Year 8 3D Shapes Worksheets
All worksheets are created by the team of experienced teachers at Cazoom Maths.
Discover How These printable Year 8 Geometry Unlocks Higher-Level Mathematical Thinking
The development of three-dimensional geometry in Year 8 establishes fundamental knowledge which supports advanced mathematics and STEM subjects in the future. Students who master spatial visualisation skills during this period achieve better results in various mathematical subjects, especially trigonometry and coordinate geometry. Students need to practice three-dimensional thinking consistently through resources that build complexity while remaining accessible. Students who solve different types of problems regularly learn to identify geometric connections in new situations, which develops their analytical abilities needed for advanced math. The systematic teaching method enables students to learn at their own pace while developing robust mathematical knowledge.
Specific learning benefits include:
• Develops an accurate visualisation of 3D objects
• Strengthens cross-sectional reasoning abilities
• Builds surface area calculation fluency
• Improves volume formula application
• Enhances spatial problem-solving strategies
• Prepares students for GCSE geometry topics
• Creates connections between algebra and shapes
Attention Maths Teachers: Cover These 3D Shape Topics for Better Results
These worksheets progress from concrete representations to abstract reasoning, with detailed solutions demonstrating each calculation step clearly. Students begin by identifying properties of familiar shapes before advancing to complex calculations involving composite solids. The materials incorporate visual aids, nets, and isometric drawings to support different learning styles whilst maintaining mathematical rigour throughout. Each topic builds systematically on previous knowledge, ensuring students develop a thorough understanding rather than memorising formulas.
The core skills covered include:
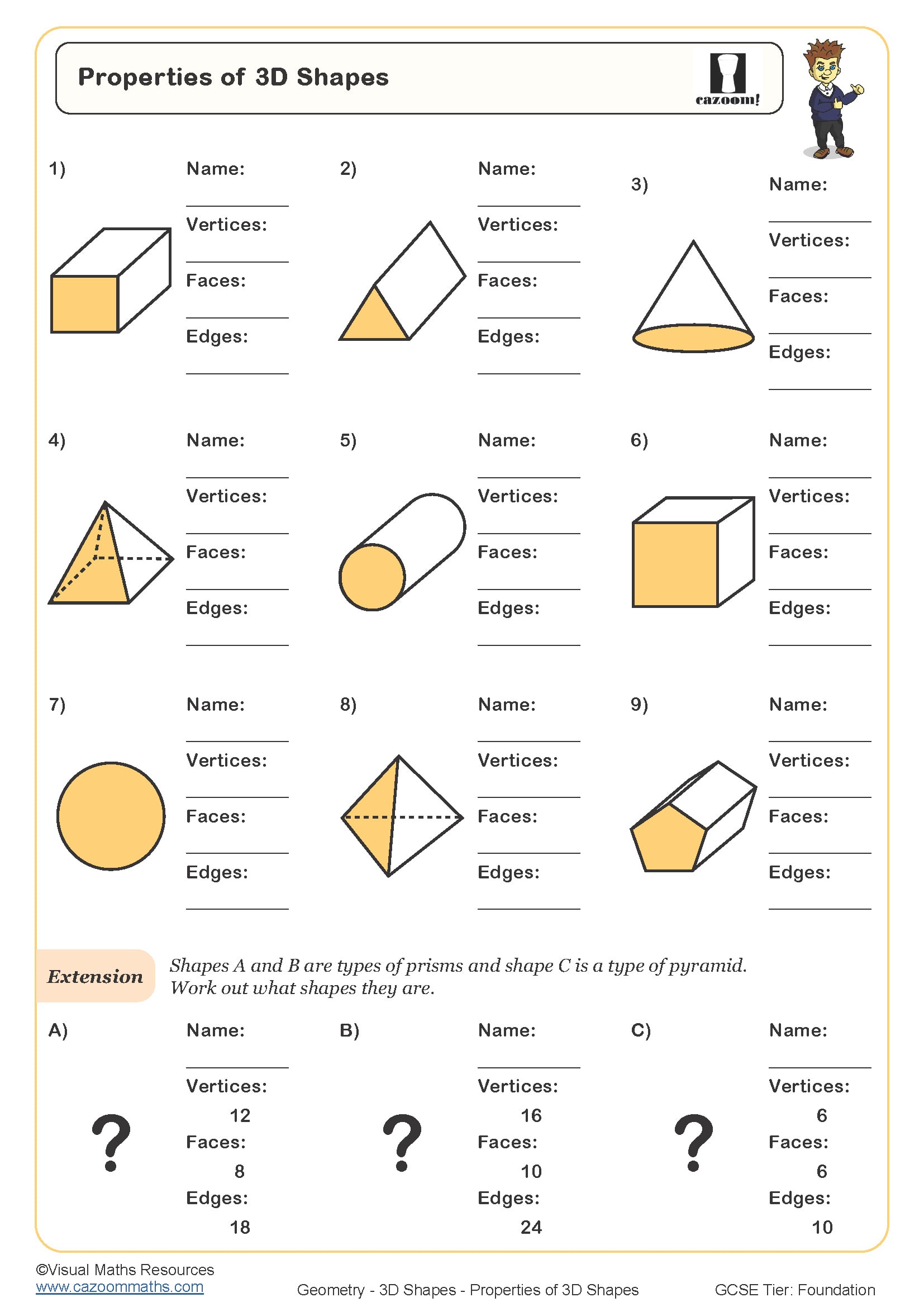
• Properties of prisms – identifying faces, edges, and vertices in various orientations
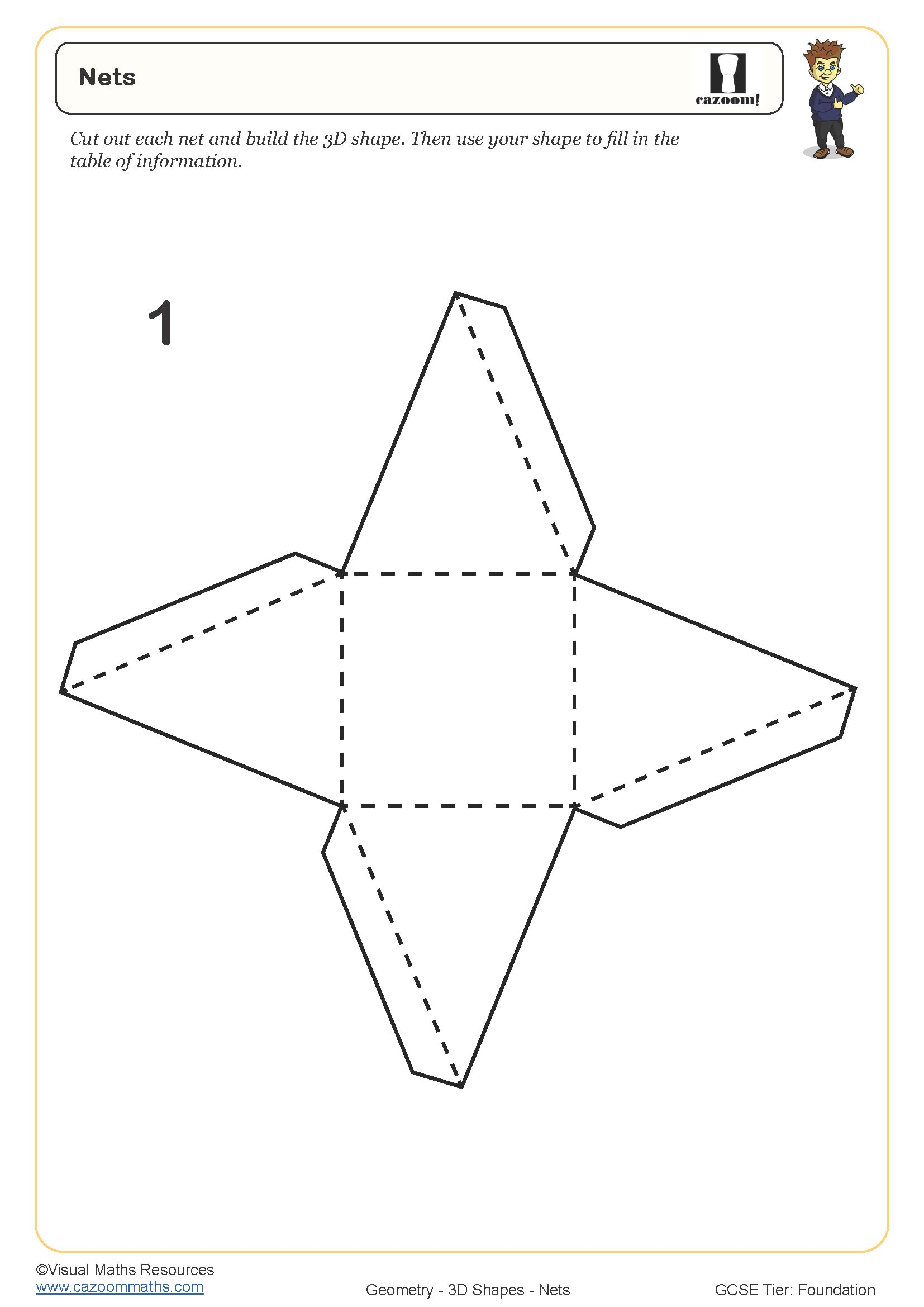
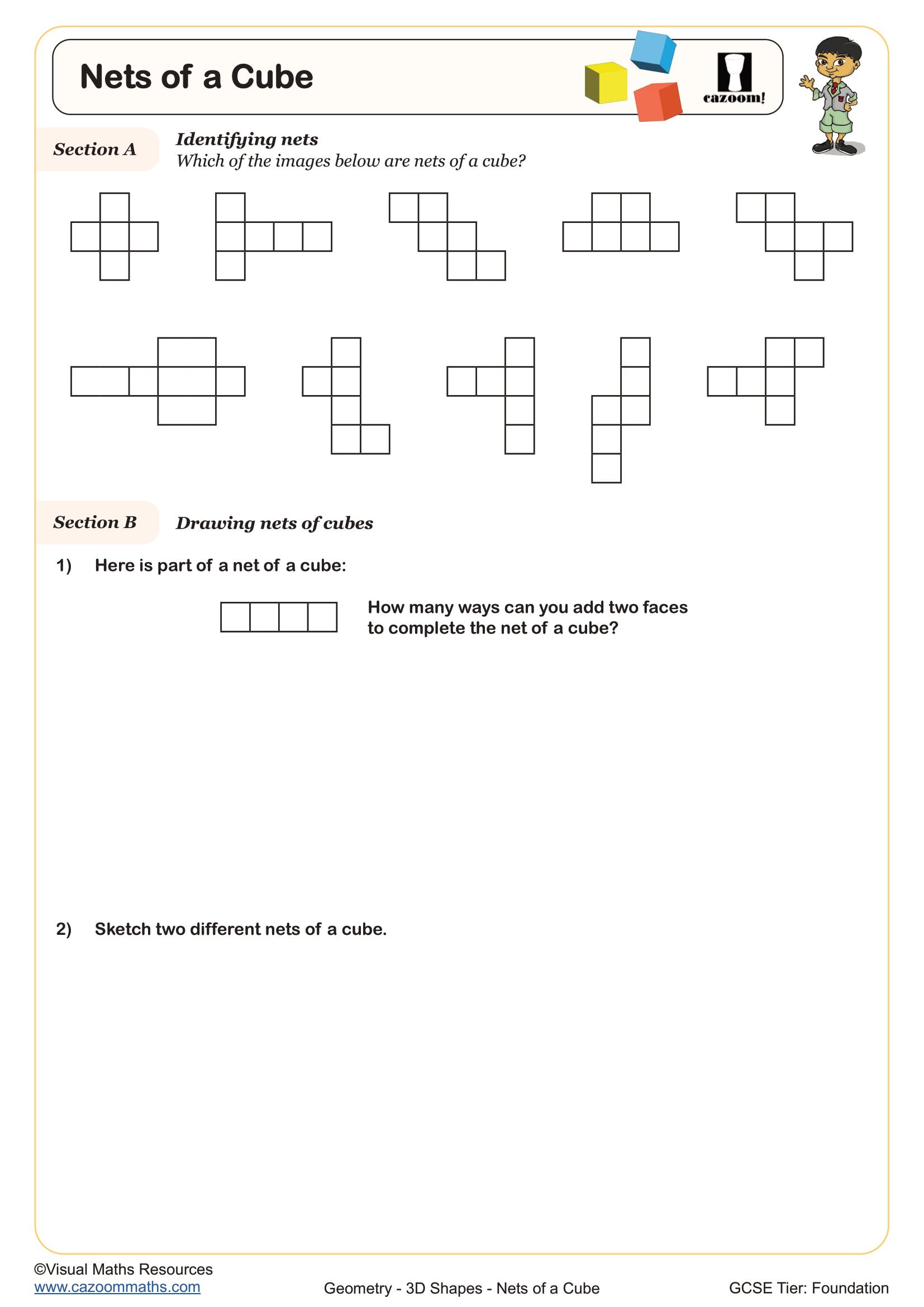
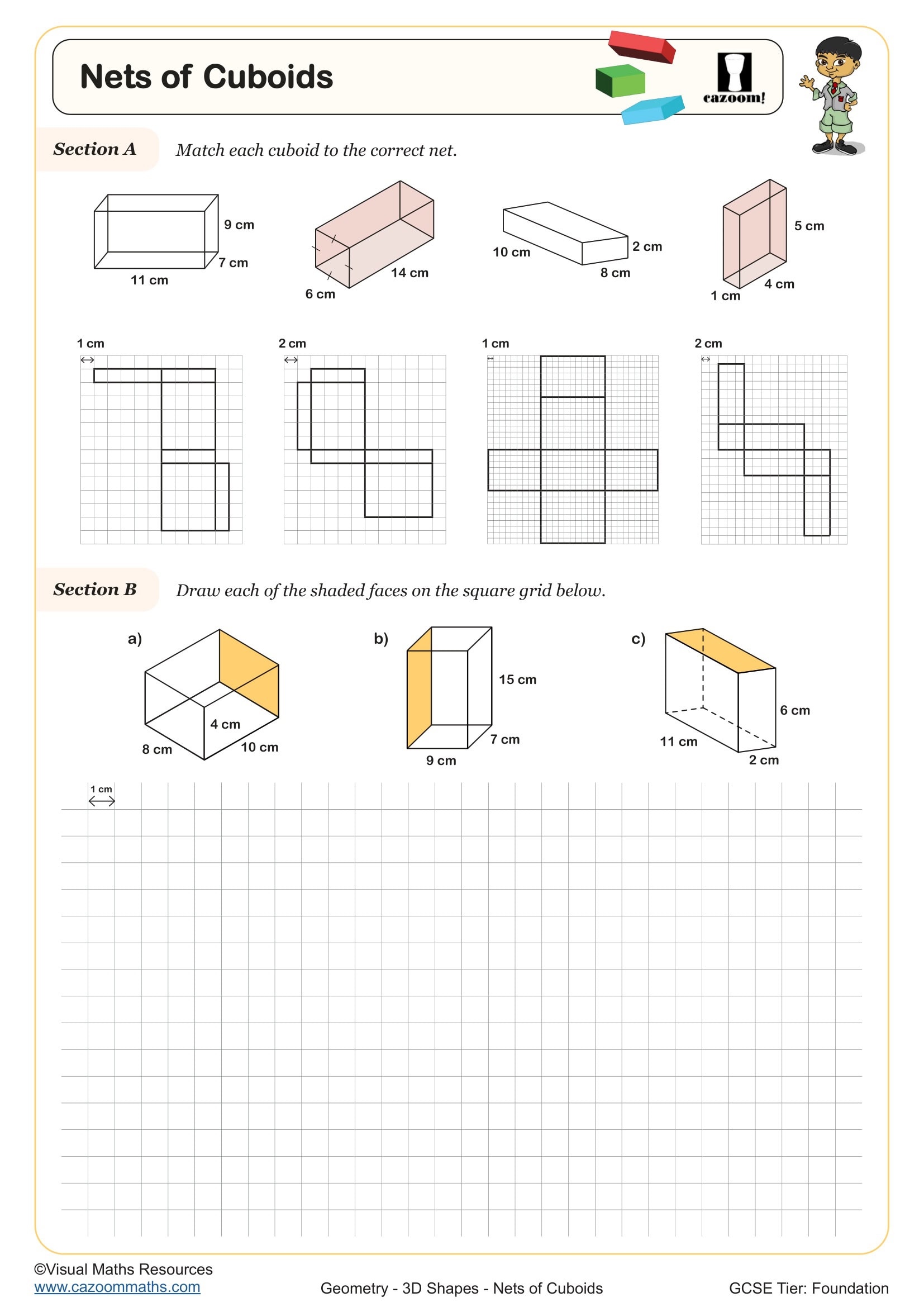
• Nets and surface area – constructing and calculating from 2D representations
• Volume of cuboids – applying length × width × height systematically
• Cylinder calculations – understanding circular cross-sections and curved surfaces
• Pyramids and cones – relating base area to volume formulas
• Composite shapes – breaking complex solids into simpler components
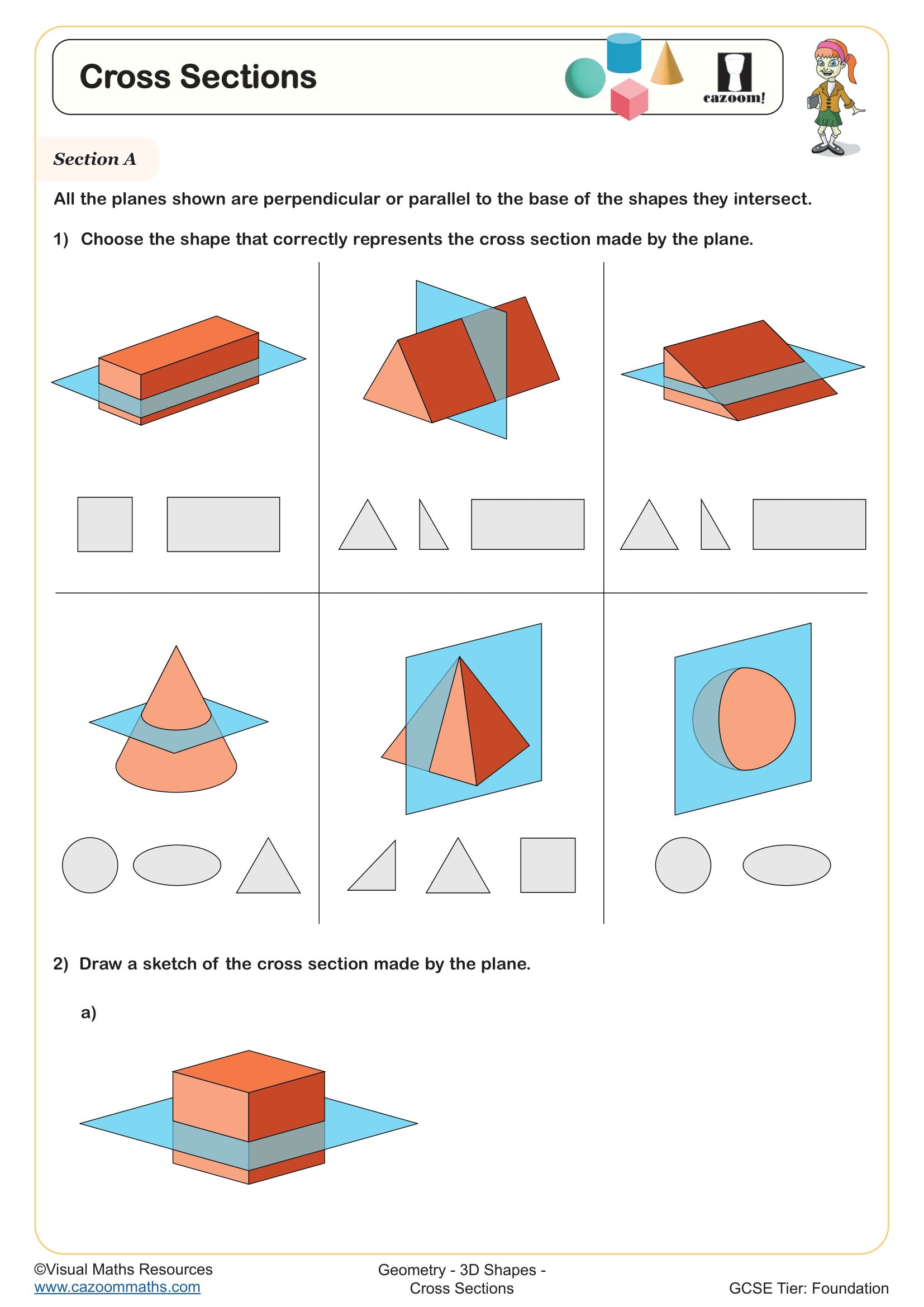
• Cross-sections – visualising slices through 3D objects
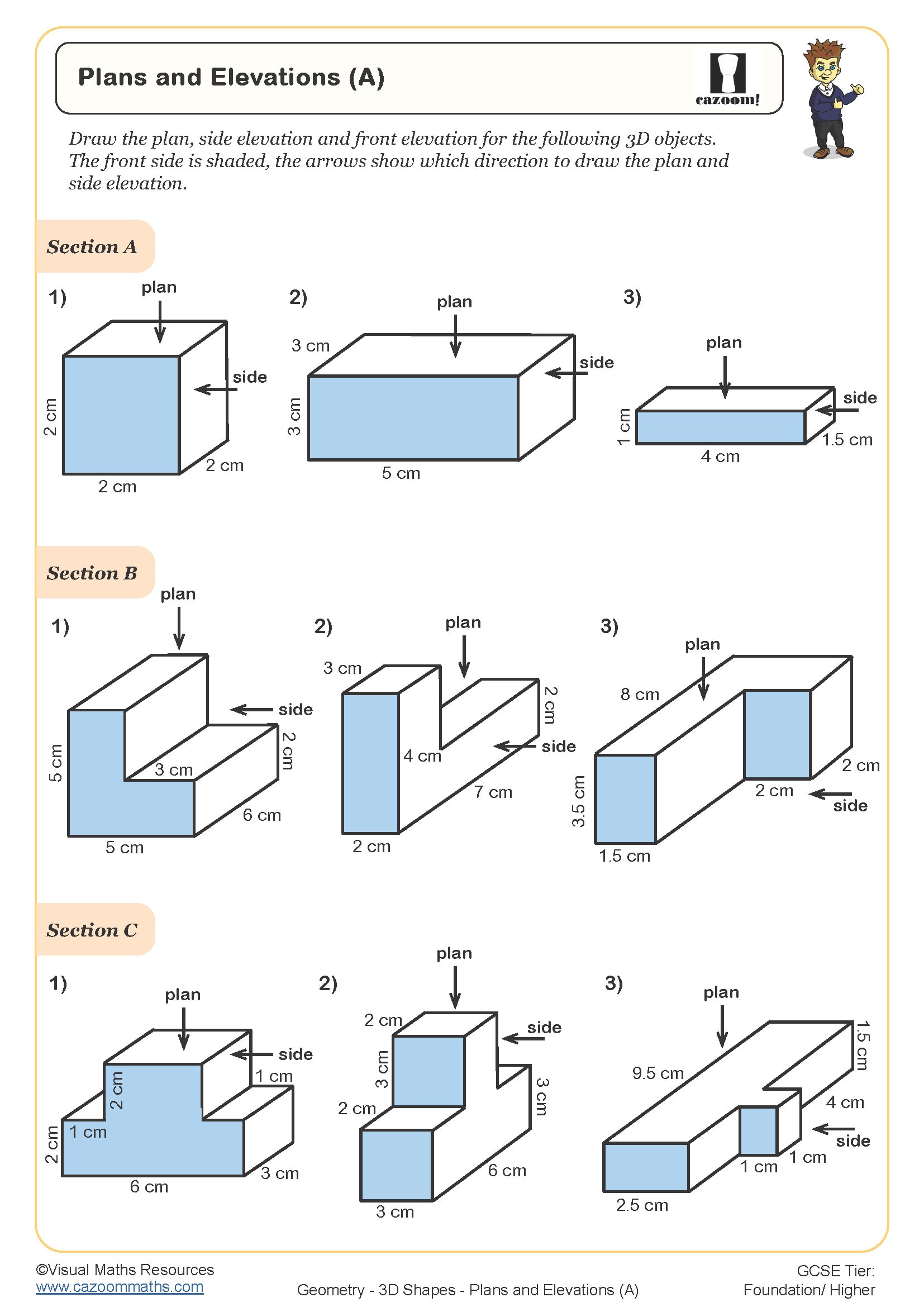
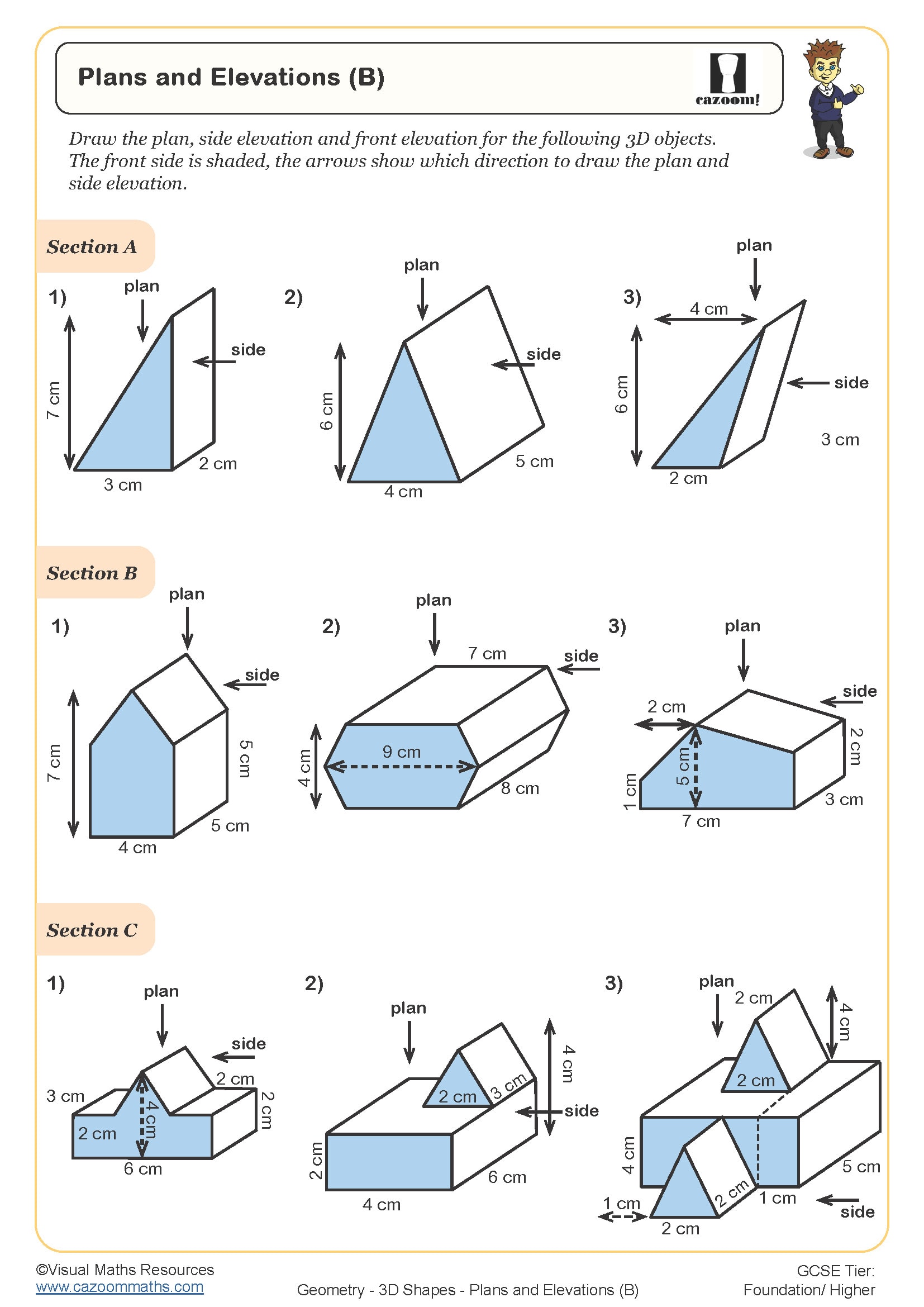
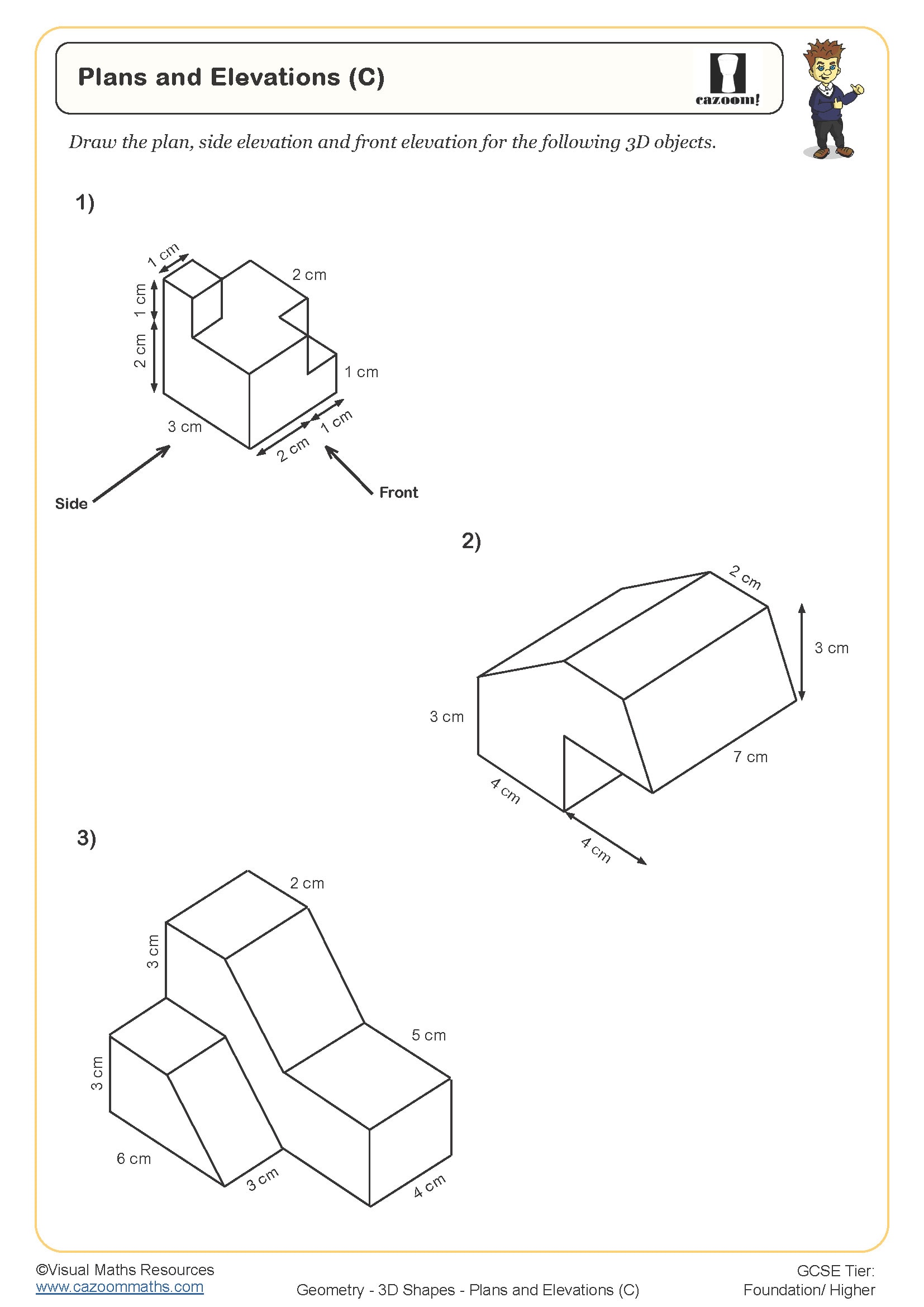
• Plans and elevations – interpreting different viewpoints of solids
• Problem-solving with 3D shapes – applying knowledge to multi-step questions
Tired of Time-Consuming Planning? Save Hours With KS3 3D Shape Resources
Secondary school Maths teachers understand that abstract geometric concepts present difficulties for students with different learning abilities. The worksheets solve this issue by providing multiple entry points for beginners and additional challenges for advanced learners. The combination of procedural fluency with conceptual understanding represents the most effective approach to teaching mathematics according to educational standards. The answer keys present step-by-step mathematical reasoning, which enables students to grasp both the method and the reasoning behind each solution. The mark schemes designed for time efficiency enable teachers to deliver specific feedback instead of spending time on repeated checks. The combination of basic calculations with intricate scenarios throughout the topic maintains lesson engagement at all times.
From Architecture to Art: Real-World Uses of 3D Shape Skills
Understanding three-dimensional shapes extends far beyond the mathematics classroom, influencing career paths and daily decision-making.
Real-world applications include:
• Architecture and design – calculating material requirements for buildings
• Packaging efficiency – determining optimal box sizes and arrangements
• Sports equipment – understanding ball volumes and container capacities
• DIY projects – estimating paint coverage for room surfaces
Gaming and animation – creating realistic 3D environments
• Engineering solutions – designing components with specific volumes
• Environmental science – calculating water tank capacities
• Food preparation – understanding portion sizes and container volumes