Percentage Increase and Decrease RESOURCE (FREE DOWNLOAD)
Percentage Increase and Decrease RESOURCE DESCRIPTION
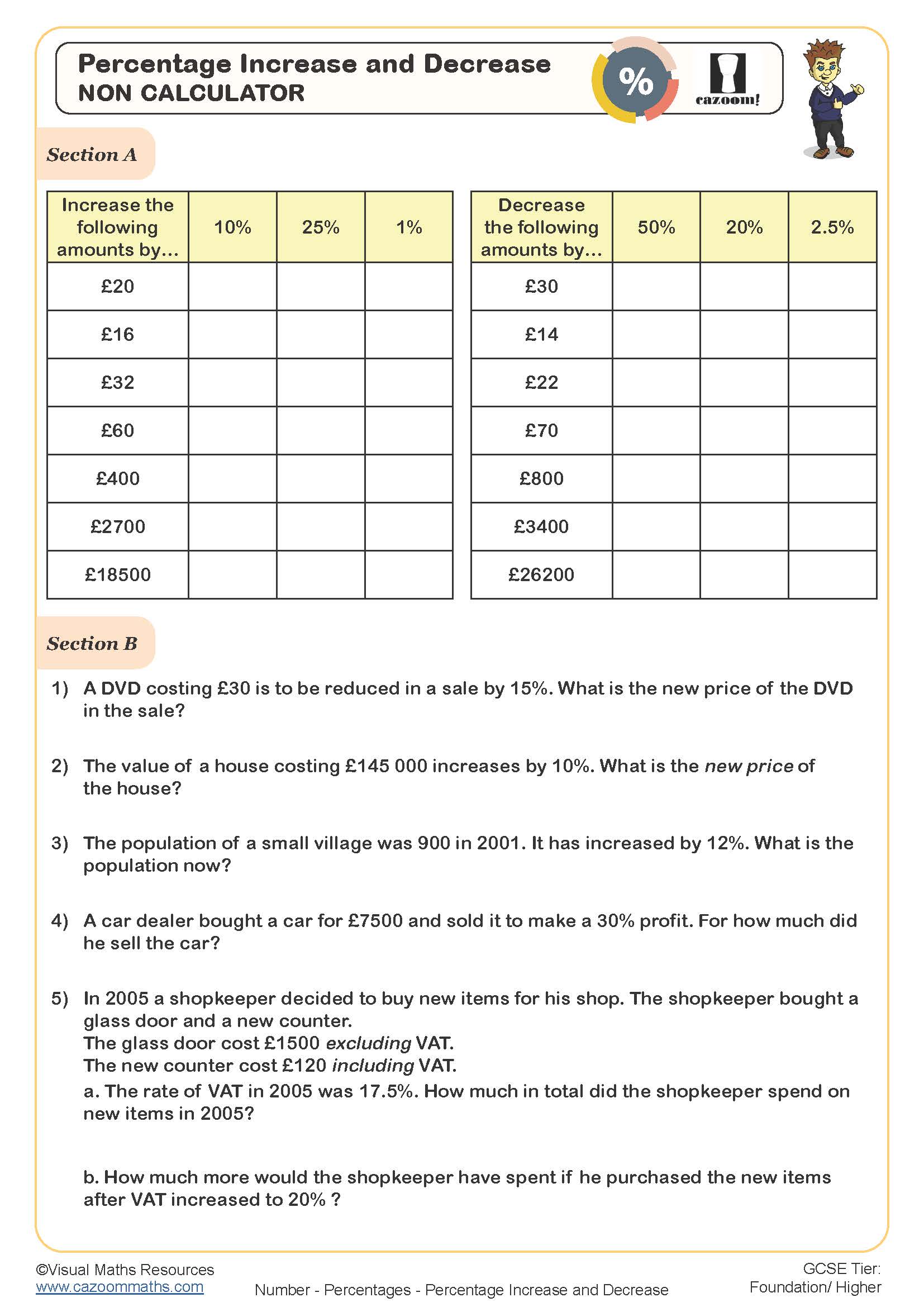
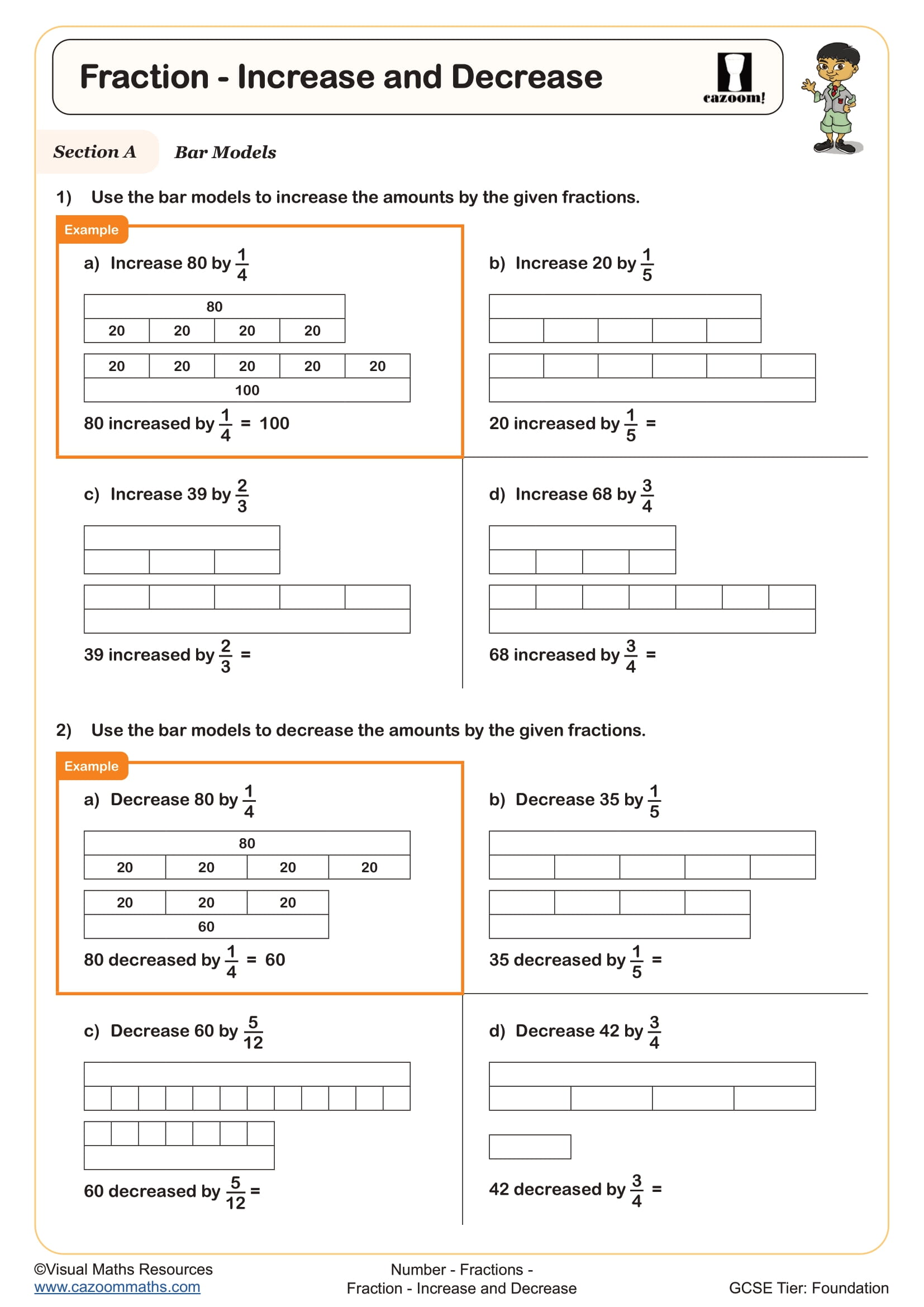
Here are four examples of calculating percentage increases and decreases over two pages. The method of finding the percentage to be increased/decreased by and then adding or subtracting from the original is used.
How to Calculate Percentage Increase and Decrease
Understanding percentage increase and decrease is an essential skill in maths, used in real-life applications such as finance, discounts, and population growth. This guide will explain step-by-step how to calculate percentage increases and decreases with clear examples.
:
🔢 What is Percentage Increase?
A percentage increase happens when a value grows by a certain percentage of its original amount.
Formula:
New Value = Original Value + (Percentage × Original Value)
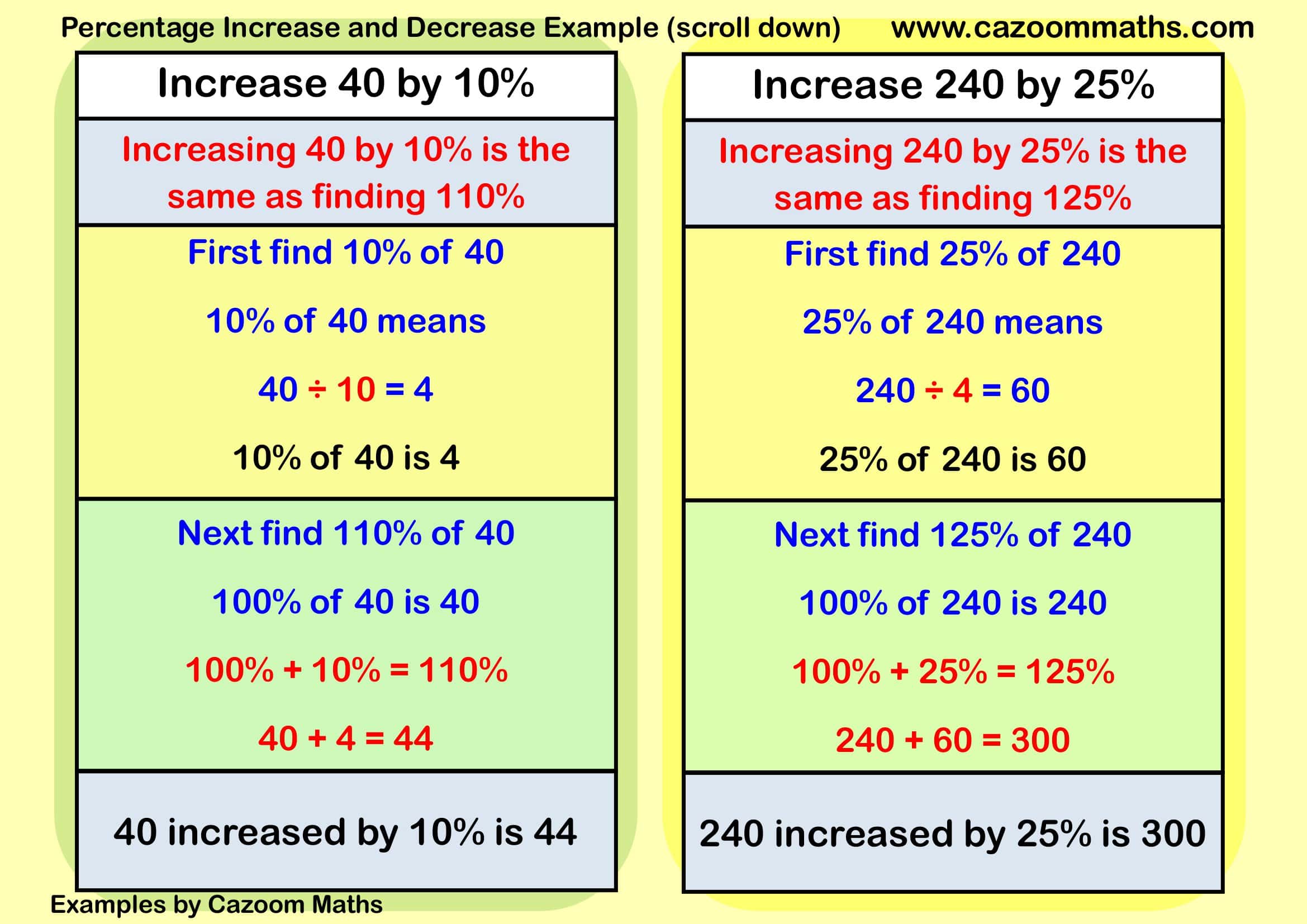
✅ Example 1: Increase 40 by 10%
10% of 40 = 40 ÷ 10 = 4
New value = 40 + 4 = 44
✔️ 40 increased by 10% is 44.
✅ Example 2: Increase 240 by 25%
25% of 240 = 240 ÷ 4 = 60
New value = 240 + 60 = 300
✔️ 240 increased by 25% is 300.
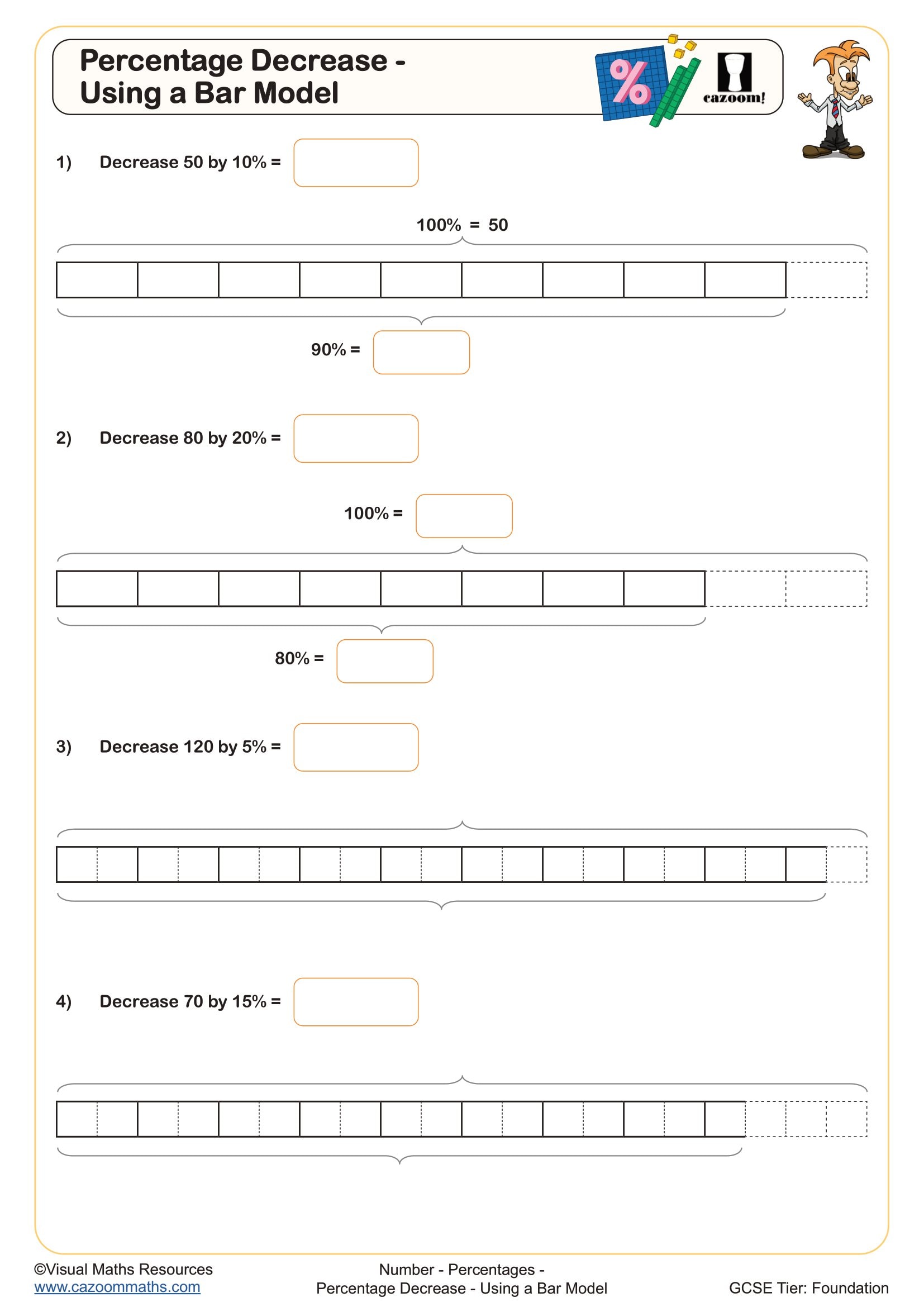
📉 What is Percentage Decrease?
A percentage decrease happens when a value is reduced by a given percentage of its original amount.
Formula:
New Value = Original Value − (Percentage × Original Value)
✅ Example 1: Decrease 80 by 15%
15% of 80 = 80 × 0.15 = 12
New value = 80 − 12 = 68
✔️ 80 decreased by 15% is 68.
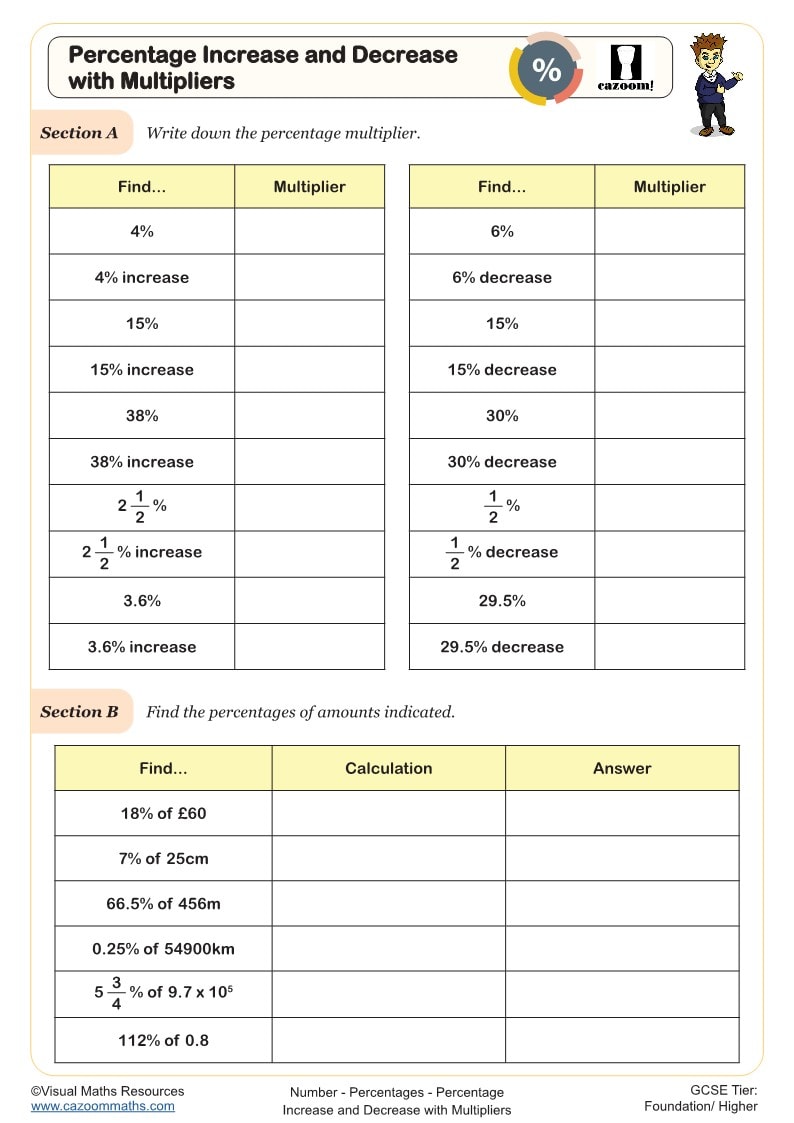
⚡ Quick Trick for Percentage Changes
Instead of calculating the percentage separately, multiply the original number by a multiplier:
Increase by 20% → Multiply by 1.20
Decrease by 30% → Multiply by 0.70
✅ Example: Increase 150 by 20%
150 × 1.20 = 180
✔️ 150 increased by 20% is 180.
✅ Example: Decrease 200 by 30%
200 × 0.70 = 140
✔️ 200 decreased by 30% is 140.
Common Mistakes When Working with Percentages
🚫 Adding percentages incorrectly – Always apply percentage calculations to the original number, not previous results.
🚫 Mixing percentage increase and percentage decrease – Increasing by 50% then decreasing by 50% does NOT bring you back to the original value.
All worksheets are created by the team of experienced teachers at Cazoom Maths.