Year 7 Surveys and Sampling Worksheets
All worksheets are created by the team of experienced teachers at Cazoom Maths.
How Year 7 Printable PDF Samples and Surveys Activities Build Statistical Thinking
Moving into Year 7 statistics requires students to think critically about data collection rather than simply processing given information. These worksheets develop understanding of bias, representation, and reliability—concepts that underpin all future statistical work. Students learn to question data sources and methods, discovering why poorly designed surveys produce misleading results. The progression from identifying sample types to designing unbiased questionnaires mirrors real research processes. Regular practice helps students recognise statistical manipulation in advertising, social media polls, and news reports. This foundation proves essential when encountering hypothesis testing, correlation studies, and experimental design in GCSE mathematics.
Specific learning benefits include:
• Recognises different sampling methods and their uses
• Identifies potential sources of bias
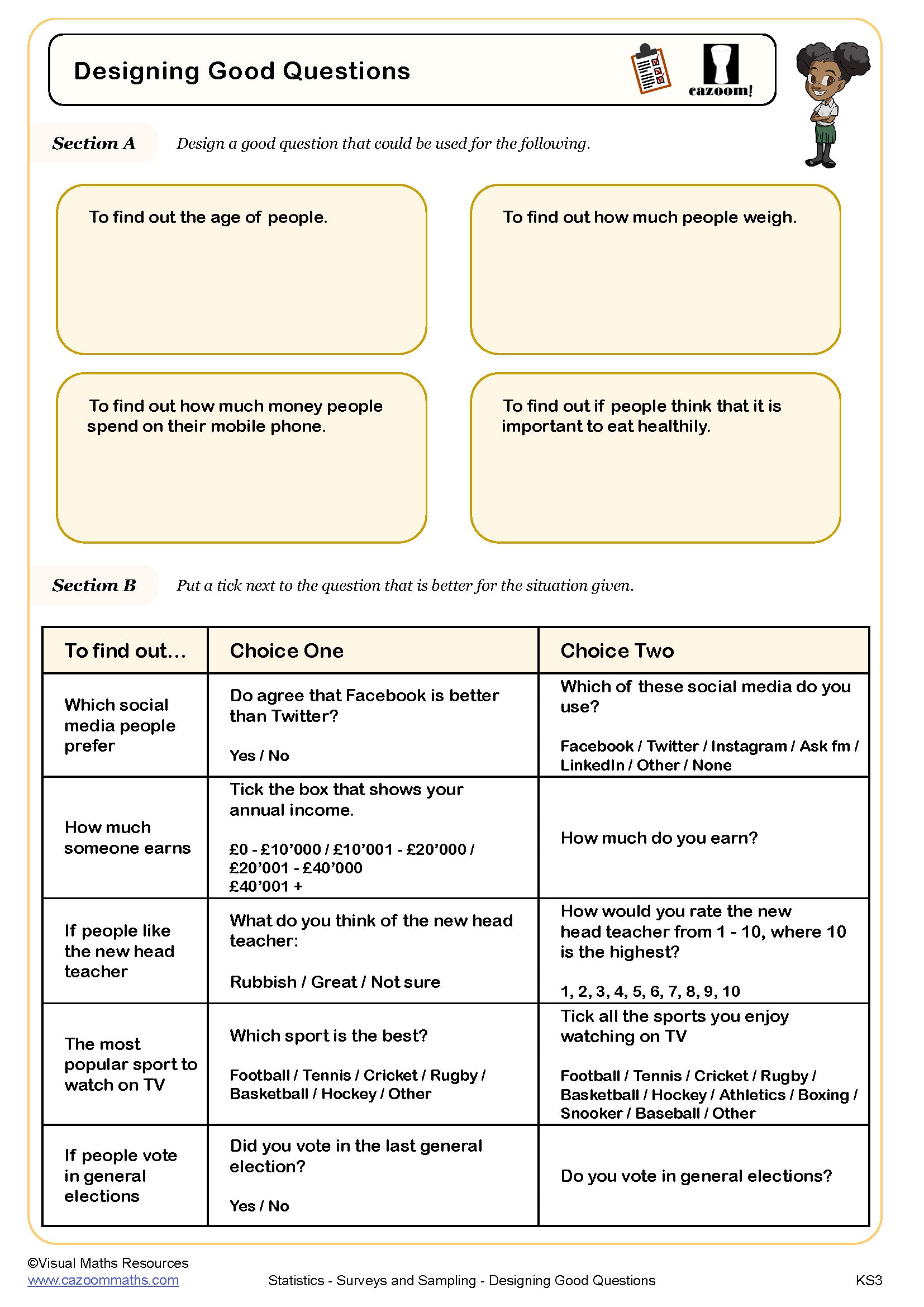
• Designs effective survey questions
• Evaluates data collection reliability
• Interprets sample results appropriately
• Develops critical thinking about statistics
• Prepares for GCSE statistical investigation
Year 7 Samples and Surveys Worksheets That Deliver Results
These worksheets scaffold learning from concrete examples using school-based scenarios to abstract statistical principles. Students examine real survey examples, identify their flaws, and then apply improved methods to their own investigations. The materials balance theoretical understanding with practical application, ensuring students grasp why random sampling often beats convenience sampling. Visual representations connect abstract sampling concepts to tangible outcomes, while answer keys demonstrate proper statistical reasoning at each stage.
The core skills covered include:
• Random sampling – selecting participants without bias using various methods
• Systematic sampling – choosing every nth item from a population list
• Stratified sampling – dividing populations into groups for proportional representation
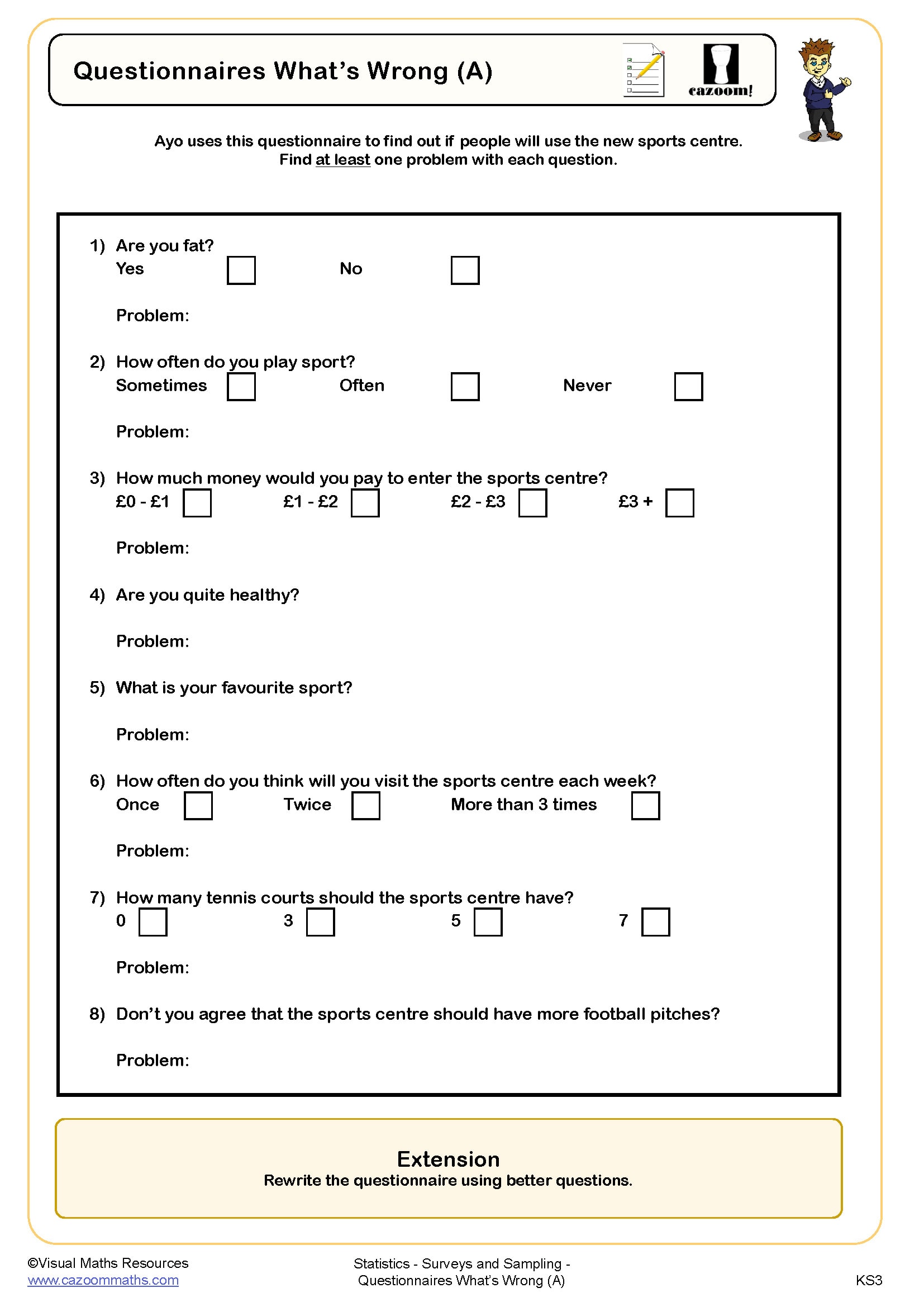
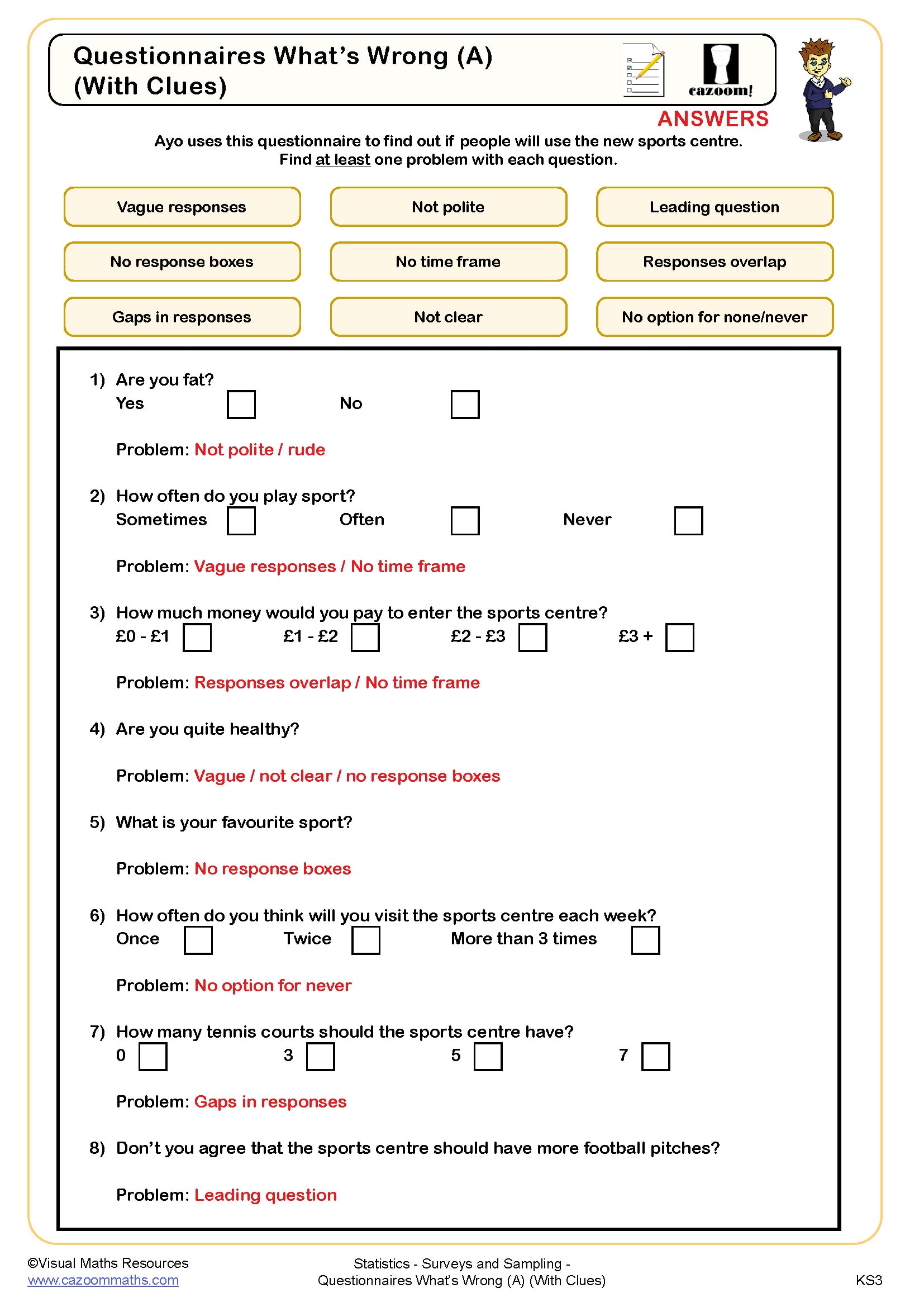
• Survey question design – avoiding leading questions and ambiguous wording
• Sample size considerations – understanding how size affects reliability
• Bias identification – recognising selection and response bias in studies
• Data collection planning – choosing appropriate methods for different investigations
• Interpreting samples – drawing valid conclusions from limited data
• Evaluating surveys – critiquing methodology and identifying limitations
The Parents’ Guide to Using Year 7 Samples and Surveys Worksheets at Home
Secondary maths departments choose these materials because they address the specific challenges of teaching statistical thinking to Year 7 students. The worksheets use contexts relevant to 11-12-year-olds—school surveys, sports statistics, and social media trends. Question progression naturally differentiates, starting with simple identification tasks before advancing to critiquing flawed methodologies. Answer sheets reduce marking workload significantly while detailed solutions reveal mathematical reasoning, particularly valuable for non-specialist teachers covering statistics. Mixed-ability classes benefit from varied difficulty levels within each worksheet, eliminating the need for multiple resource preparation. The materials align perfectly with national curriculum requirements for handling data, providing comprehensive coverage from basic sampling to survey evaluation.
Everyday Maths: Where Year 7 Students Use These Statistics Skills in Real Life
Understanding sampling and surveys empowers students to navigate an increasingly data-driven world. These statistical skills apply directly to situations young people encounter daily.
• Social media polls – recognising when online surveys lack representative samples
• Market research – understanding how companies gather consumer preferences
• School council elections – designing fair voting systems and opinion surveys
• Scientific experiments – selecting test subjects for reliable results
• News interpretation – questioning statistics quoted in articles and broadcasts
• Gaming statistics – analysing player data and achievement distributions
• Environmental studies – sampling techniques for wildlife populations and pollution monitoring
• Product reviews – evaluating whether reviewer samples represent typical users