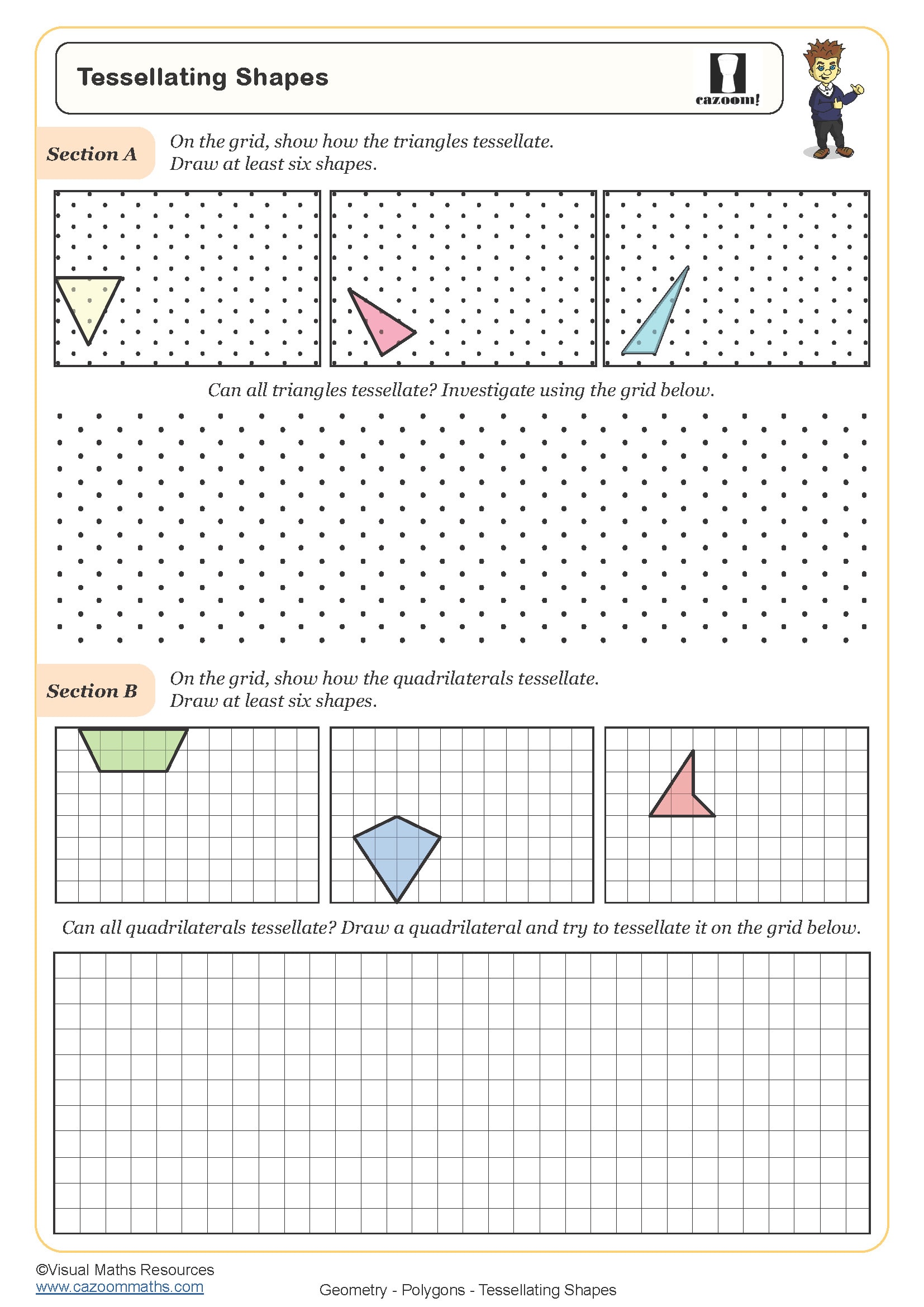
KS3 Polygons Worksheets
What are the properties of irregular polygons?
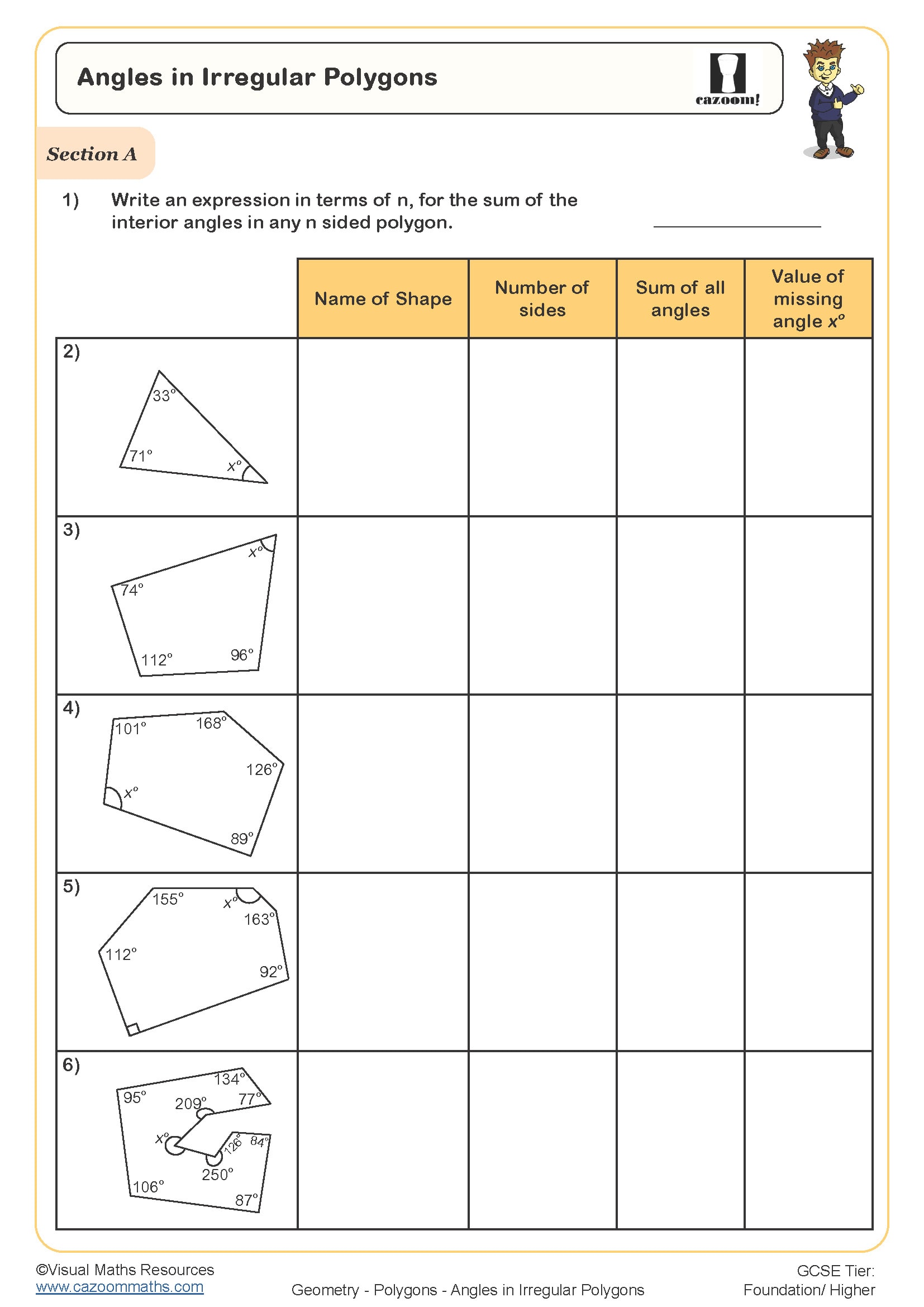
Irregular polygons are closed shapes with straight sides where not all sides are equal in length or not all interior angles are equal. Unlike regular polygons, which have uniform sides and angles, irregular polygons can have any combination of different side lengths and angle measures, provided they remain closed shapes with straight edges. This definition applies across all polygons, from triangles through to complex many-sided figures.
Students frequently lose marks on exam questions by stating only that sides are different lengths, without mentioning that angles can also differ. Teachers typically see students struggle when asked to identify whether a polygon is regular or irregular from a diagram without measurements, as they rely on visual appearance rather than checking all sides and angles systematically. The worksheets address this by presenting irregular polygons in various orientations and asking students to justify their classifications using geometric properties.
Which year groups study polygons at KS3?
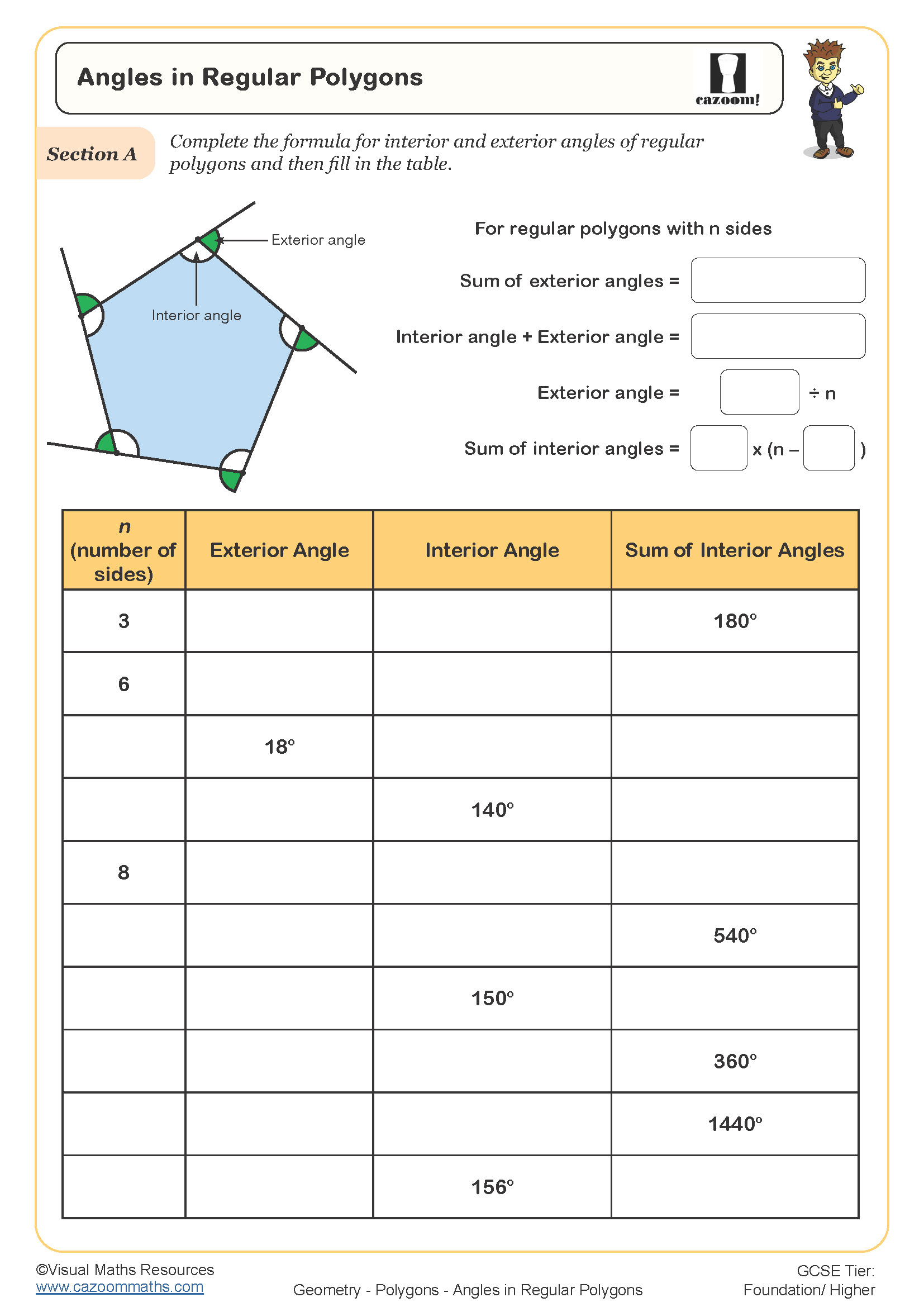
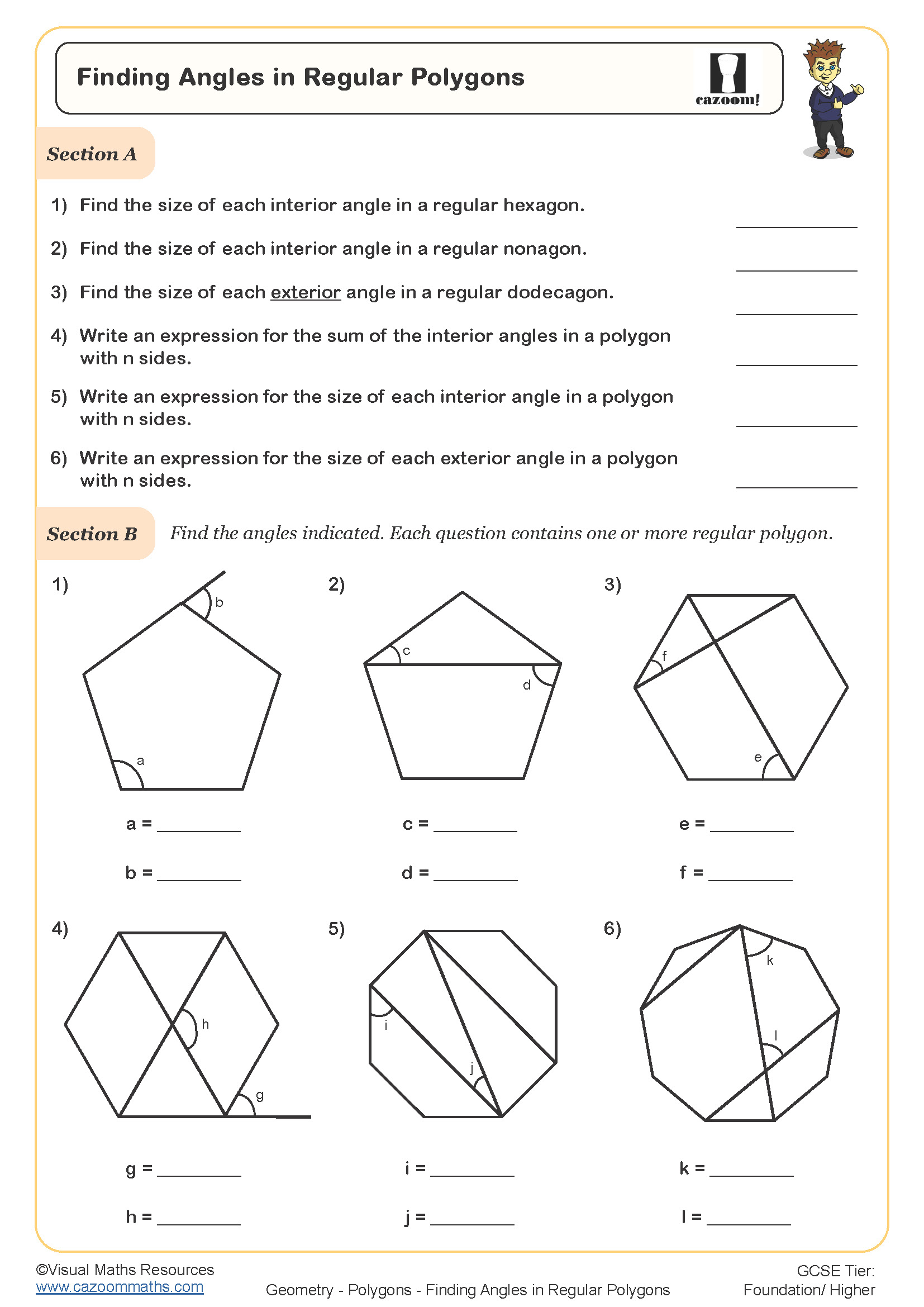
Polygon work appears across Year 7, Year 8, and Year 9 as part of the KS3 geometry curriculum. The National Curriculum requires students to derive and use the sum of angles in a triangle and use it to deduce the angle sum in any polygon, whilst also identifying properties of triangles, quadrilaterals, and other polygons. This topic connects directly to earlier work on 2D shapes from primary school and extends into GCSE topics including bearings, constructions, and proof.
The progression across KS3 typically moves from basic identification and naming of polygons in Year 7, through to calculating interior and exterior angles in Year 8, and finally to more complex problem-solving involving polygon properties in Year 9. Students who struggle with reflective symmetry in polygons often find it reappears as a barrier in transformation geometry and later when working with graphs of functions, making secure understanding at this stage valuable for future topics.
How does reflective symmetry relate to polygon classification?
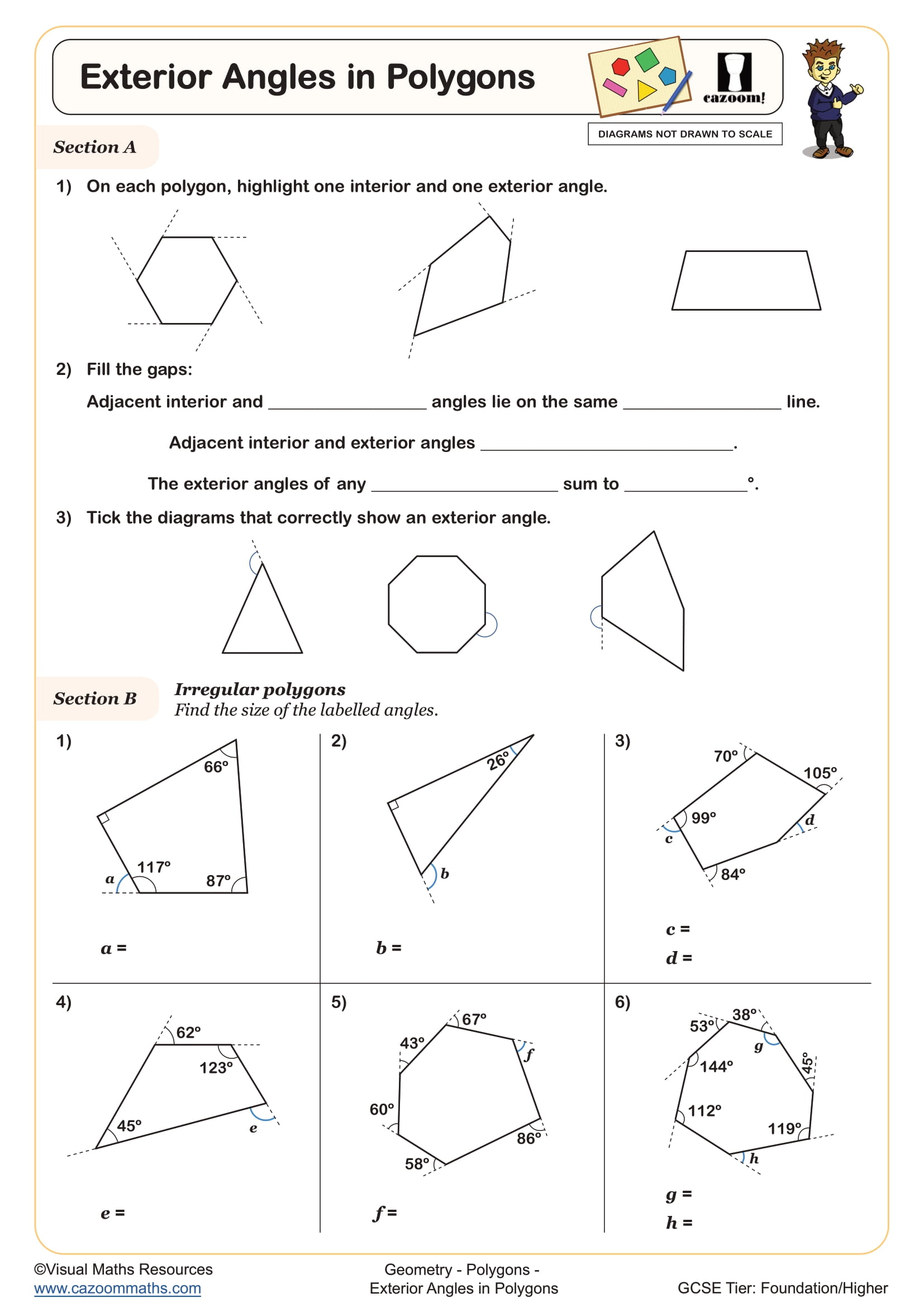
Reflective symmetry occurs when a polygon can be folded along a line so that one half matches exactly onto the other half. Regular polygons have multiple lines of symmetry equal to their number of sides, whilst irregular polygons may have one, several, or no lines of symmetry at all. Identifying lines of symmetry requires students to visualise or test whether each potential mirror line creates two identical halves, checking both side lengths and angles on either side.
Reflective symmetry has direct applications in design, architecture, and engineering. Structural engineers use symmetrical polygons in bridge trusses and building frameworks because symmetry distributes weight evenly and creates stable structures. Teachers can point to examples like the Pentagon building in Washington or honeycomb structures in nature, where hexagonal symmetry provides strength with minimal material. Understanding how symmetry affects structural properties helps students see why certain polygon shapes appear repeatedly in construction and natural formations.
How do these worksheets help students learn polygon properties?
The worksheets build skills progressively, starting with recognition and naming tasks before moving to more analytical questions about properties and symmetry. Each worksheet includes varied question types, from identifying irregular polygons in diagrams to drawing lines of symmetry and explaining reasoning using correct geometric vocabulary. The answer sheets provide complete solutions, allowing students to check their understanding and see correct geometric notation and terminology modelled consistently.
Teachers find these resources particularly useful for differentiation, as the three worksheets can be assigned according to student confidence levels or used sequentially to build mastery. They work well as starter activities to assess prior knowledge, as homework to reinforce classwork, or during intervention sessions with small groups who need additional practice. The answer sheets also support peer assessment activities, where students mark each other's work and discuss common errors, helping them recognise misconceptions before they become embedded.