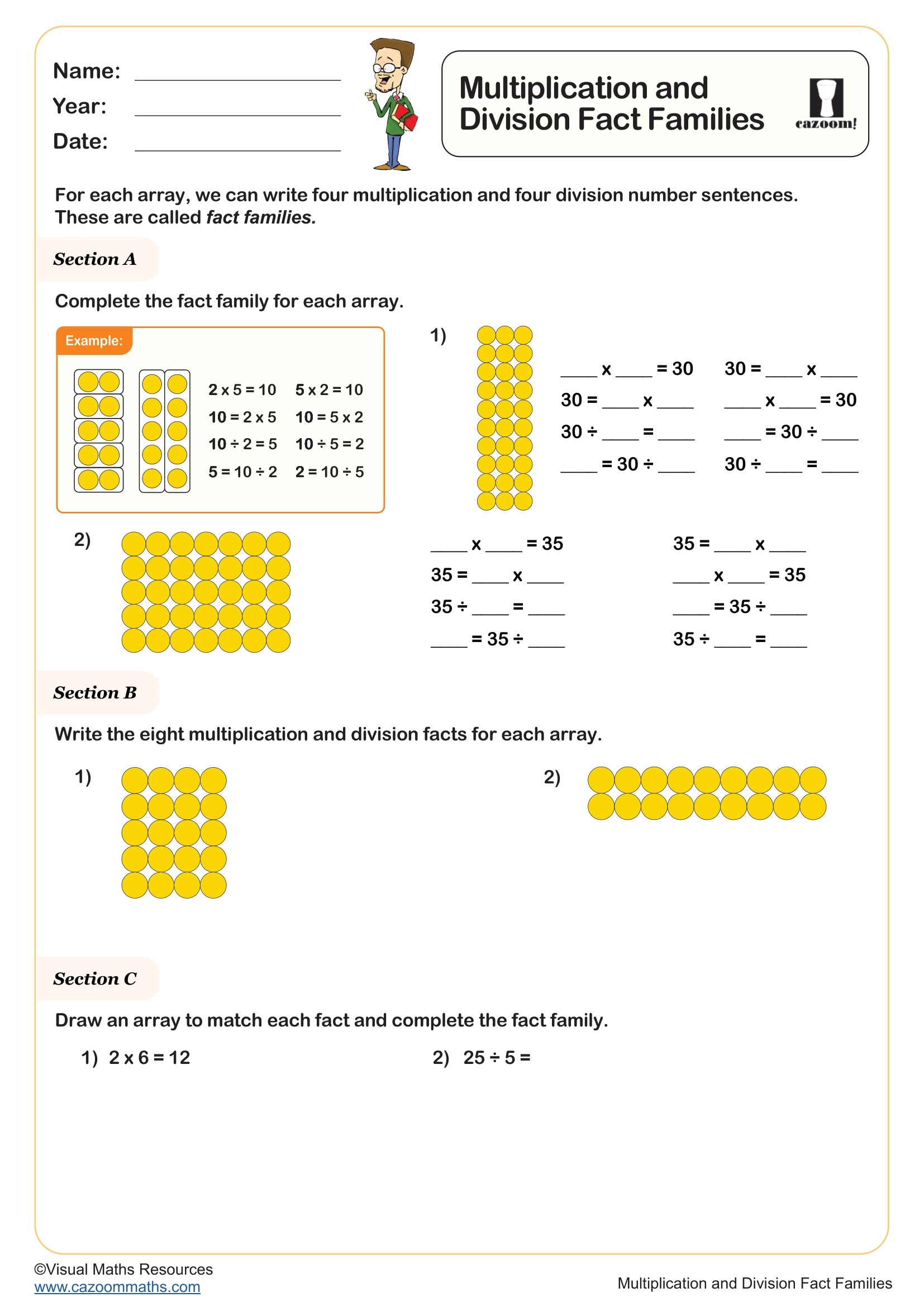
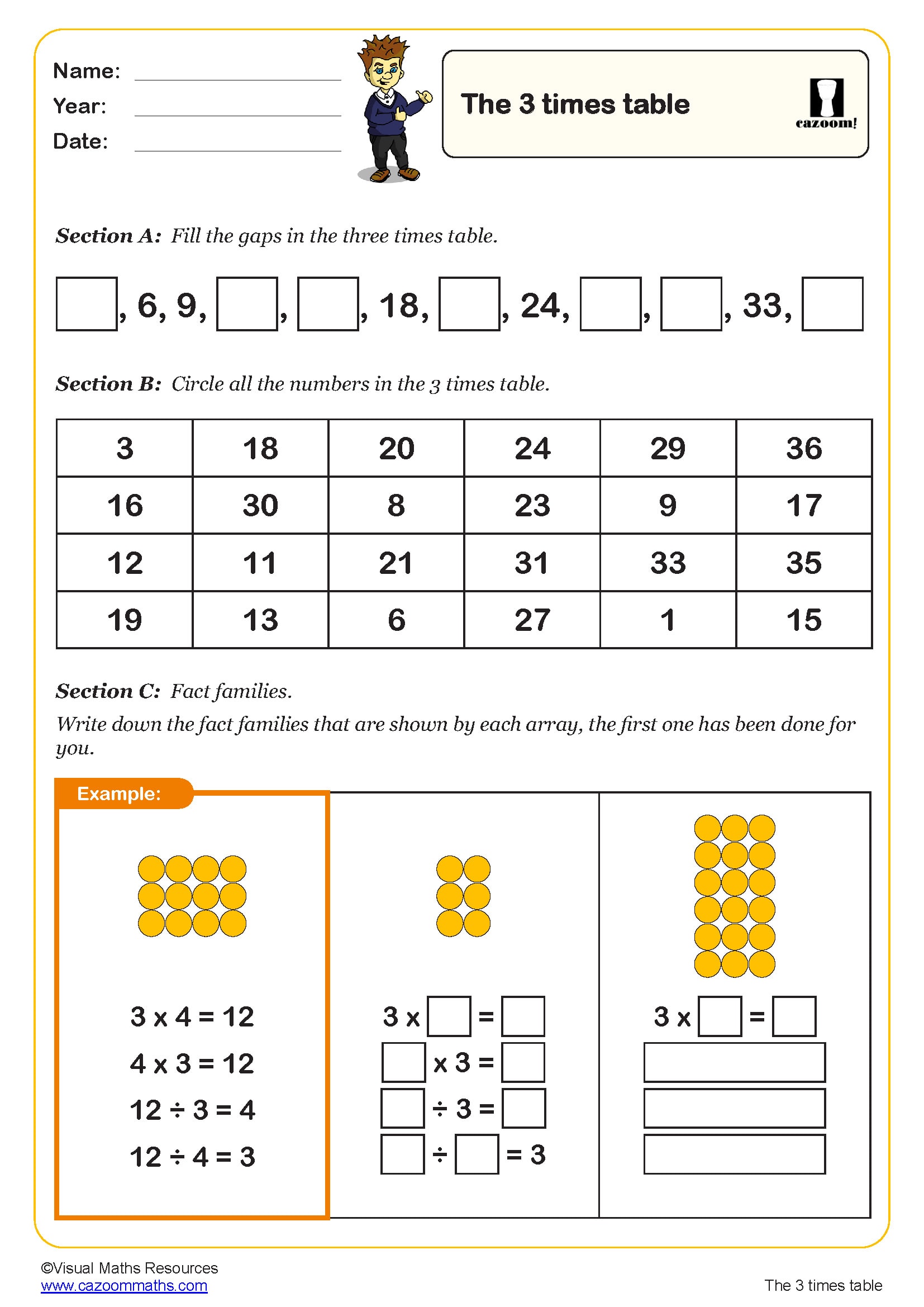
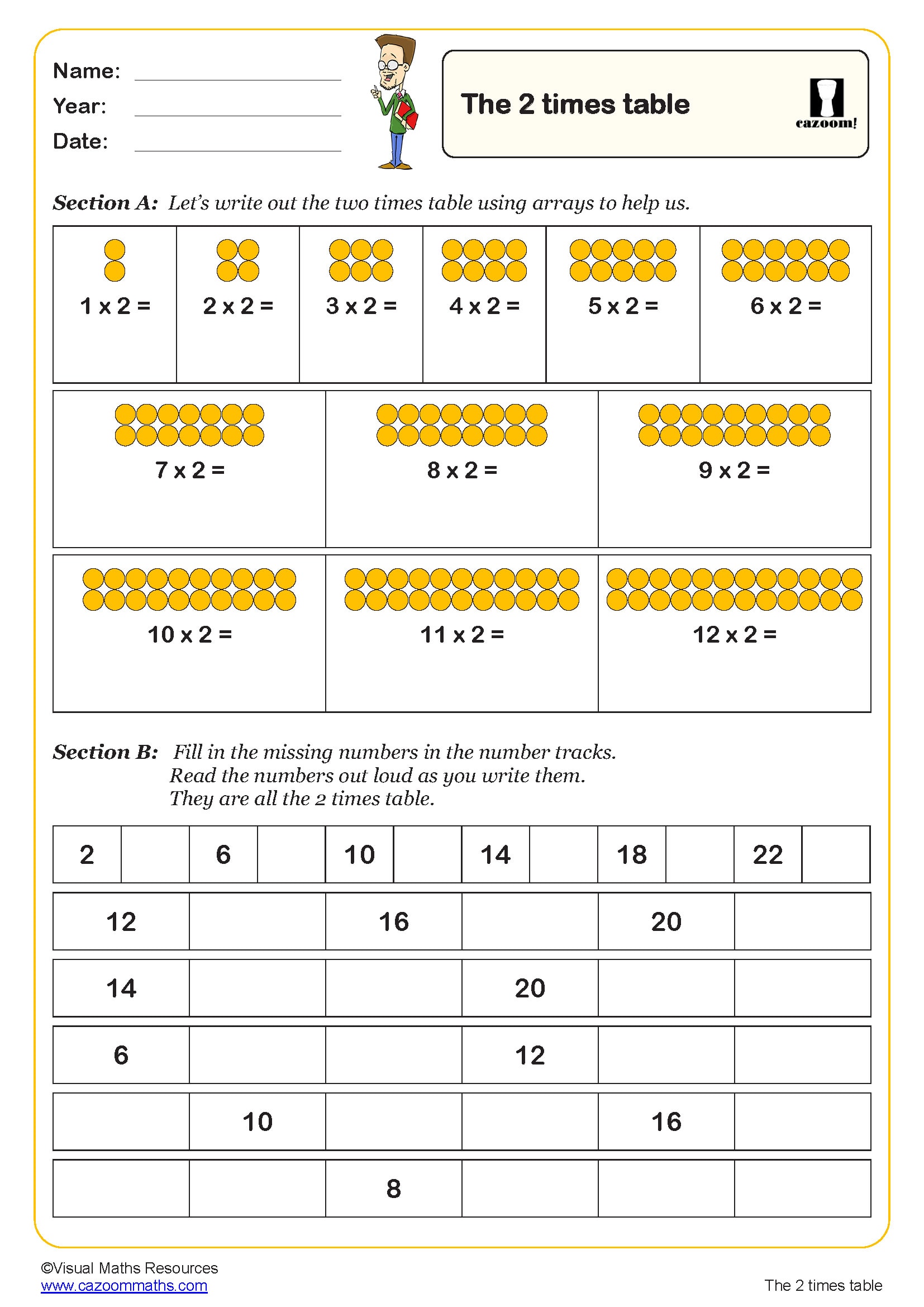
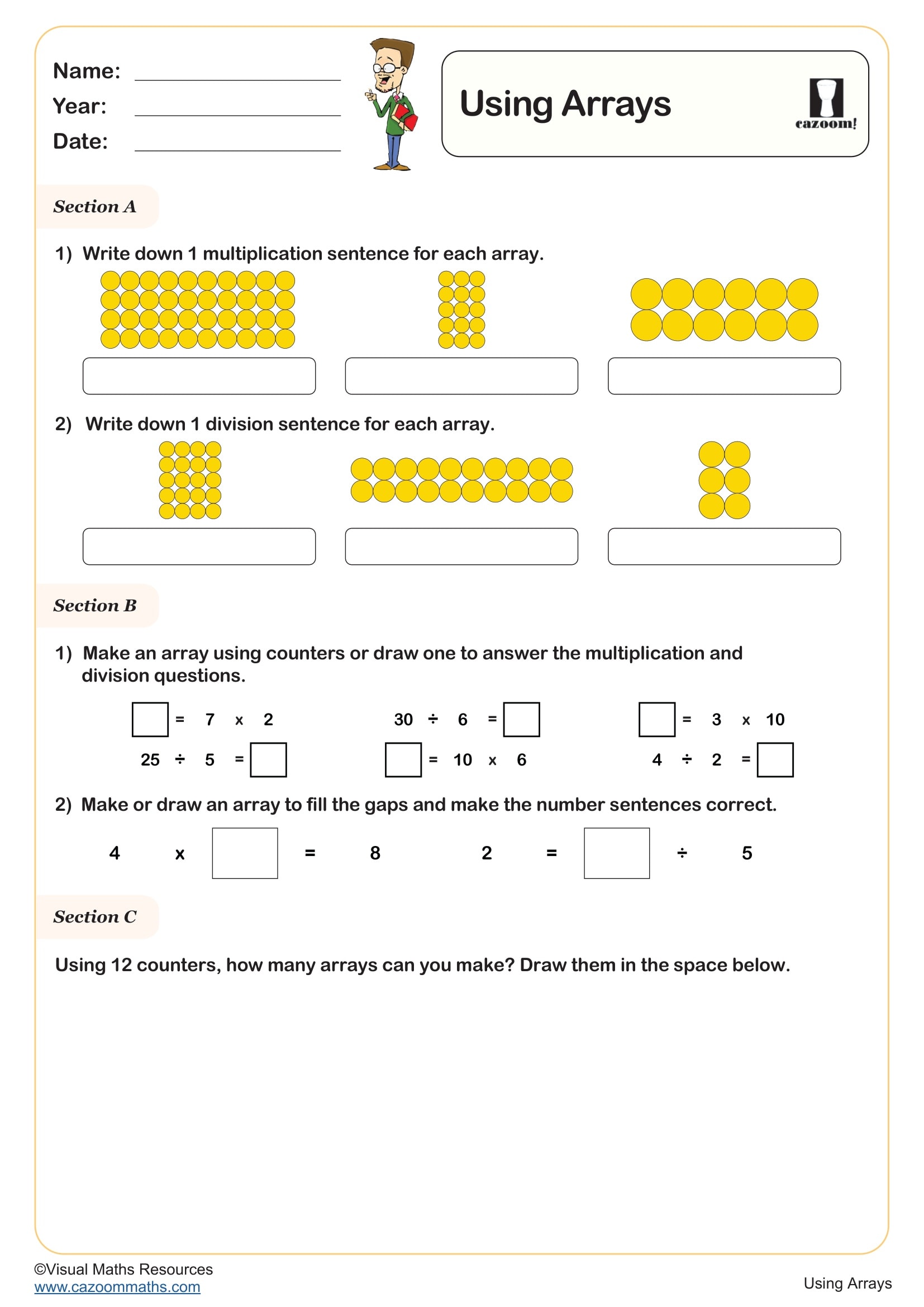
An array is an arrangement of objects, pictures or numbers organised in equal rows and columns. In primary mathematics, arrays help children visualise multiplication as repeated addition and understand that multiplication can be represented visually. For example, an array showing 3 rows of 4 counters demonstrates that 3 × 4 = 12. Arrays are introduced in the National Curriculum from Year 1, initially as equal groups, then explicitly as arrays in Year 2 where pupils learn to write multiplication sentences to describe them. The rows-and-columns structure makes multiplication commutative properties visible—children can see that 3 rows of 4 gives the same total as 4 rows of 3. This concrete representation supports children's understanding before moving to abstract number facts, making arrays an essential foundation for multiplication and division throughout primary school.
Which year groups study arrays?
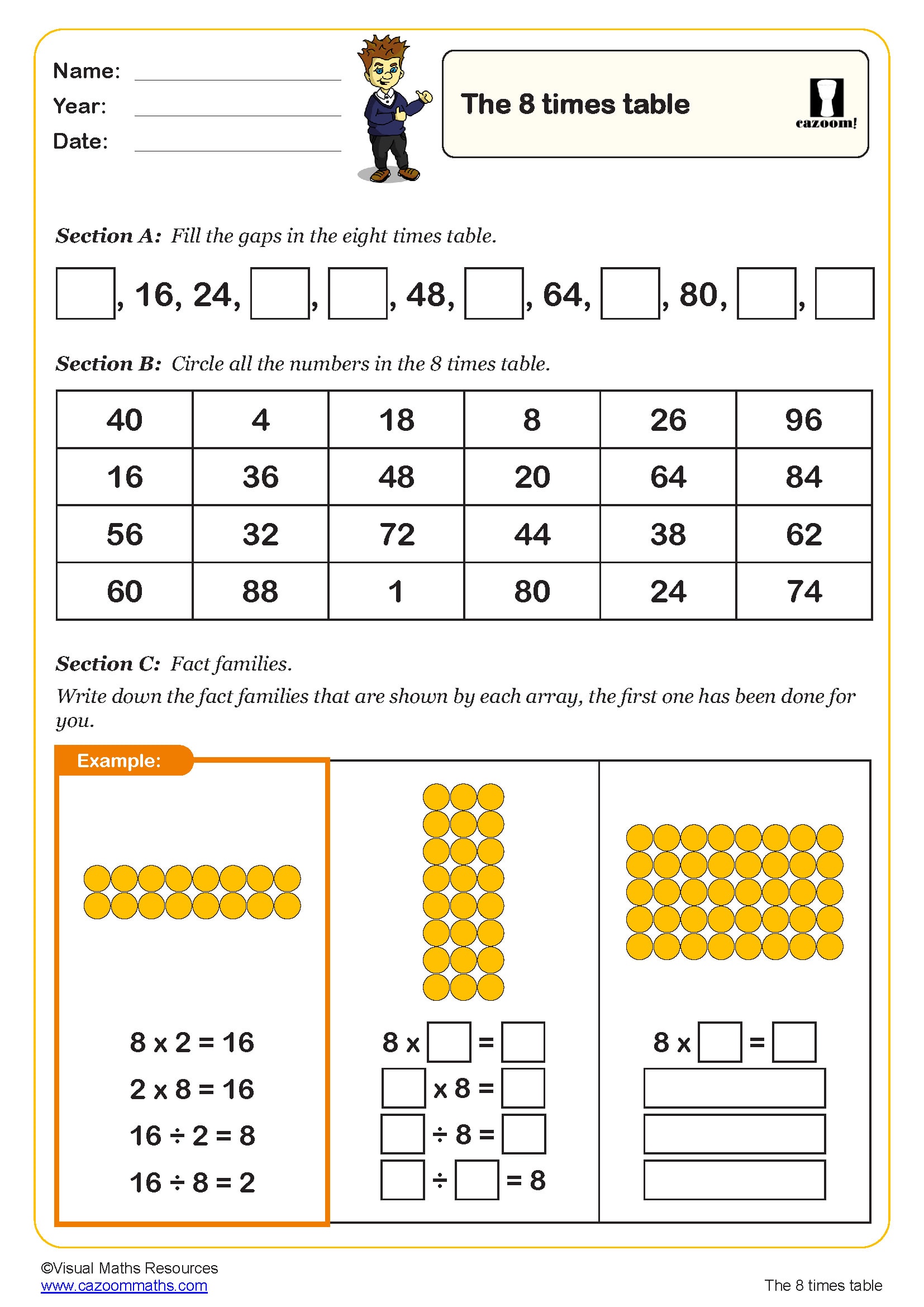
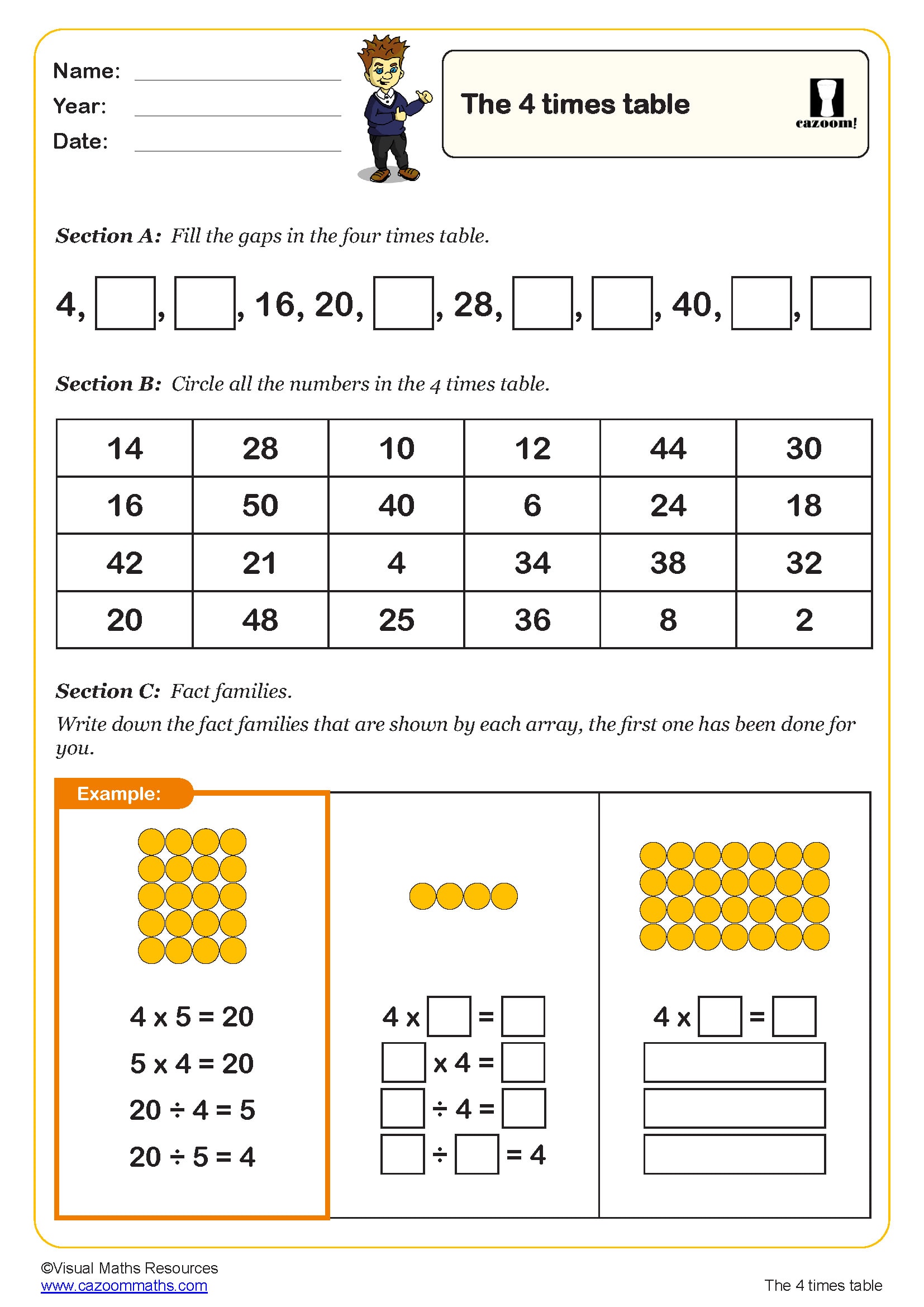
Our arrays worksheets cover Year 1, Year 2, Year 3, Year 4 and Year 5, spanning both Key Stage 1 and Key Stage 2. In Year 1, children begin recognising equal groups and simple patterns, preparing them for array work. Year 2 introduces arrays formally, with pupils learning to recognise them in different orientations and write multiplication sentences to describe what they see. By Year 3, children use arrays confidently to calculate multiplication facts and explore related division facts. Year 4 worksheets extend arrays to larger numbers and connect them to the grid method for multiplication. In Year 5, arrays support understanding of factor pairs and prime numbers. This progression ensures children build fluency with arrays as a multiplication strategy throughout their primary education, developing from concrete representations to more abstract mathematical thinking.
How do arrays help with multiplication tables?
Arrays provide a visual model that makes multiplication facts more memorable and meaningful. Rather than learning times tables through rote memorisation alone, children who work with arrays understand why 4 × 6 equals 24—they can see four rows of six objects. This visual approach supports different learning styles and helps children spot patterns in multiplication. Arrays make the commutative property obvious: turning an array on its side shows that 4 × 6 and 6 × 4 give the same answer. They also reveal connections between times tables—a 4 × 6 array can be split into two 2 × 6 arrays, showing how the 4 times table relates to the 2 times table. When children draw or manipulate arrays, they develop stronger mental images of multiplication, improving recall and building number sense alongside procedural fluency.
Do these worksheets include answers?
Yes, every arrays worksheet in this collection includes a complete answer sheet. This feature supports both teachers and parents by making marking efficient and consistent. Answer sheets allow you to check work quickly during lessons or homework review, and they enable pupils to self-mark when appropriate, promoting independence and immediate feedback. For home learning, answer sheets give parents confidence when supporting their children, even if they're uncertain about teaching methods. The answers show correct working where relevant, helping you identify where misconceptions occur—whether in counting the array, writing the multiplication sentence, or calculating the total. Having answers readily available means you can focus your time on addressing misunderstandings rather than working through exercises yourself. This makes the worksheets practical for use in busy classrooms, intervention sessions, or homework tasks.