Year 9 Compound Measures Worksheets
All worksheets are created by the team of experienced teachers at Cazoom Maths.
Discover the Secret to Faster Compound Measures Calculations With Our PDF Worksheets
Compound measures hinge on two essentials: consistent units and reliable proportional reasoning. Students learn conversion skills and solve multi-step journey problems by using density and population density topics, which extend the distance–speed–time work in the curriculum. The short focused tasks help students develop fluency, while non-calculator questions appear occasionally to maintain their number sense abilities and calculator questions teach efficient methods over mindless keystroke entry. The curriculum requires students to solve rate problems on a regular basis because these problems appear in science and geography classes with similar structures. The subsequent part shows what specific learning accomplishments students achieve.
Specific learning benefits include:
• Secures fluency with distance = speed × time
• Strengthens kph ↔ m/s and other unit conversions
• Builds confidence in rearranging common rate formulas
• Encourages accurate substitution with consistent units
• Improves reasoning across multi-stage journey problems
• Supports targeted homework and intervention routines
Cazoom Maths Worksheets: Complete KS3 Compound Measures Topic Coverage at a Glance
Concepts develop from concrete contexts (tables of journeys, cube models) to pictorial supports (conversion ladders, formula triangles, annotated diagrams) and finally to abstract equations and explanations. Students learn to perform unit conversions at the right time during substitution, and they understand how to follow unit changes through each line of work, and they recognise that average rates need total distance and total time. The sets contain worked solutions which enable students to check their work against a standard example while identifying their own mistakes.
The worksheets in this collection include:
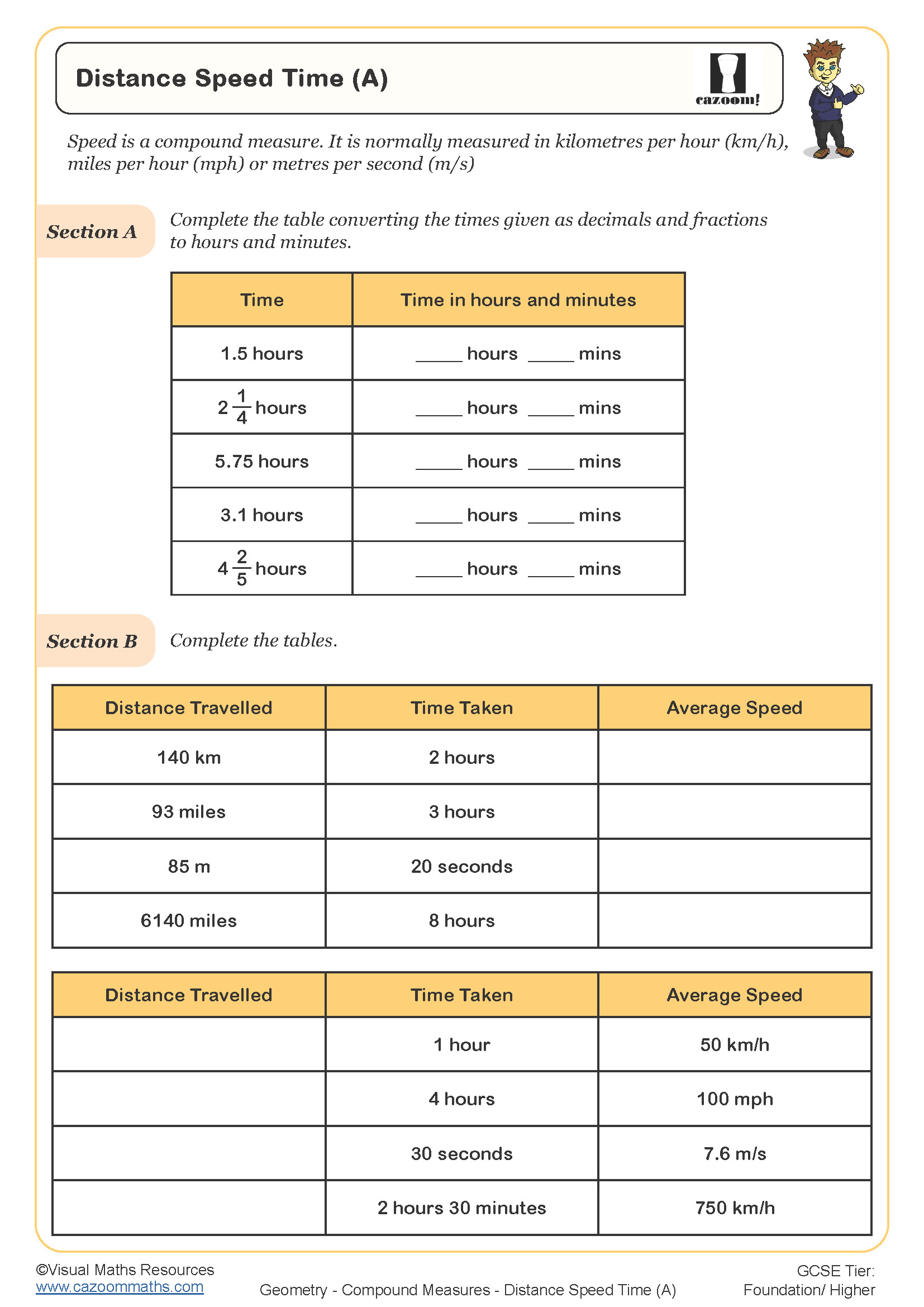
• Distance Speed Time (A) — introduces formula triangles and essential unit changes.
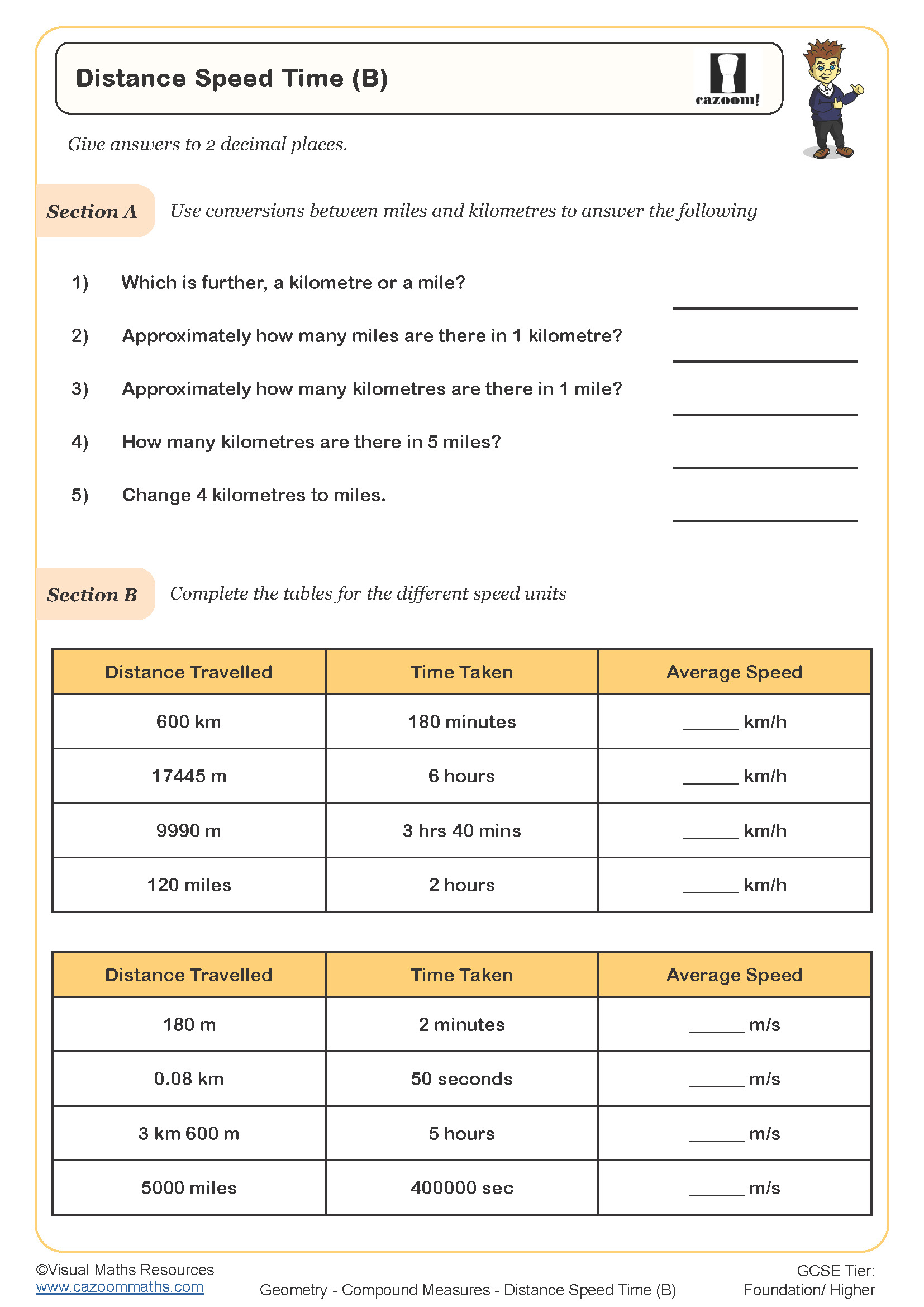
• Distance Speed Time (B) — extends to chained legs and average speed across trips.
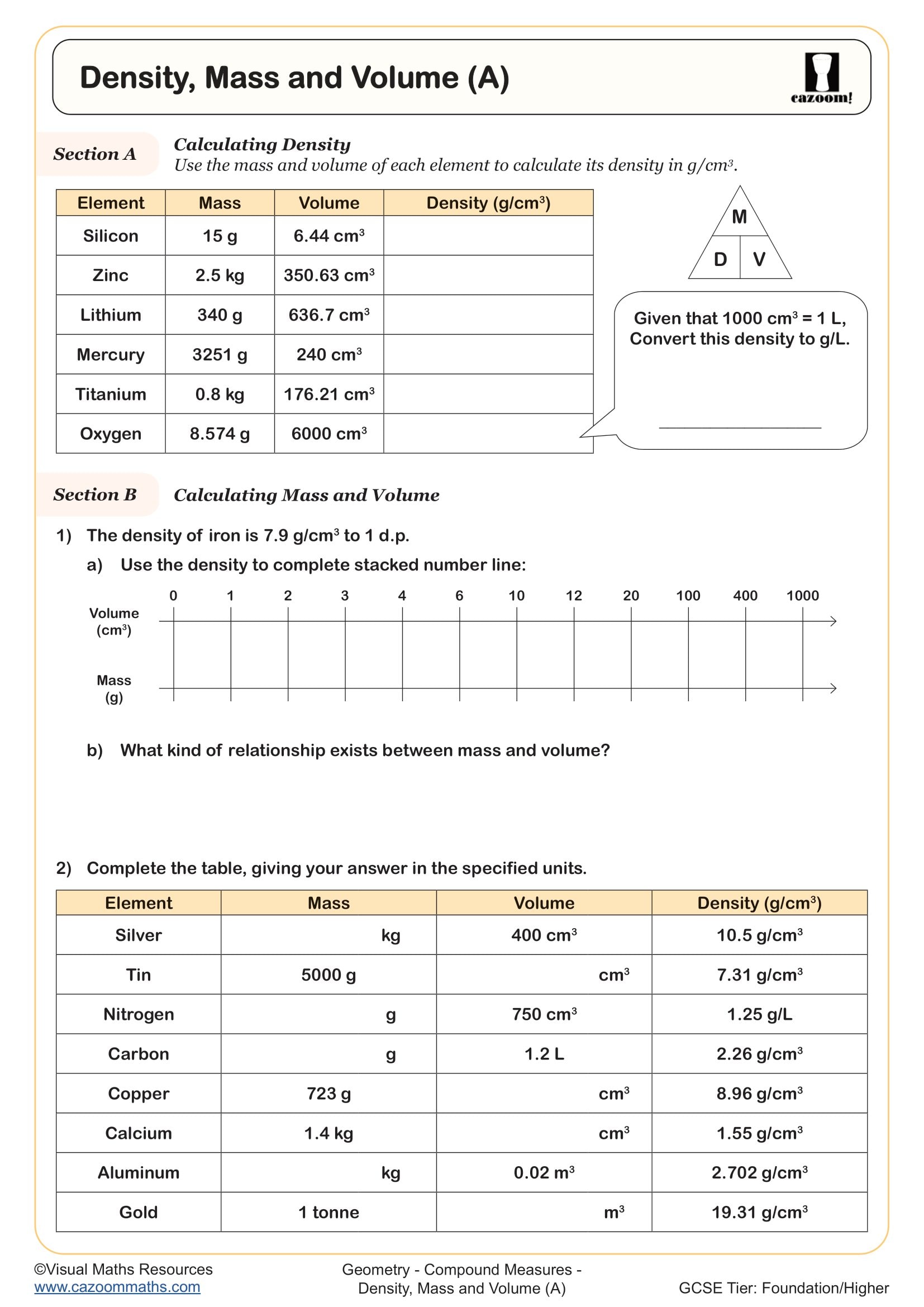
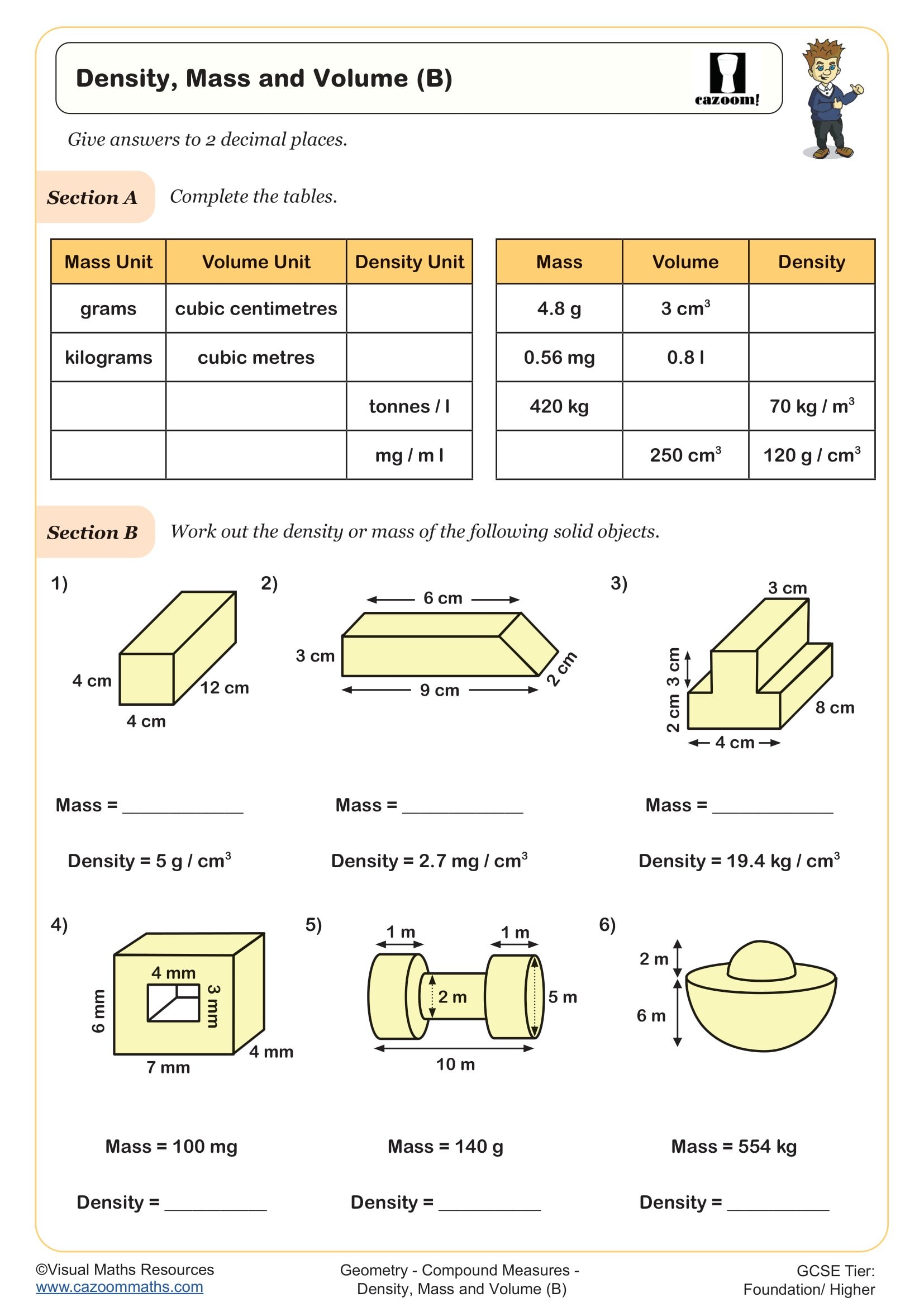
• Density, Mass and Volume (A) — models ρ=mV\rho=\frac{m}{V}ρ=Vm using cubes and tables.
• Density, Mass and Volume (B) — practices rearranging formulas and mixed unit setups.
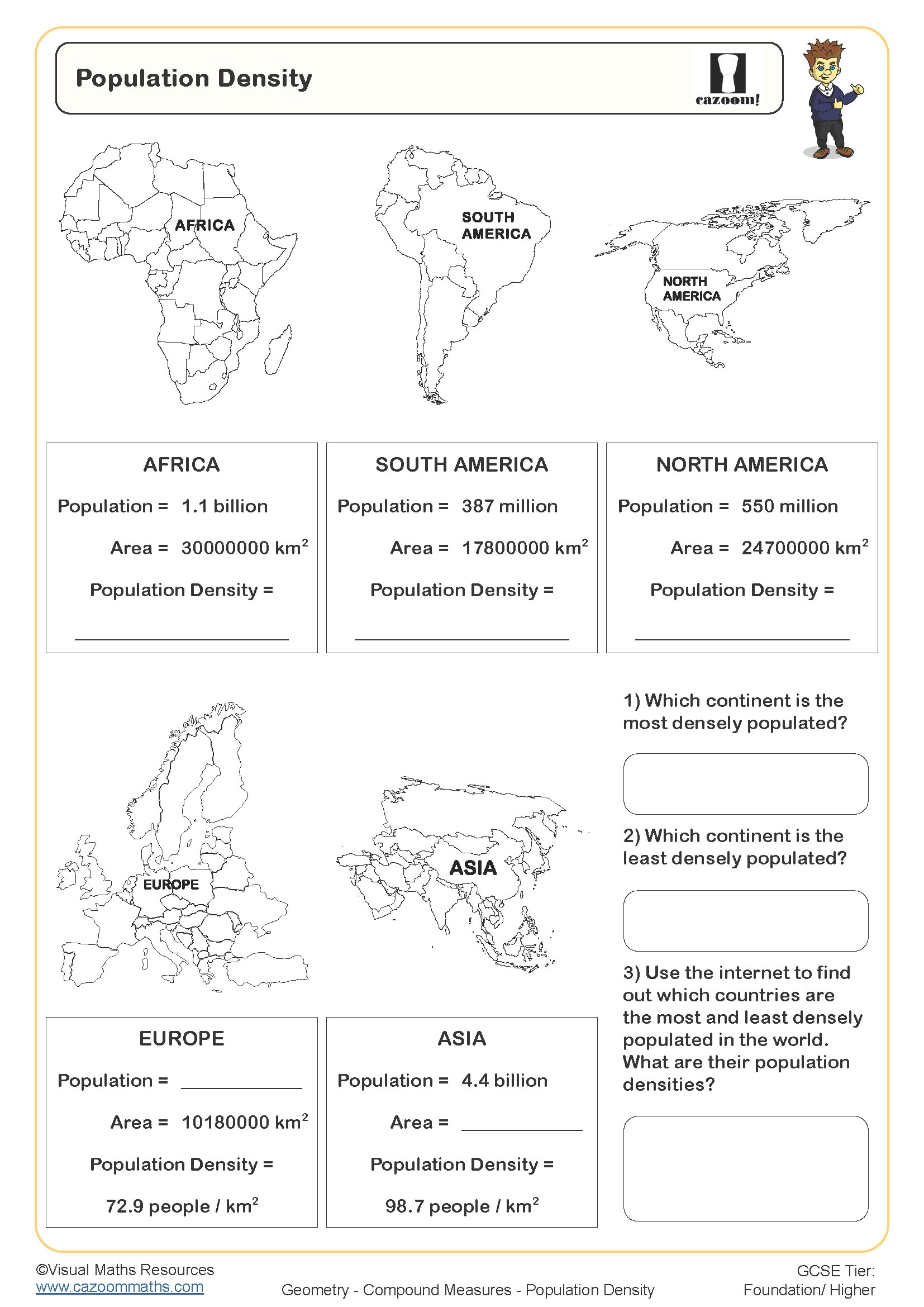
• Population Density — links area and population to interpret people per km².
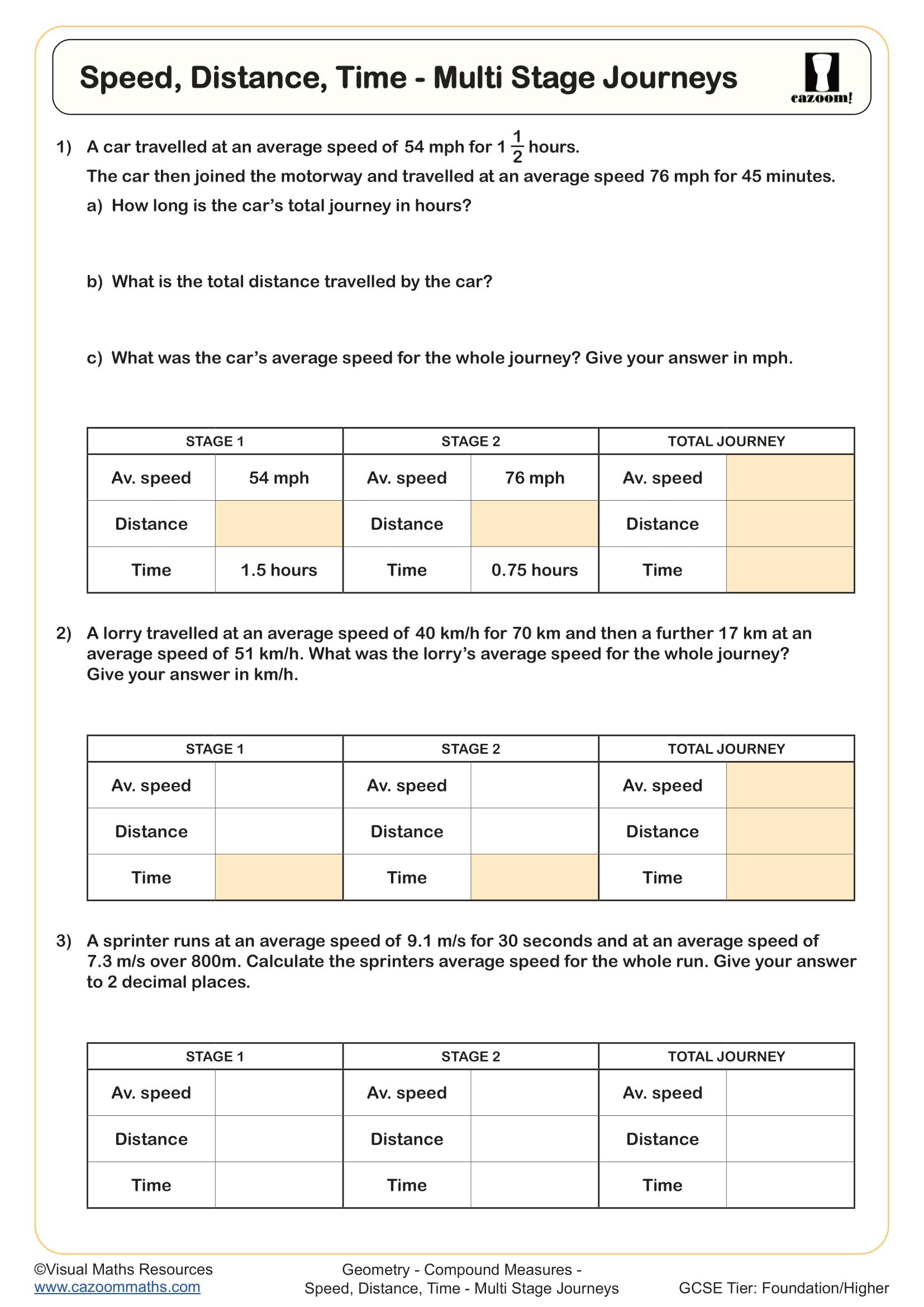
• Speed, Distance, Time – Multi-Stage Journeys — sequences timed legs, waits, and totals.
Transform Geometry Skills With Year 9 Compound Measures Worksheets
The primary focus of this set is on how the system operates in a real classroom environment. The natural sequence of Starters, main tasks and stretch items allows you to move activities between sections without needing to modify the scheme. The first step for students involves using scaffolded tools, which include models, ladders, and prompt questions, to access basic content. However, they will face more challenging material in subsequent units and contexts. Students can complete their assignments more quickly when using print-friendly layouts, as these designs reduce their mental effort. The answer sheets demonstrate student thinking through line-by-line reasoning and unit tracking, enabling them to identify mistakes and develop more effective methods for future work. These resources provide an optimal mix of support and challenge, which helps teachers save time during planning sessions for first teaching, retrieval practice, and homework checks. The department-wide use of Cazoom Maths becomes simpler because all resources follow a uniform structure, which enables easy sharing and sequence organisation.
Everyday Maths: Uses for Year 9 Compound Measures
Rate skills turn up constantly in life, from planning journeys to lab work. Students notice the same structures reappear across subjects and in their daily decisions.
• The evaluation of different routes depends on their average speed and predicted time delays.
• PE training logs require the conversion of running pace and cycling speed for proper documentation.
• The process of determining delivery time spans depends on three main factors: the delivery distance, the number of stops, and the expected traffic conditions.
• The process of understanding population density through map analysis forms a crucial part of geography case study research.
• Science experiments require students to determine density by measuring mass and volume.
• The process of planning fuel consumption and expenses for multiple stages of road travel needs thorough evaluation.
• The process of increasing production levels applies to recipes as well as DT projects and canteen planning.
• The verification process for data transfer speed and download duration takes place within computing systems.