KS1 and KS2 Fractions, Decimals and Percentages
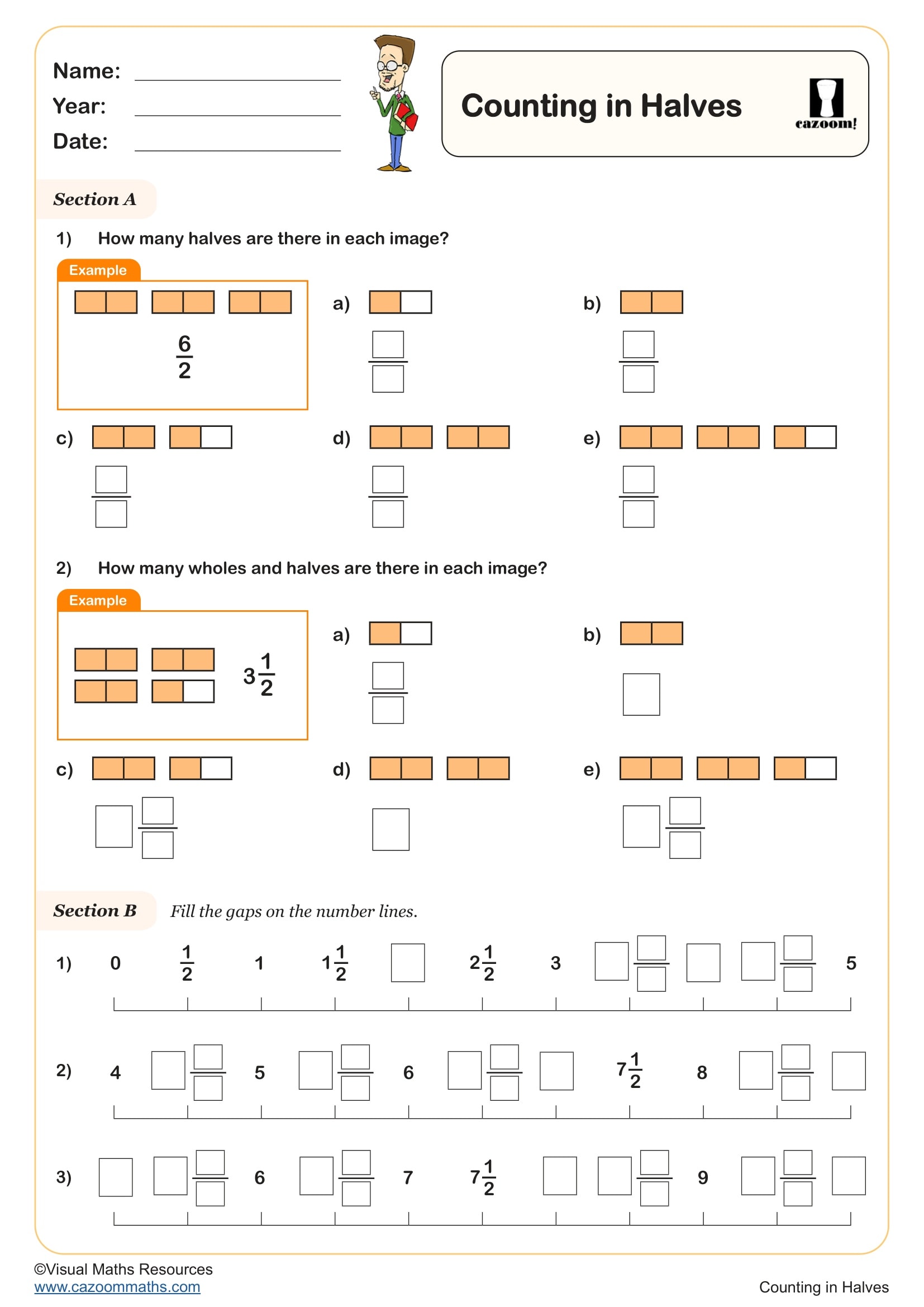
Counting in Halves
Year groups: 2
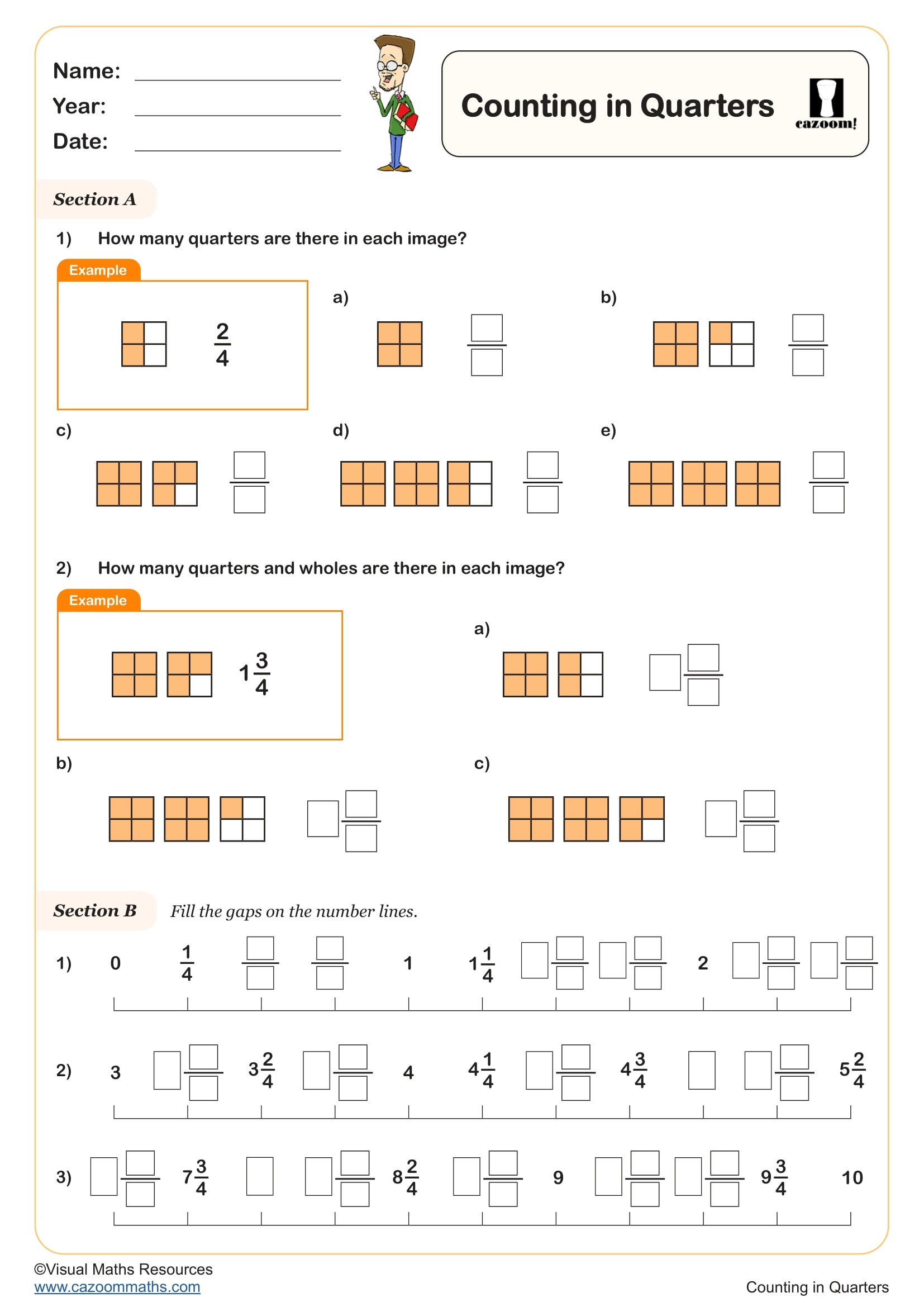
Counting in Quarters
Year groups: 2
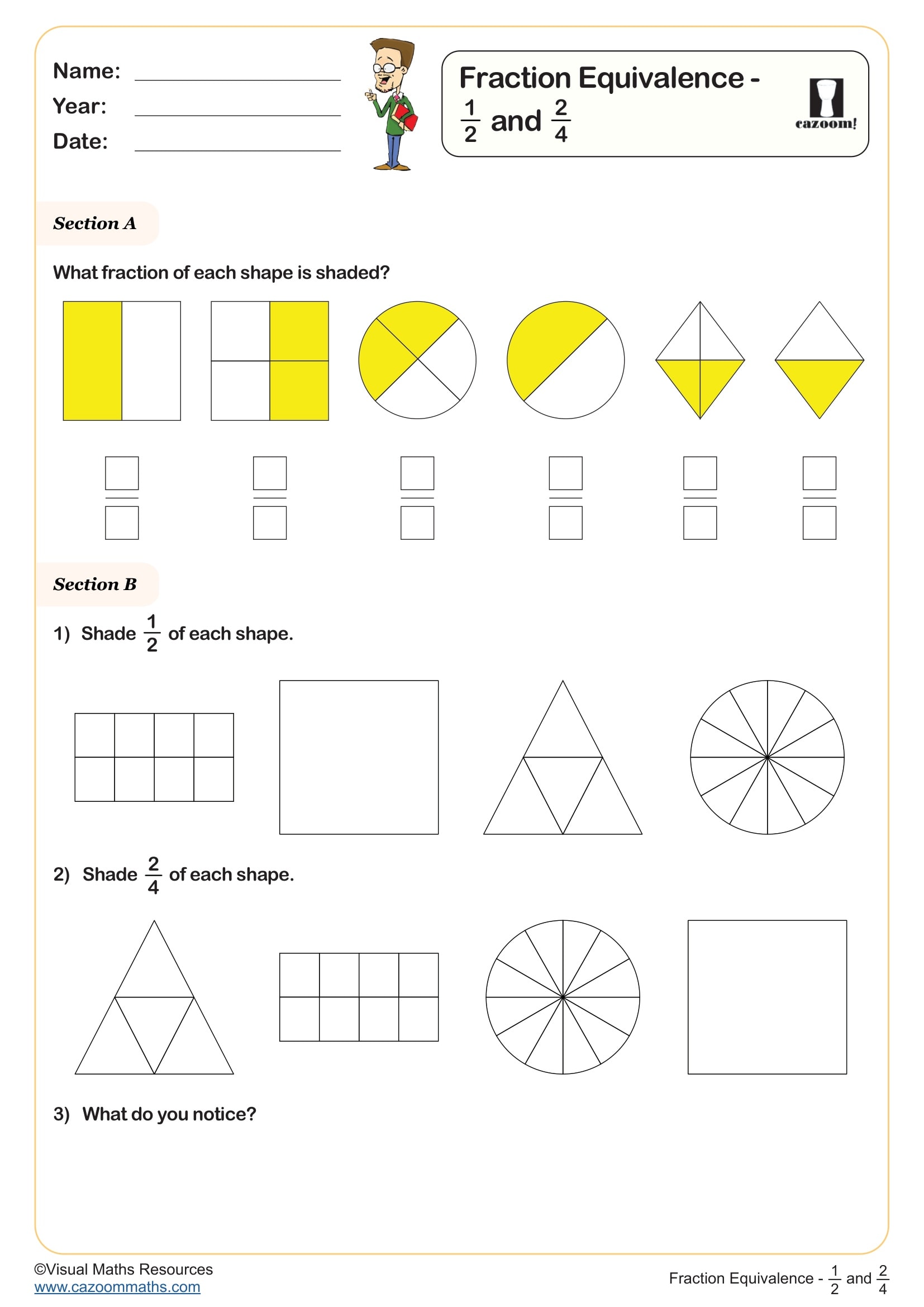
Fraction Equivalence - 1/2 and 2/4
Year groups: 2
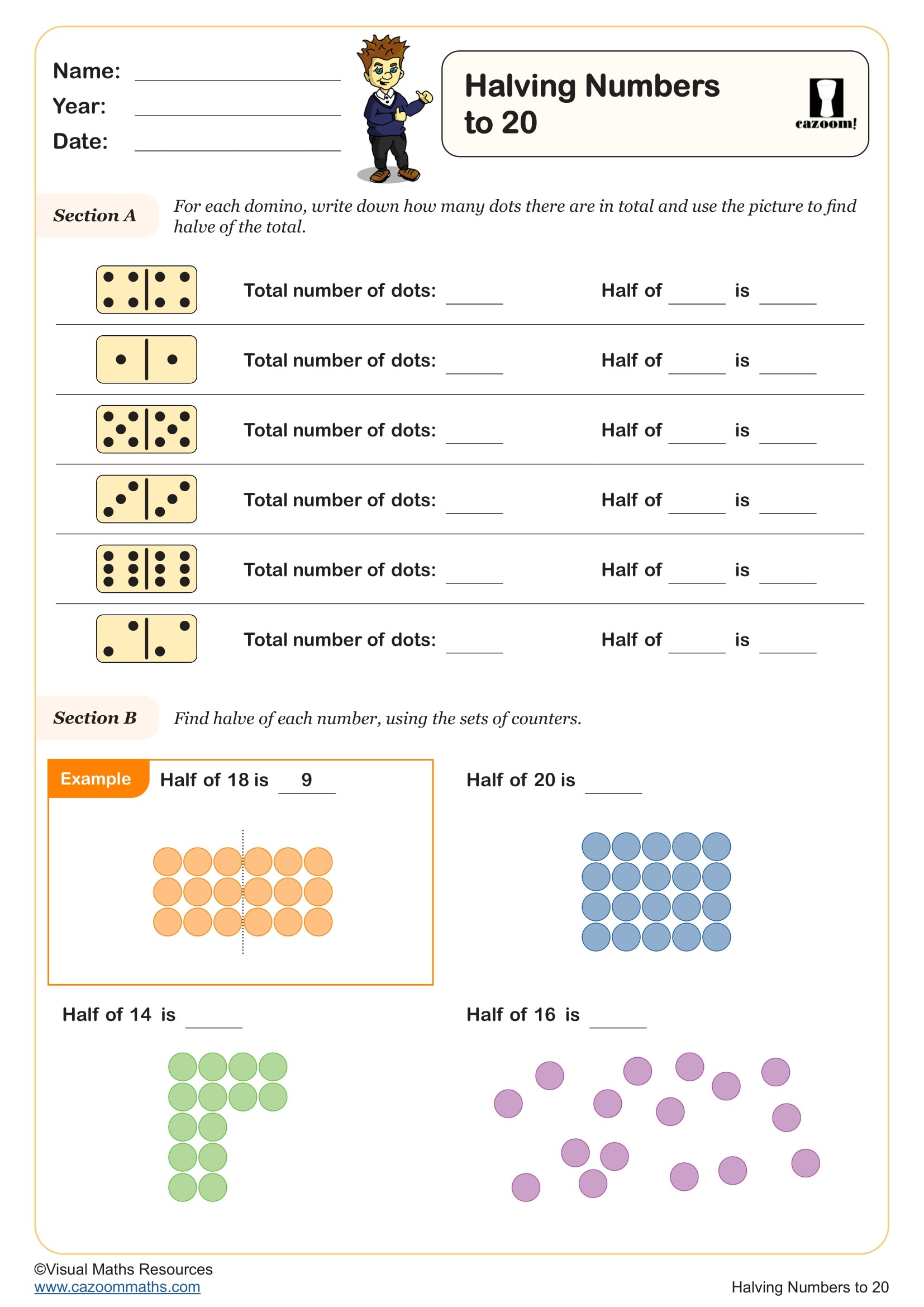
Halving Numbers to 20
Year groups: 2, 3
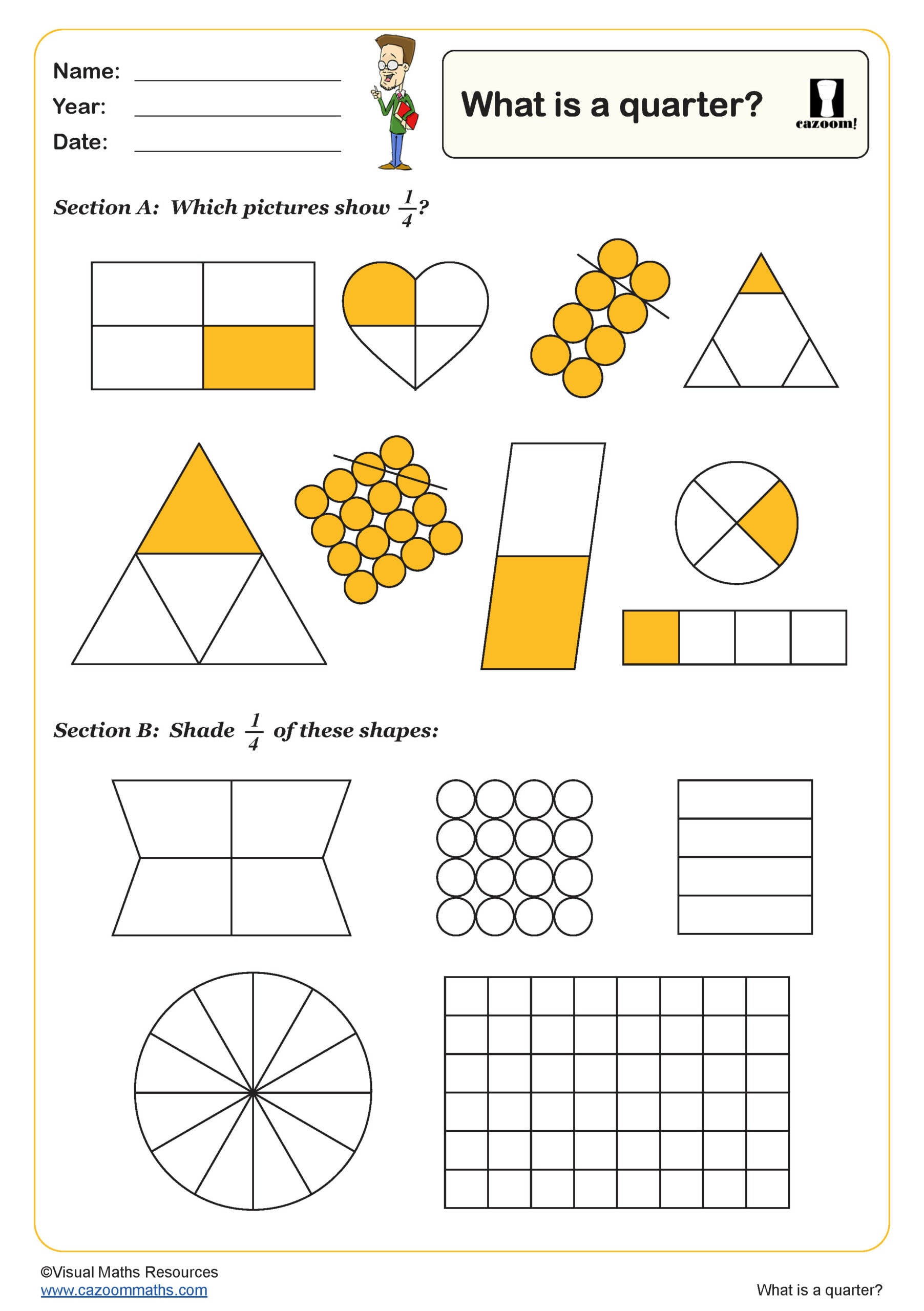
Unit Fractions
Year groups: 2
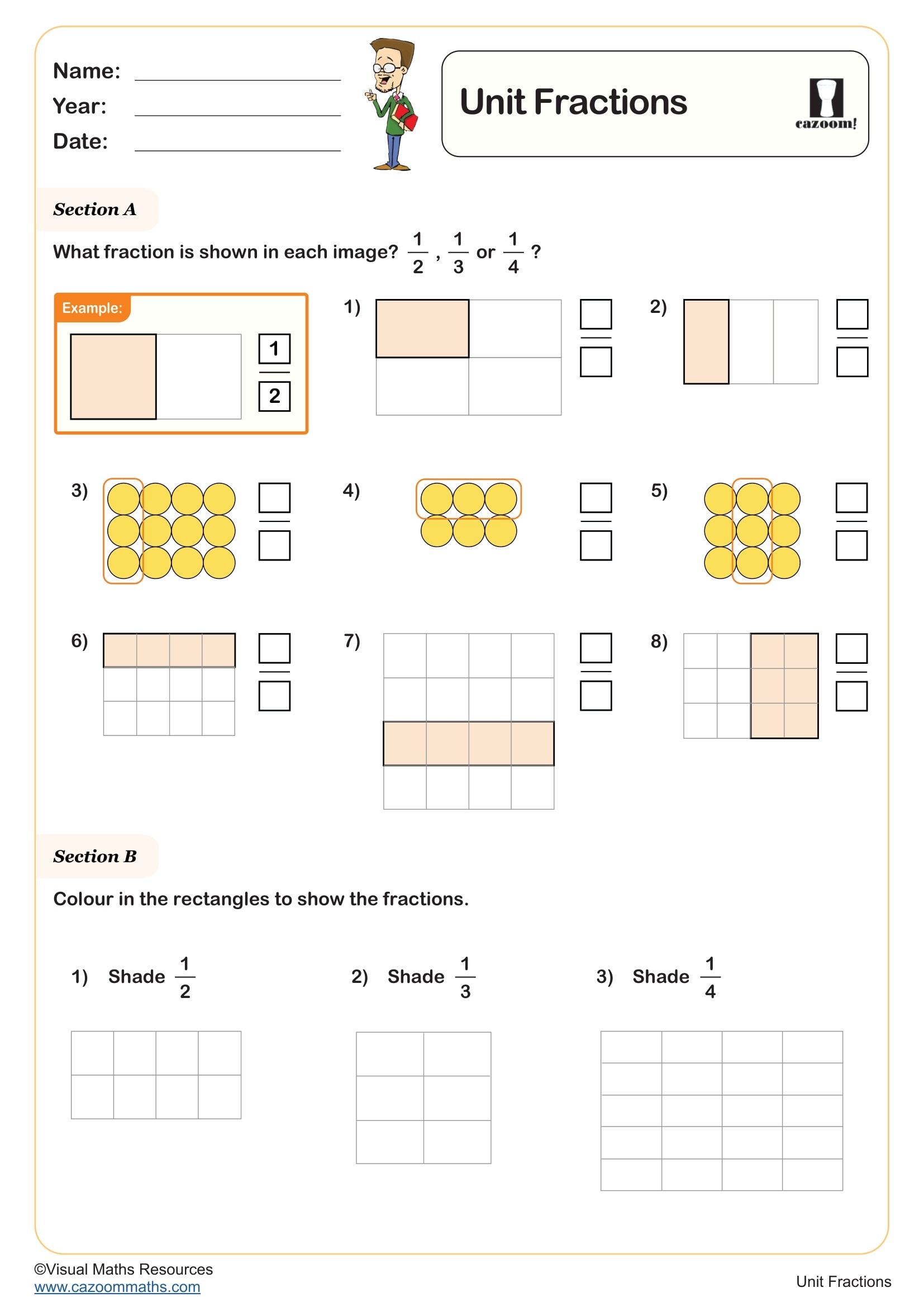
What is 3/4?
Year groups: 2
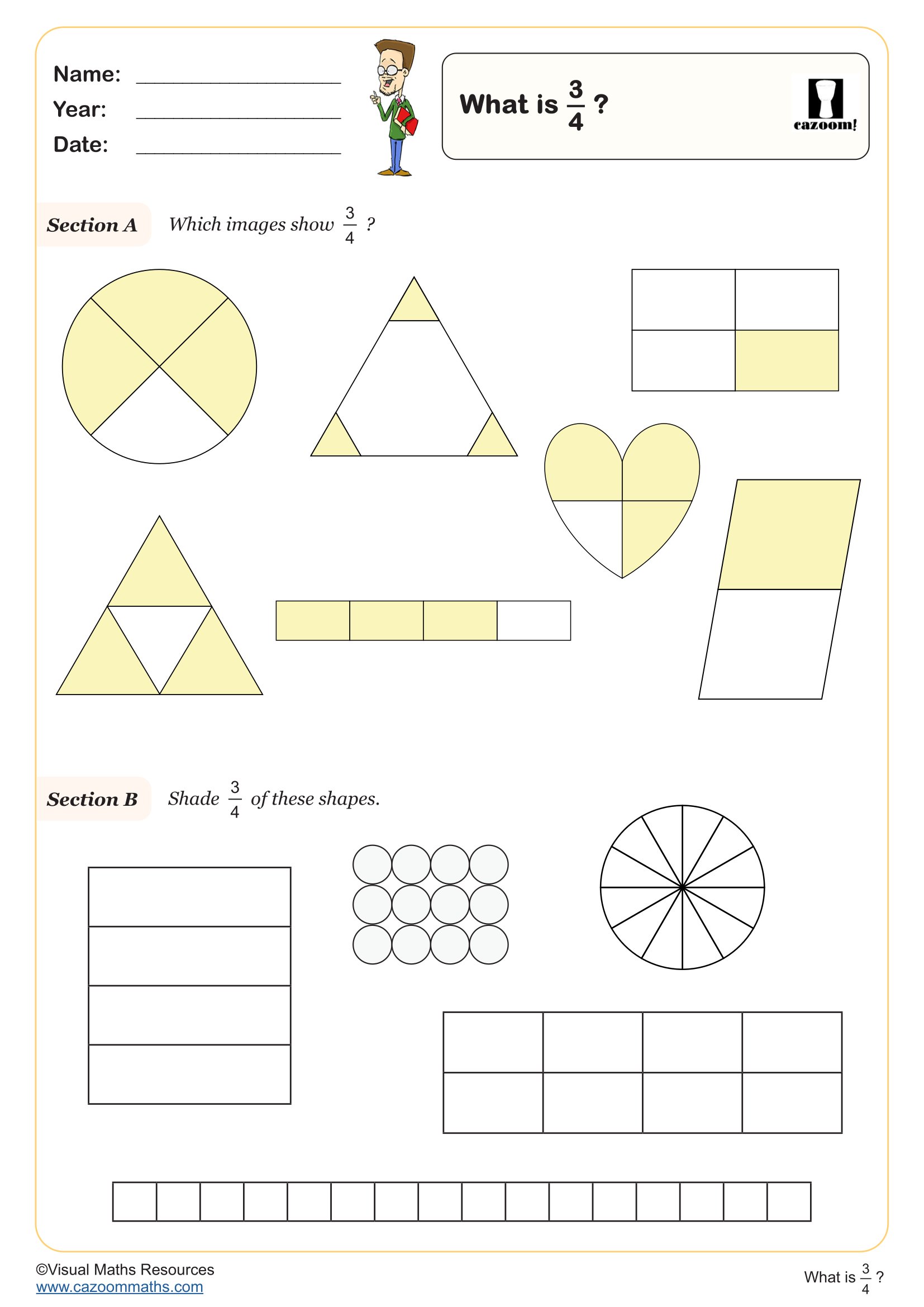
What is a Half?
Year groups: 2
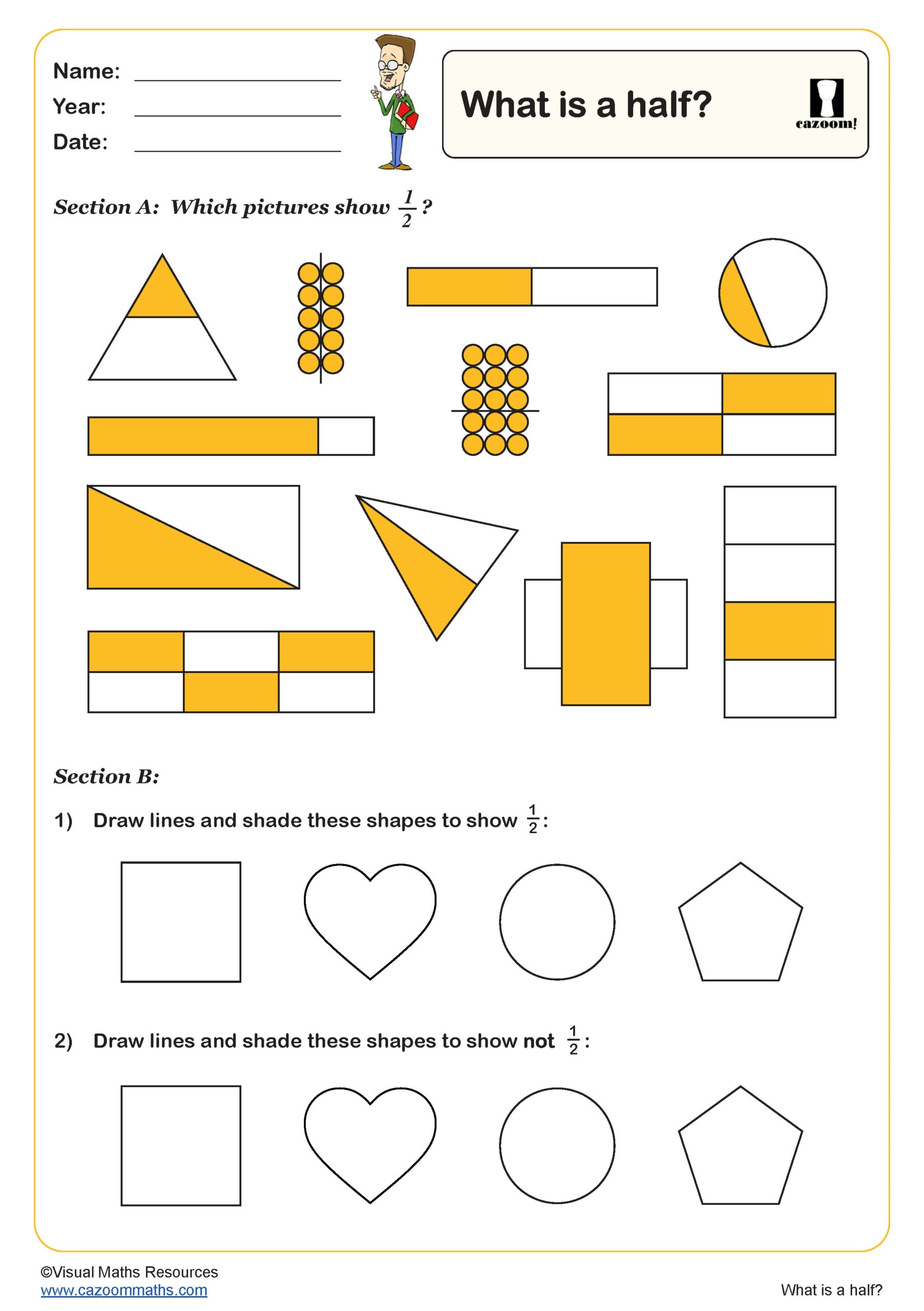
What is a Quarter?
Year groups: 2
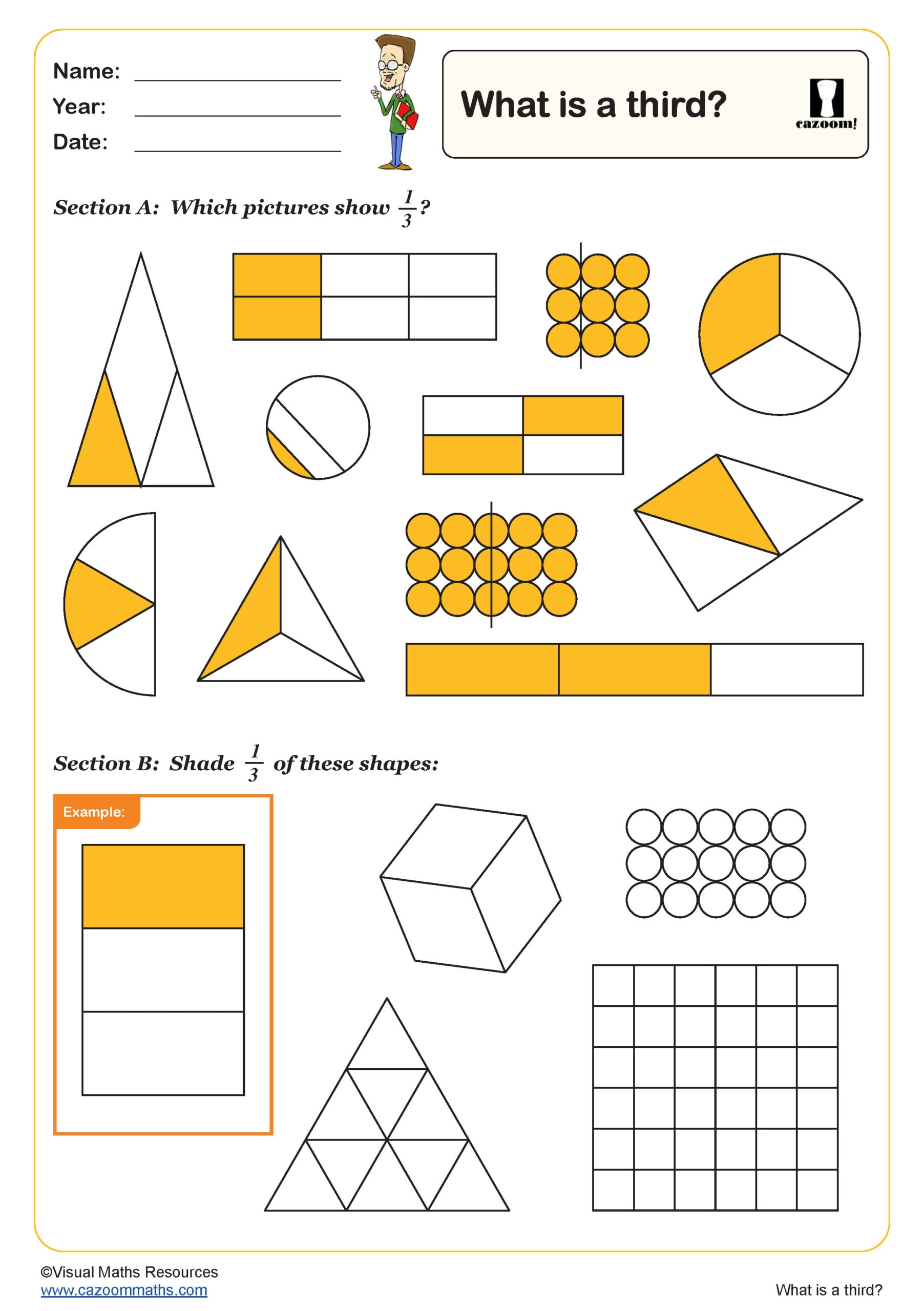
What is a Third?
Year groups: 2
Add and Subtract Fractions (A)
Year groups: 3

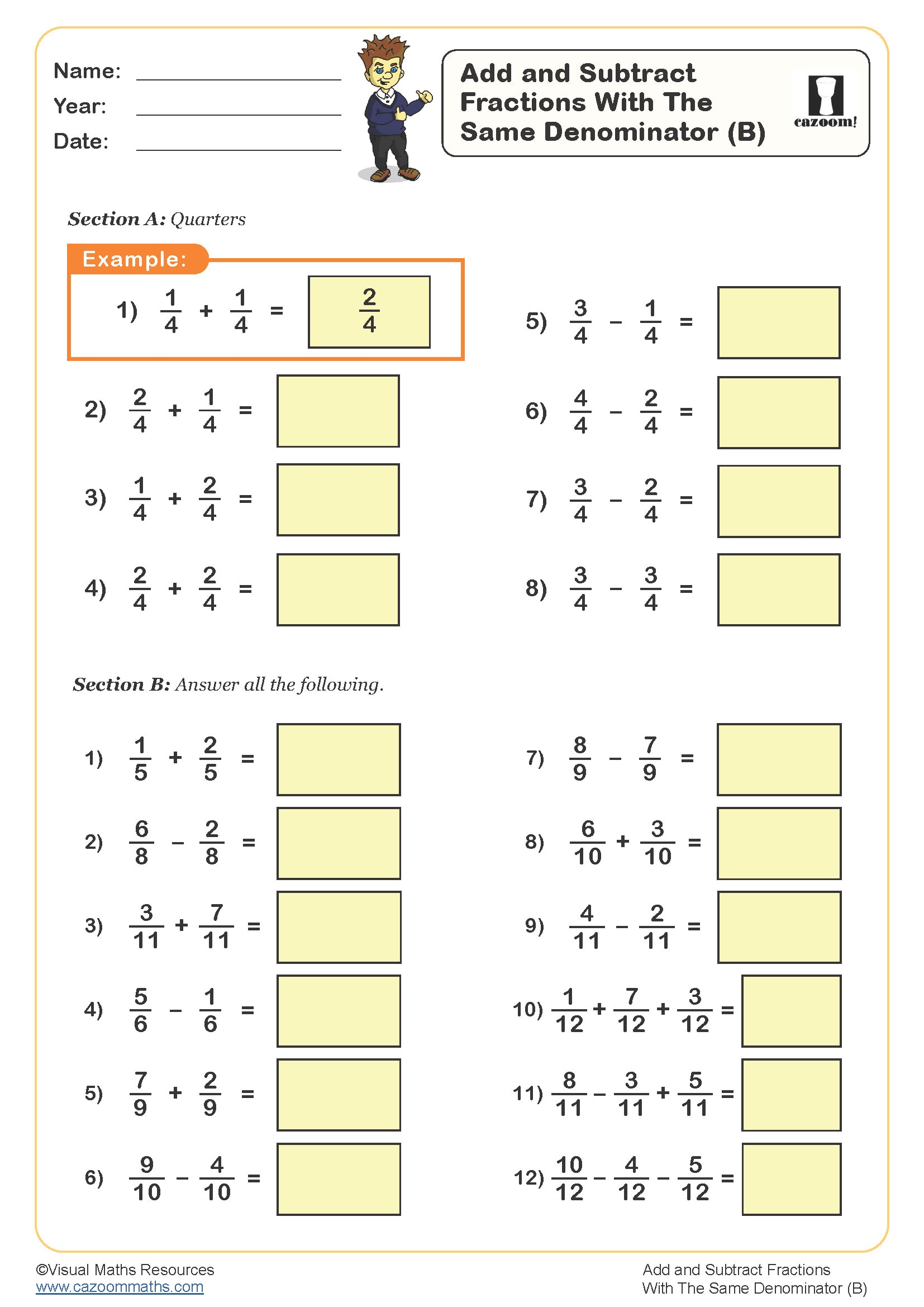
Add and Subtract Fractions (B)
Year groups: 3
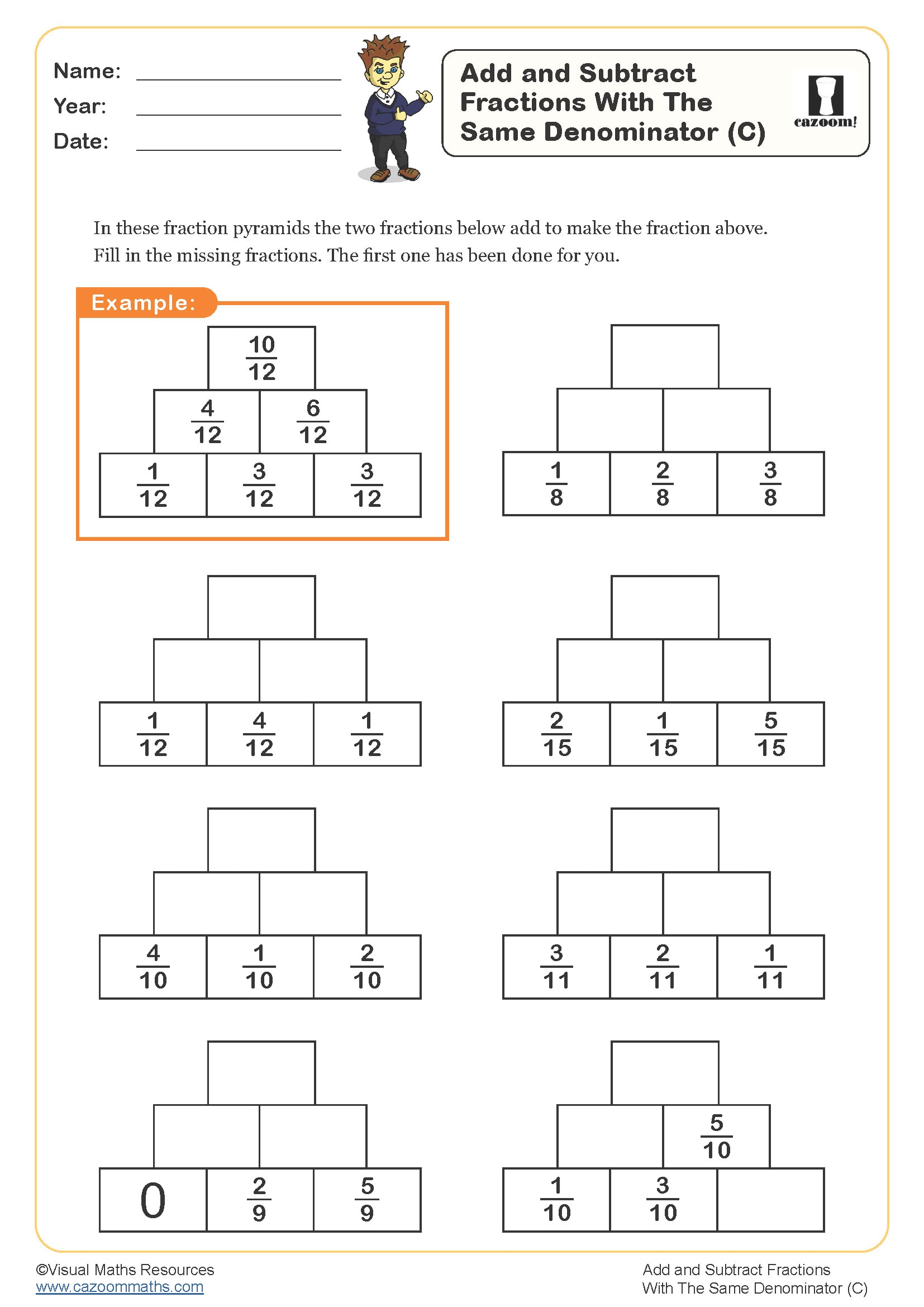
Add and Subtract Fractions (C)
Year groups: 3
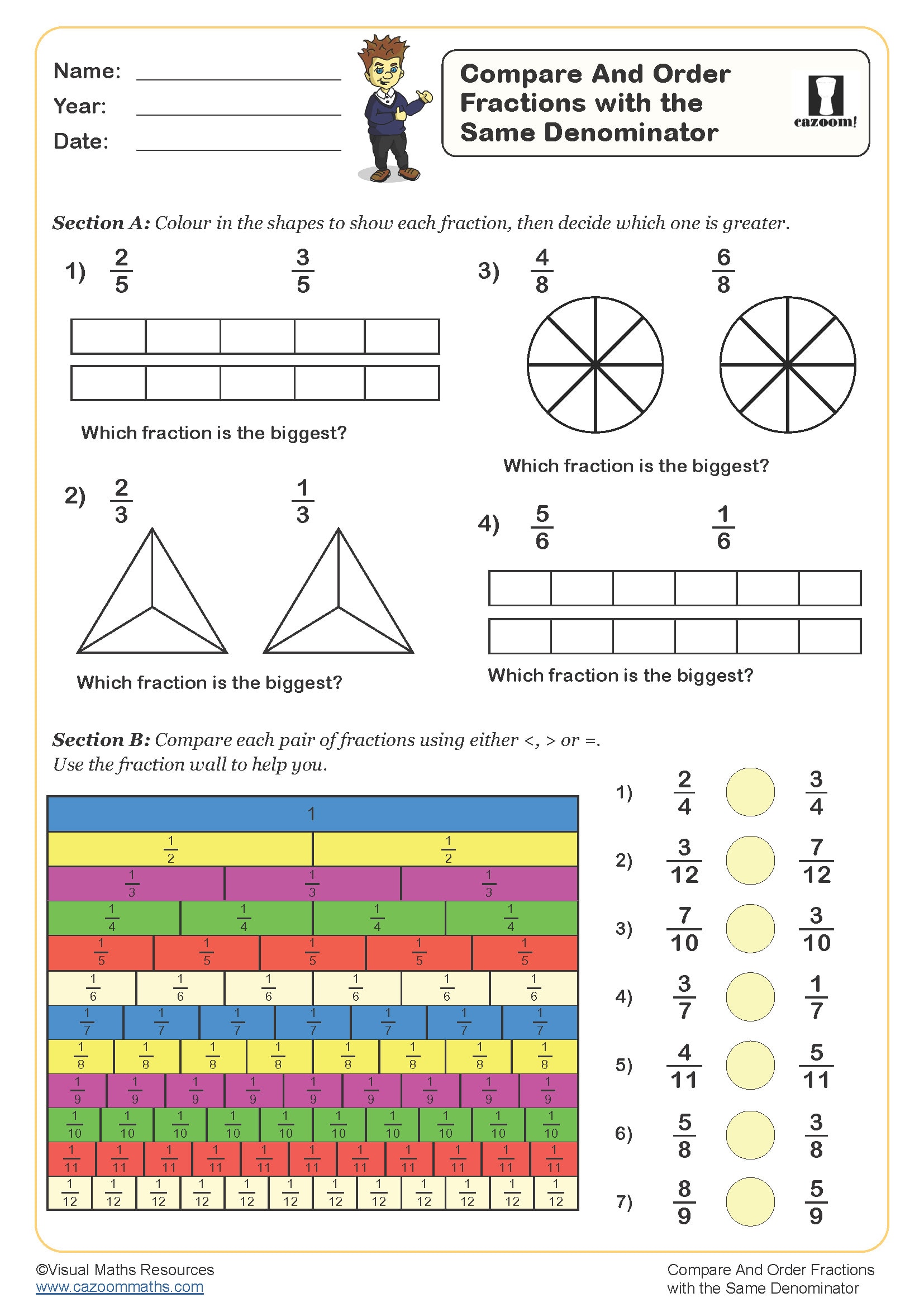
Compare and Order Fractions with the Same Denominator
Year groups: 3
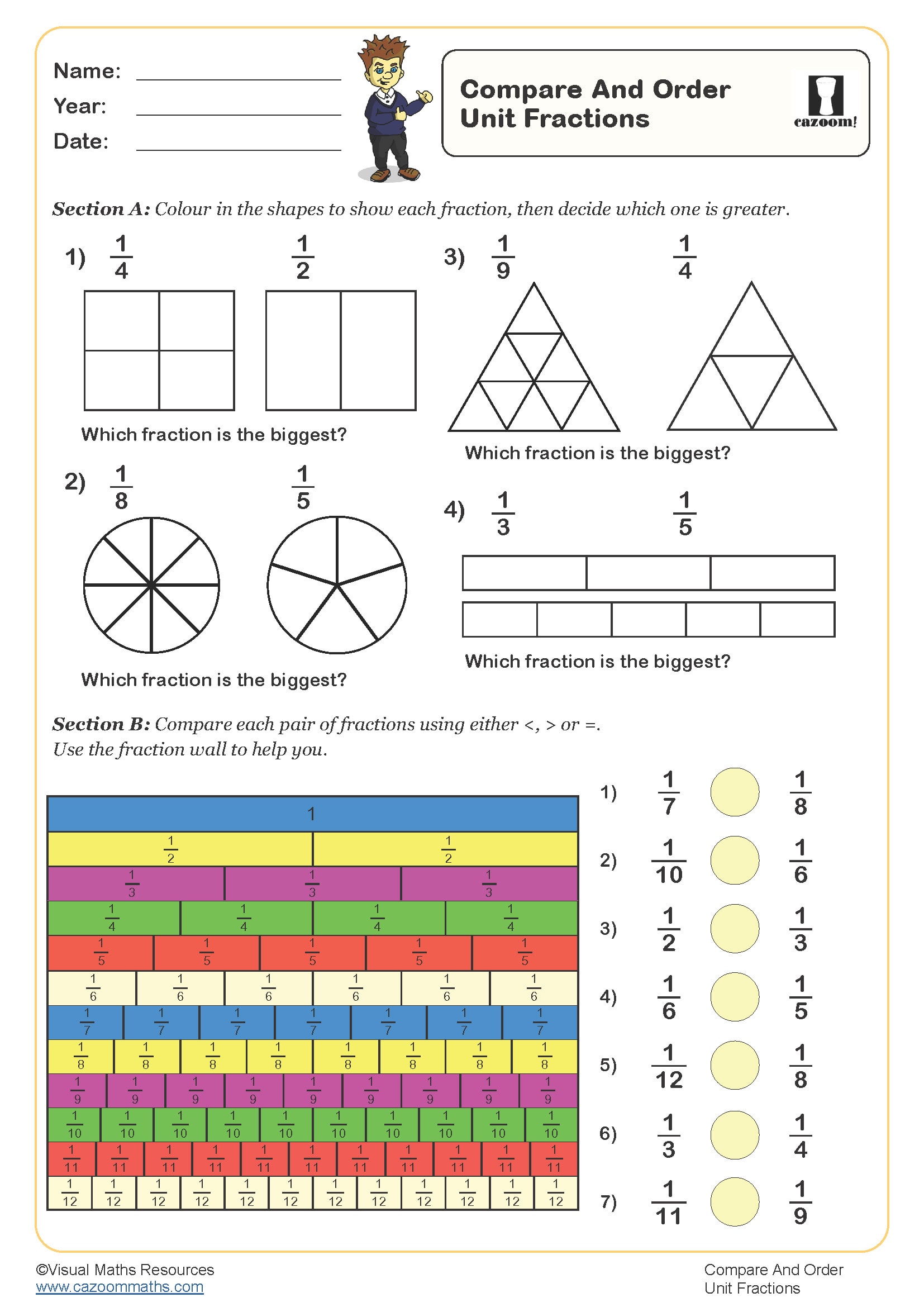
Compare and Order Unit Fractions
Year groups: 3
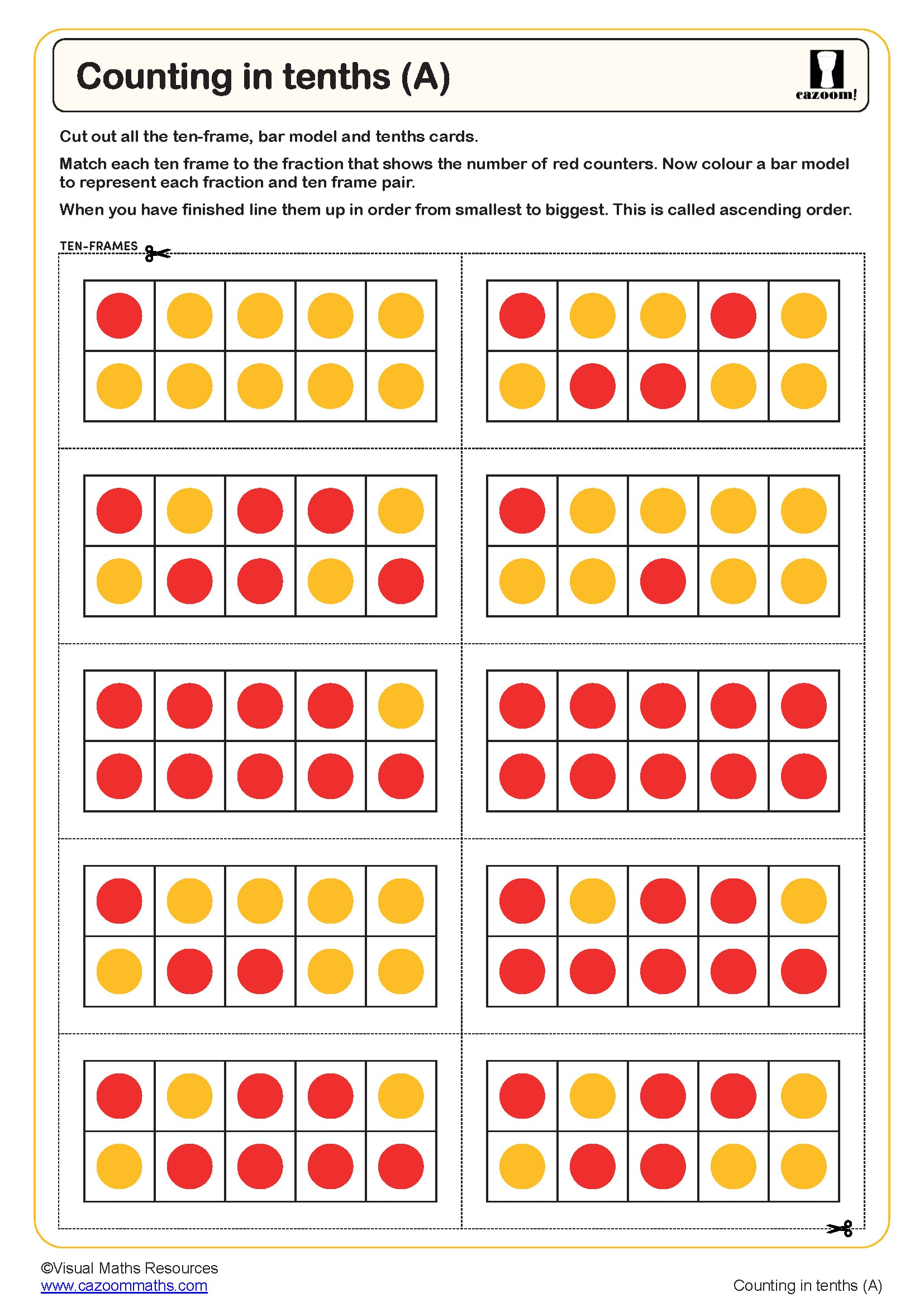
Counting in Tenths (A)
Year groups: 3
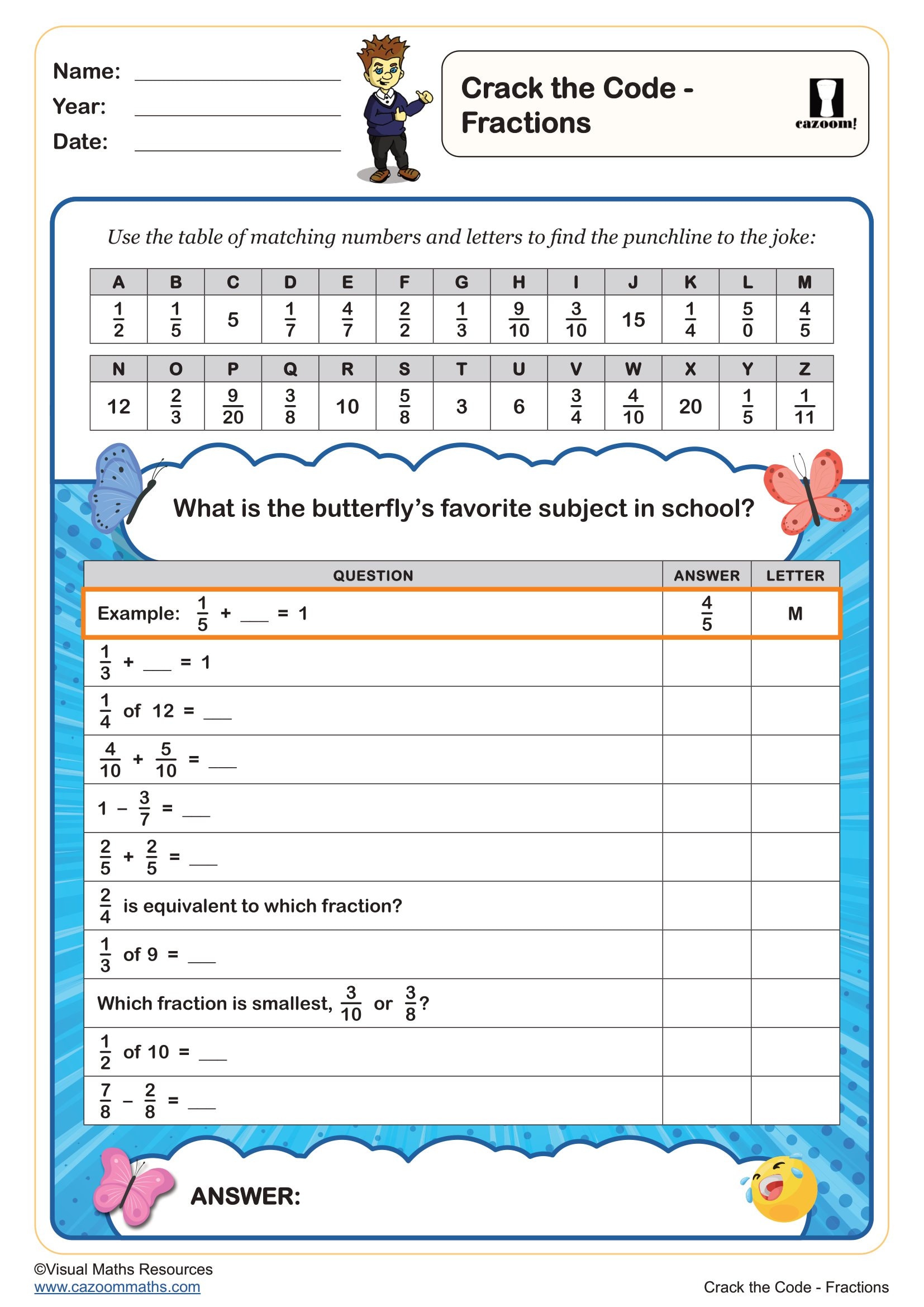
Crack the Code - Fractions
Year groups: 3, 4
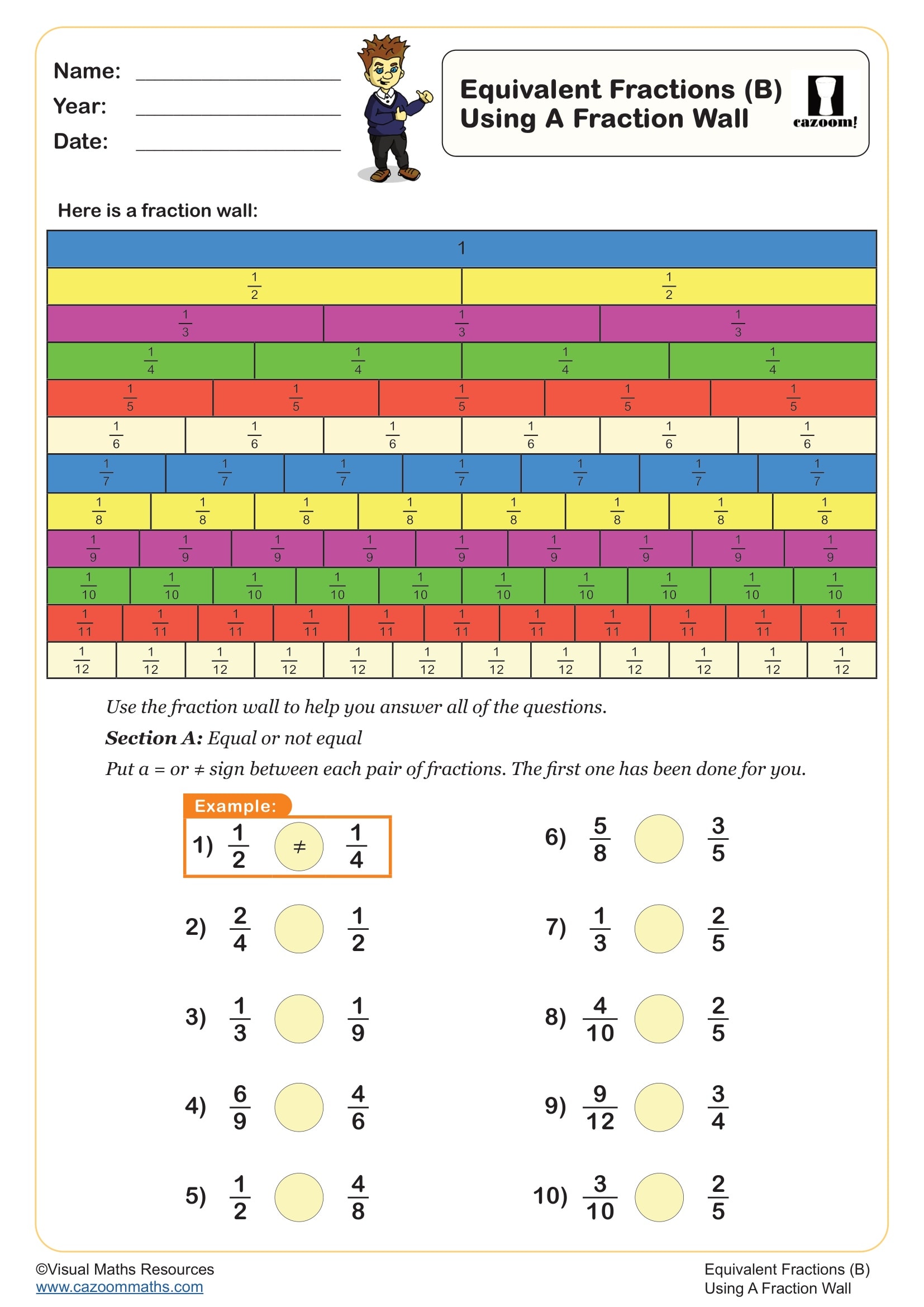
Equivalent Fractions Using a Fraction Wall (B)
Year groups: 3, 4
Equivalent Fractions Using Bar Models (A)
Year groups: 3, 4

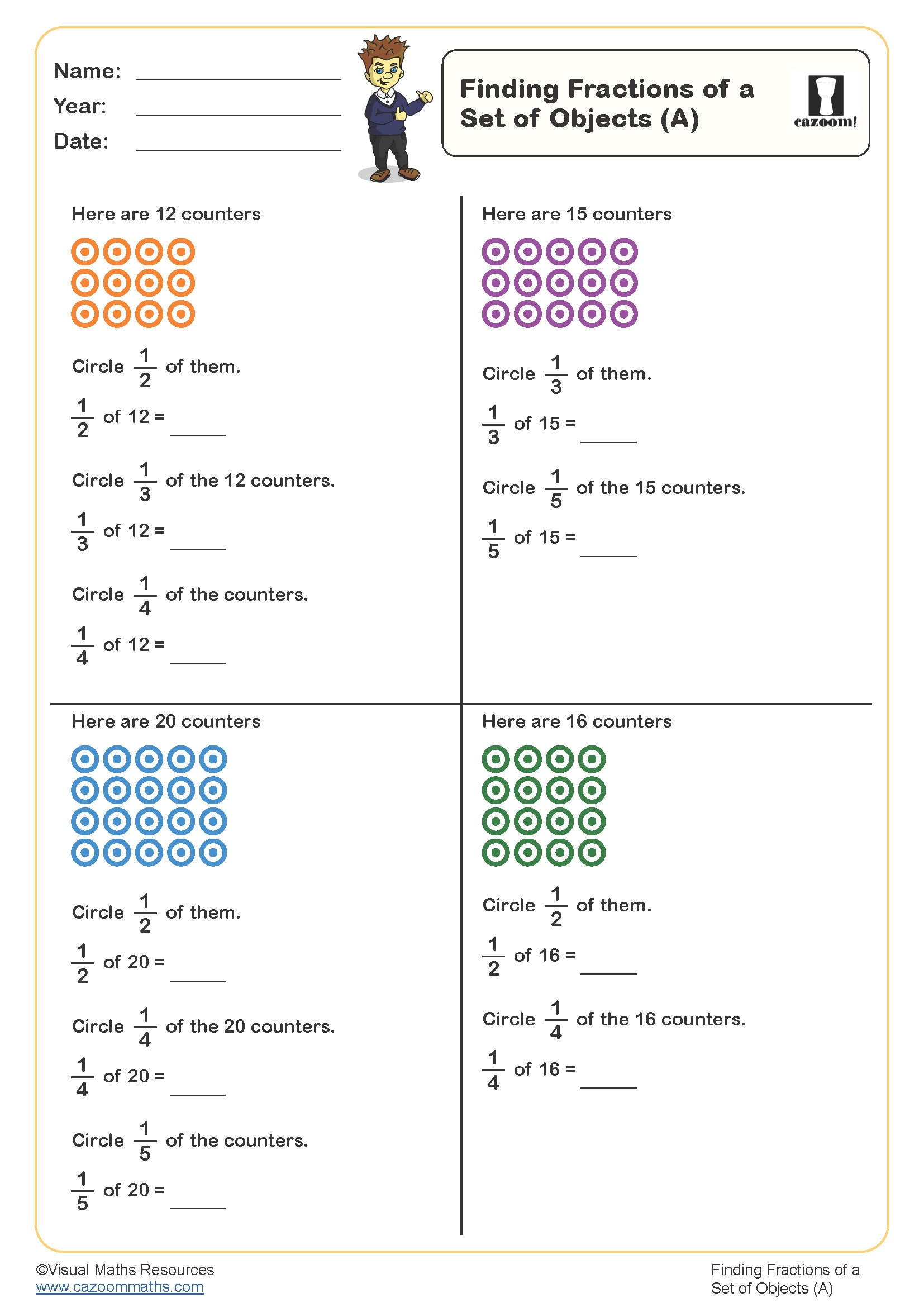
Finding fractions of a set of objects (A)
Year groups: 3
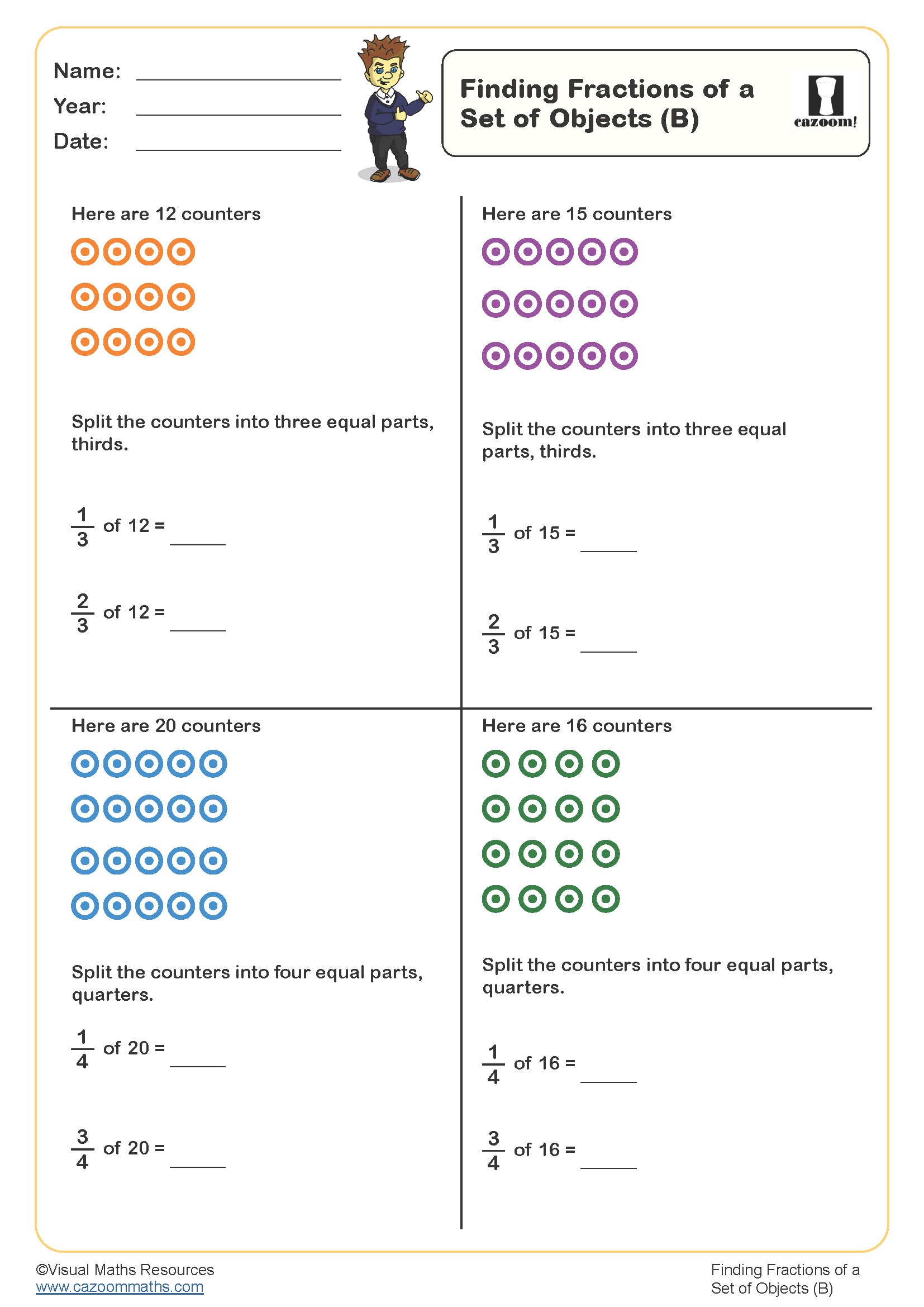
Finding fractions of a set of objects (B)
Year groups: 3
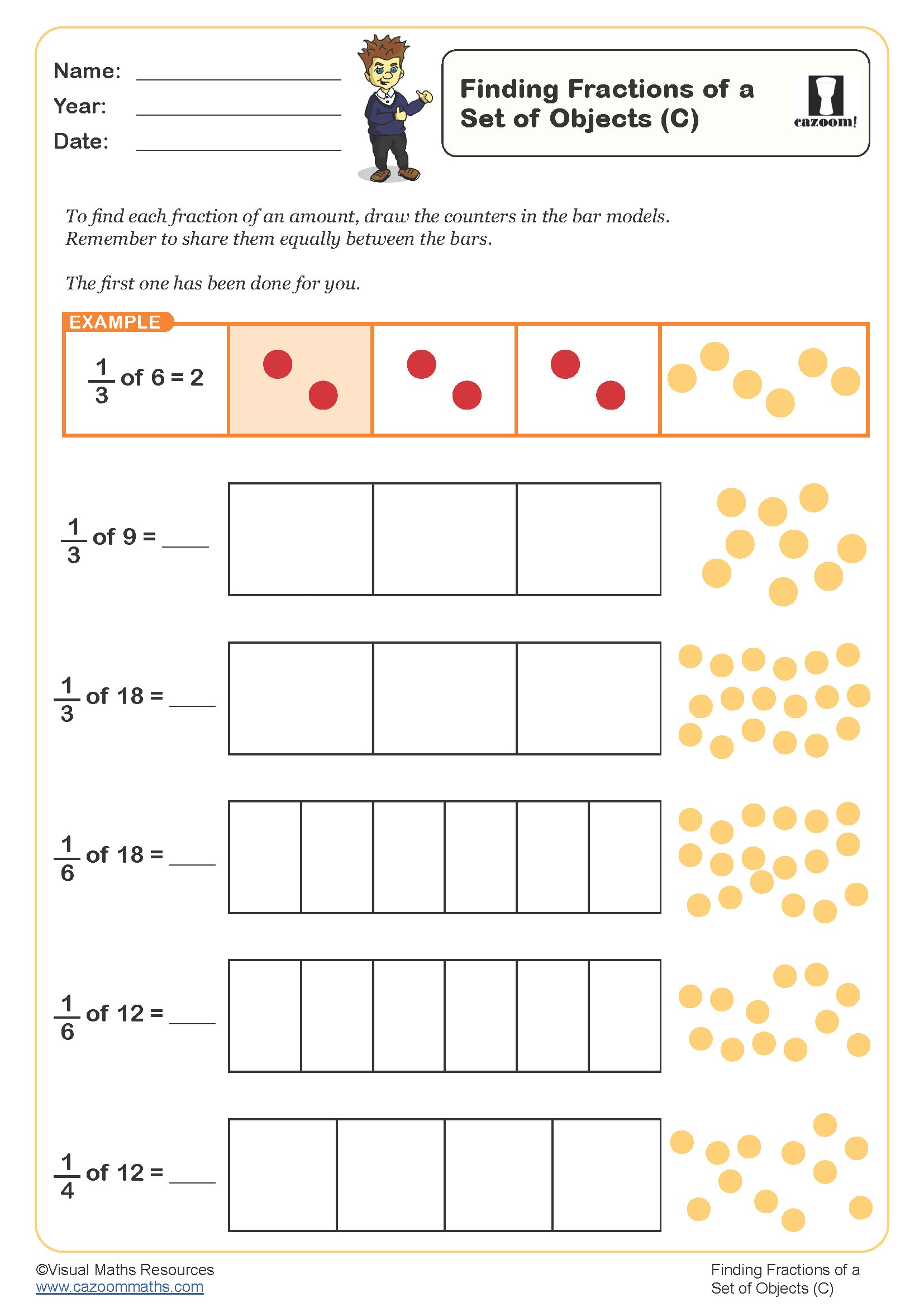
Finding fractions of a set of objects (C)
Year groups: 3
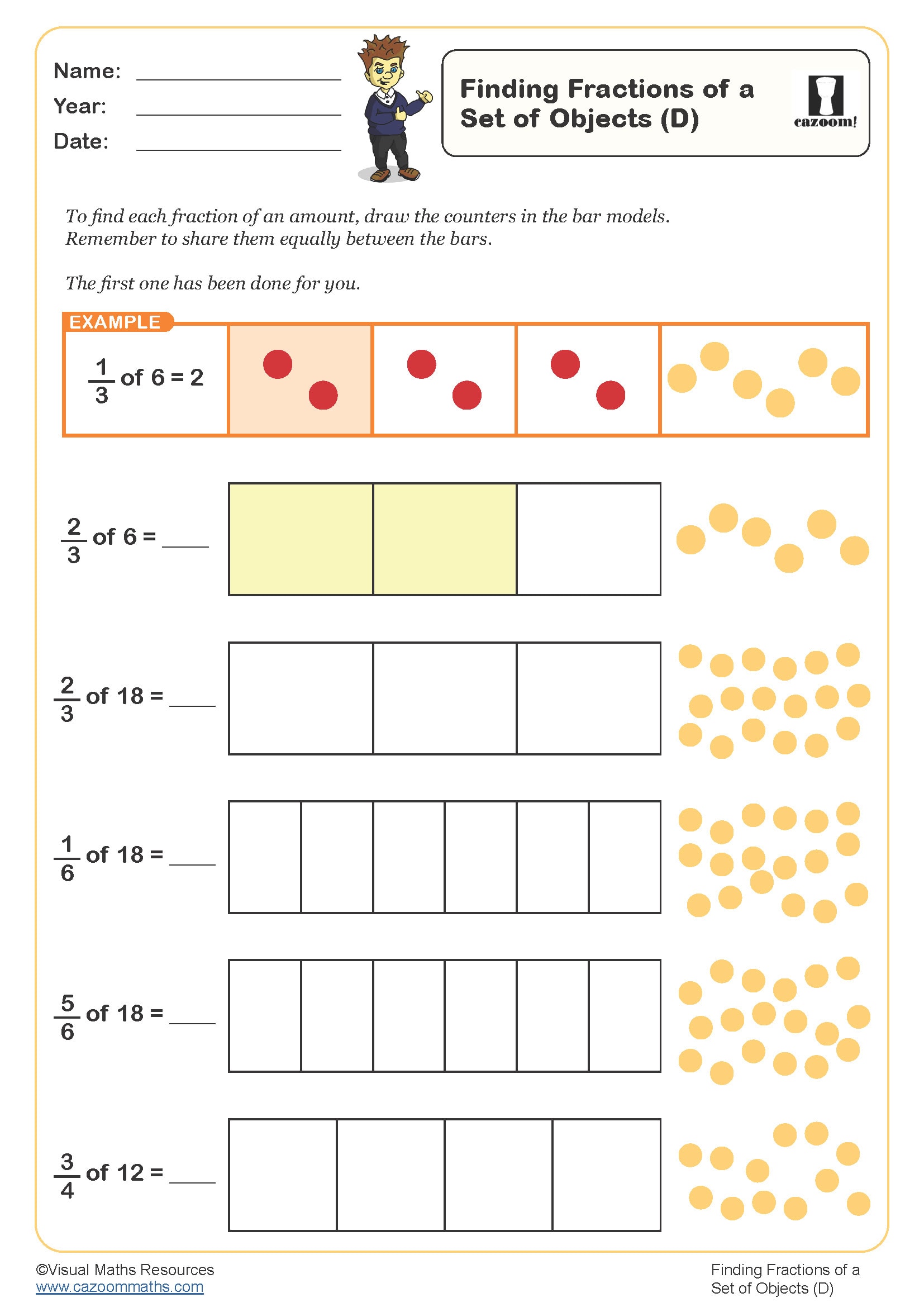
Finding fractions of a set of objects (D)
Year groups: 3
Halving 2 Digit Even Numbers
Year groups: 3, 4

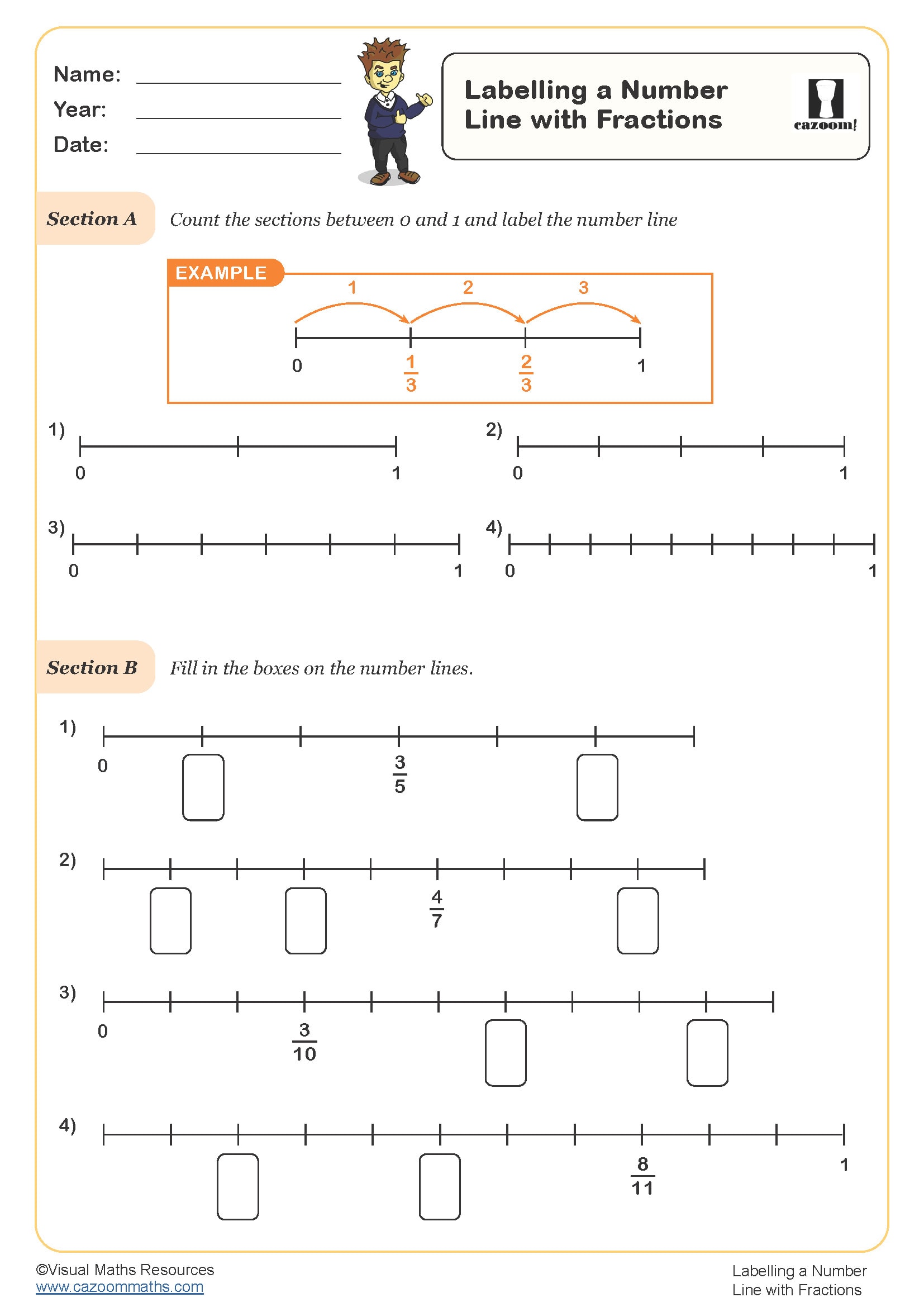
Labelling a Number Line with Fractions
Year groups: 3
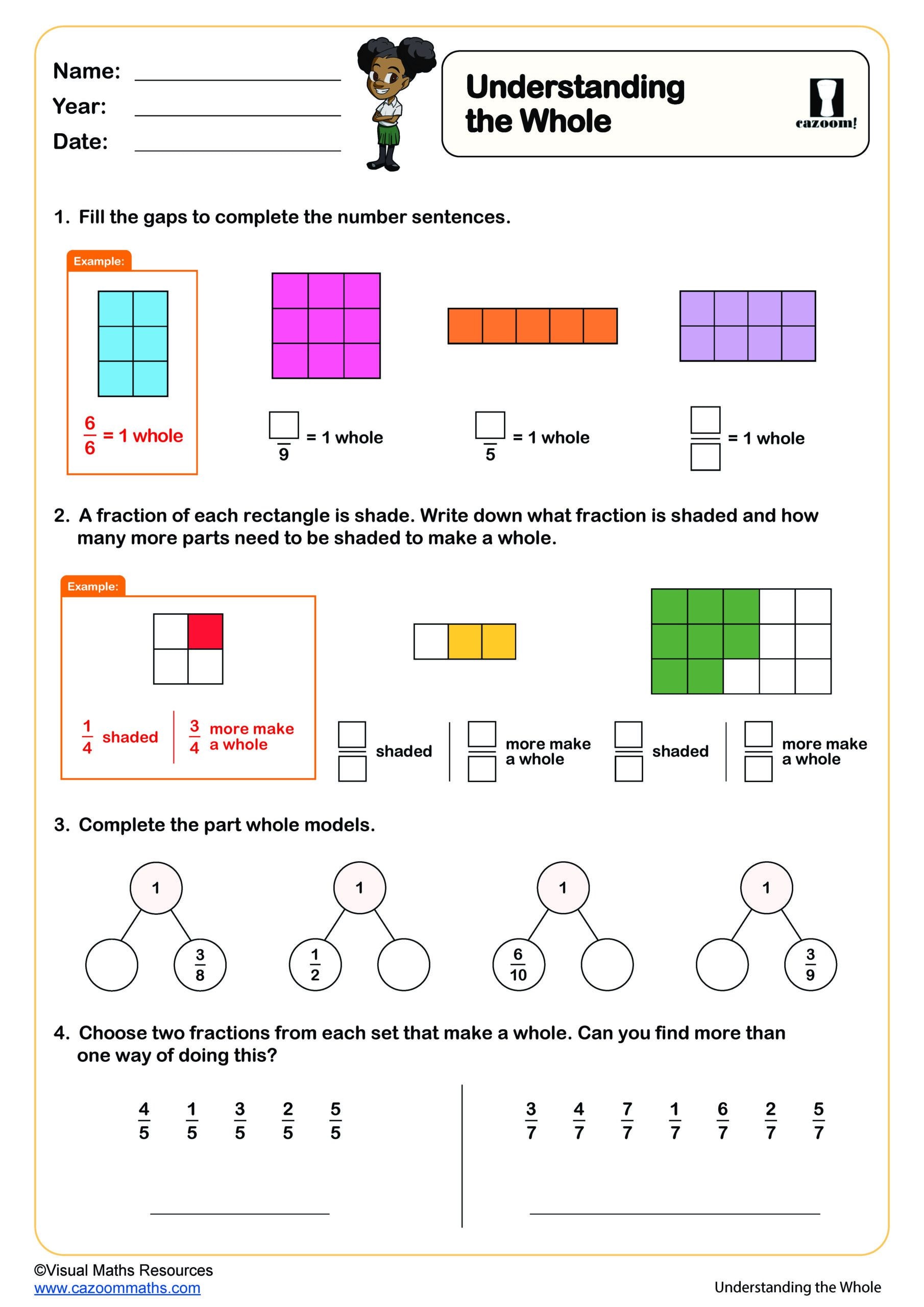
Understanding the Whole
Year groups: 3, 4
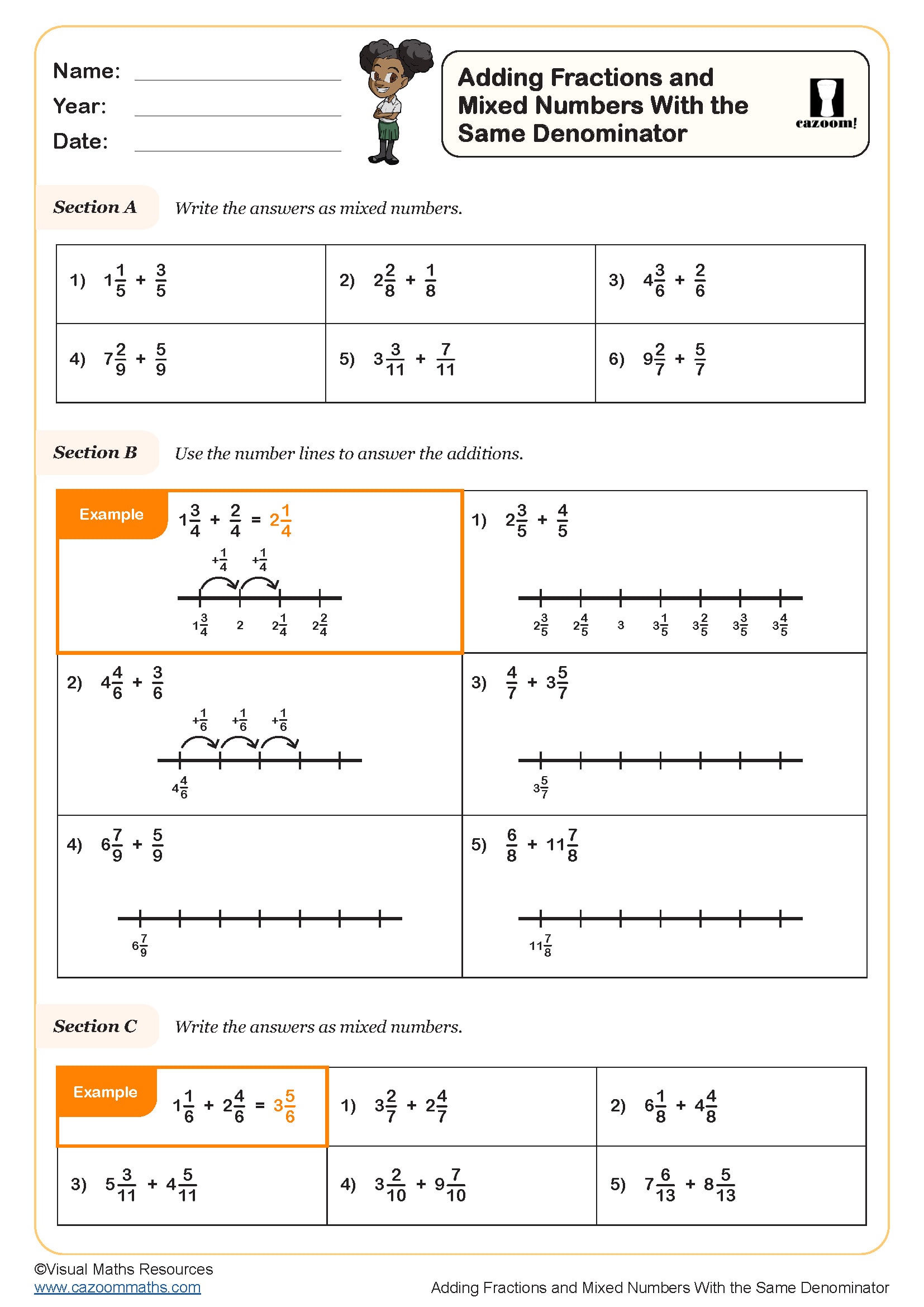
Adding Fractions and Mixed Numbers with the Same Denominator
Year groups: 4
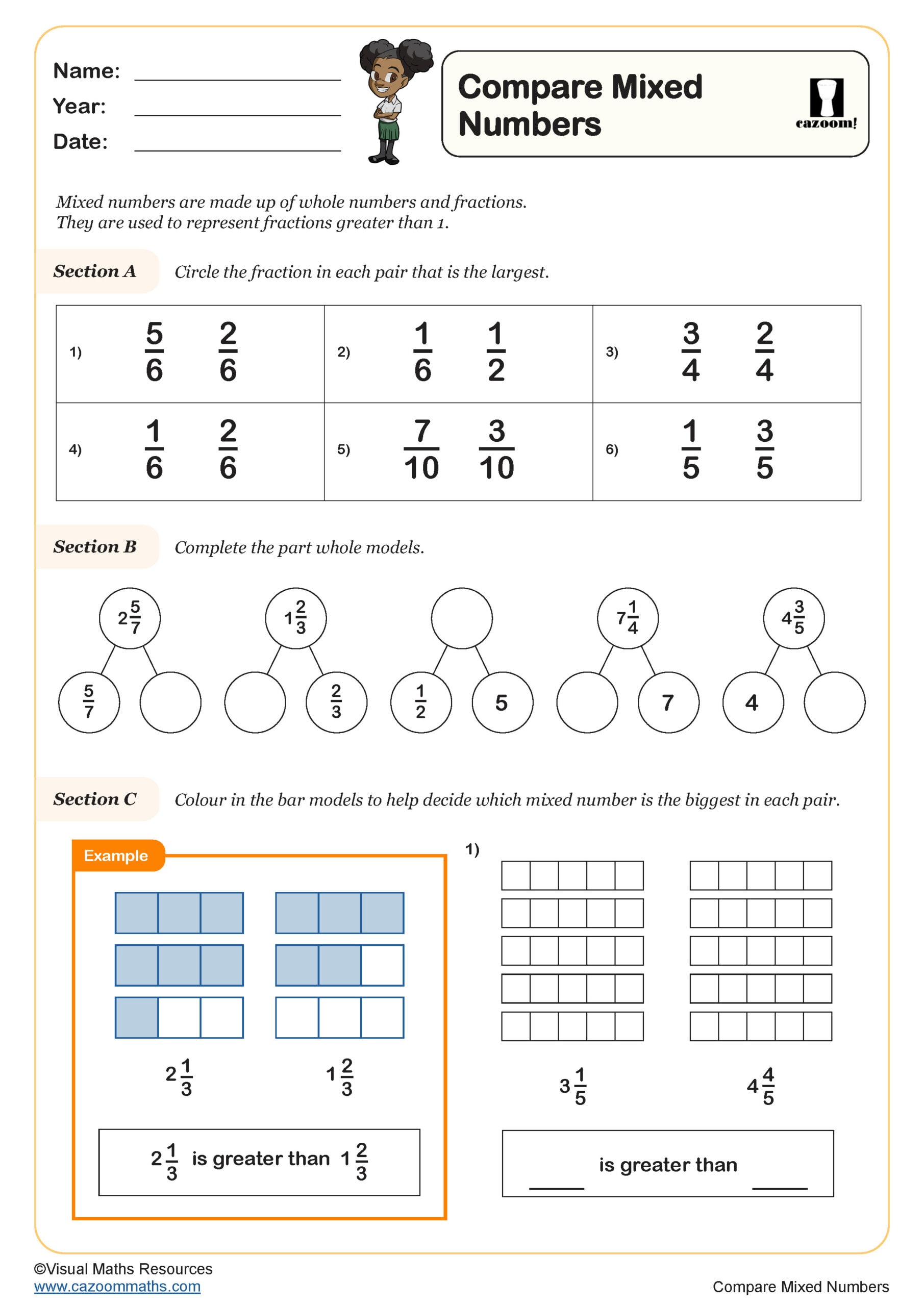
Compare Mixed numbers
Year groups: 4, 5
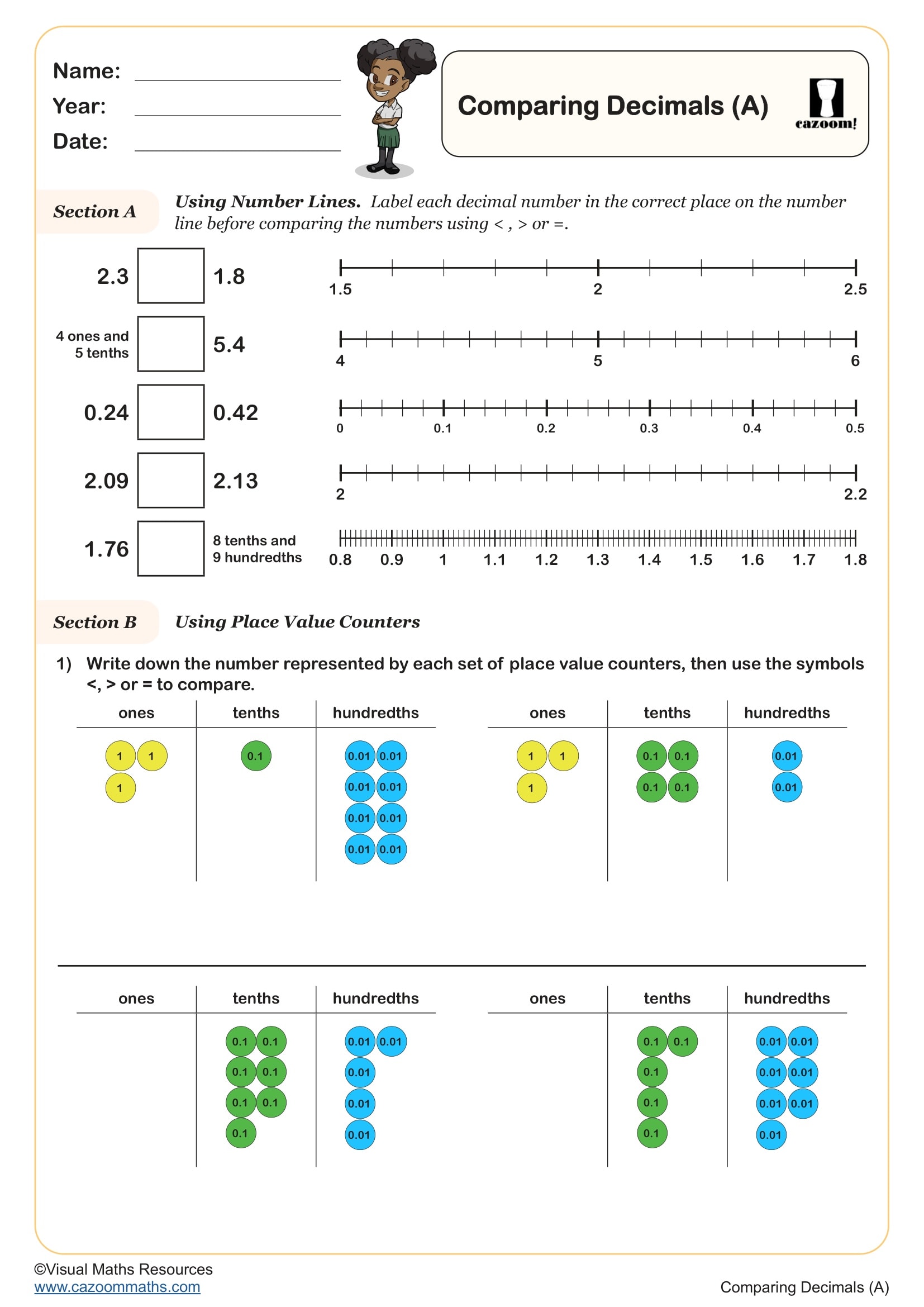
Comparing Decimals (A)
Year groups: 4
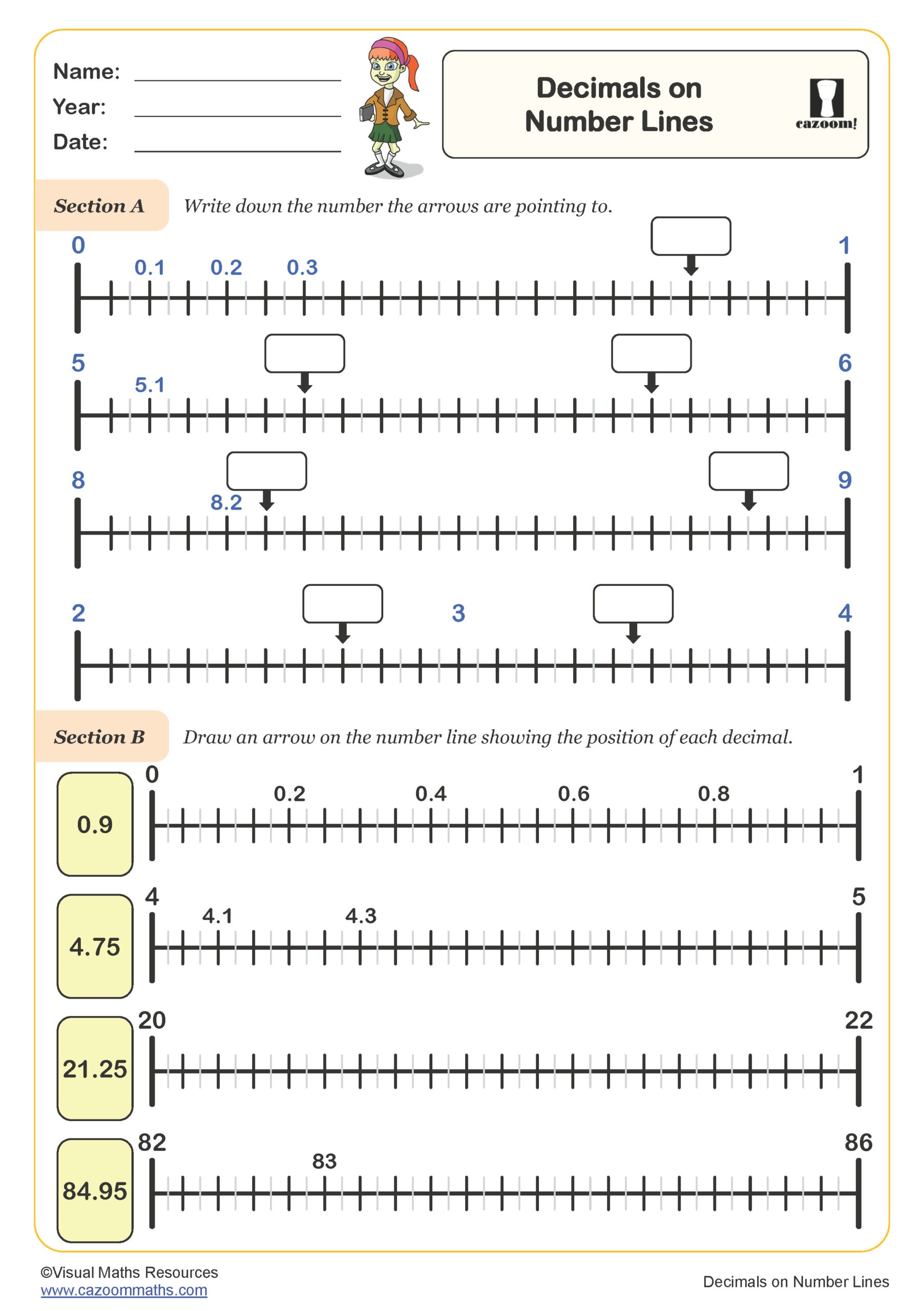
Decimals on a Number Line - Beyond 1
Year groups: 4

Decimals on a Number Line - Up to 1
Year groups: 4

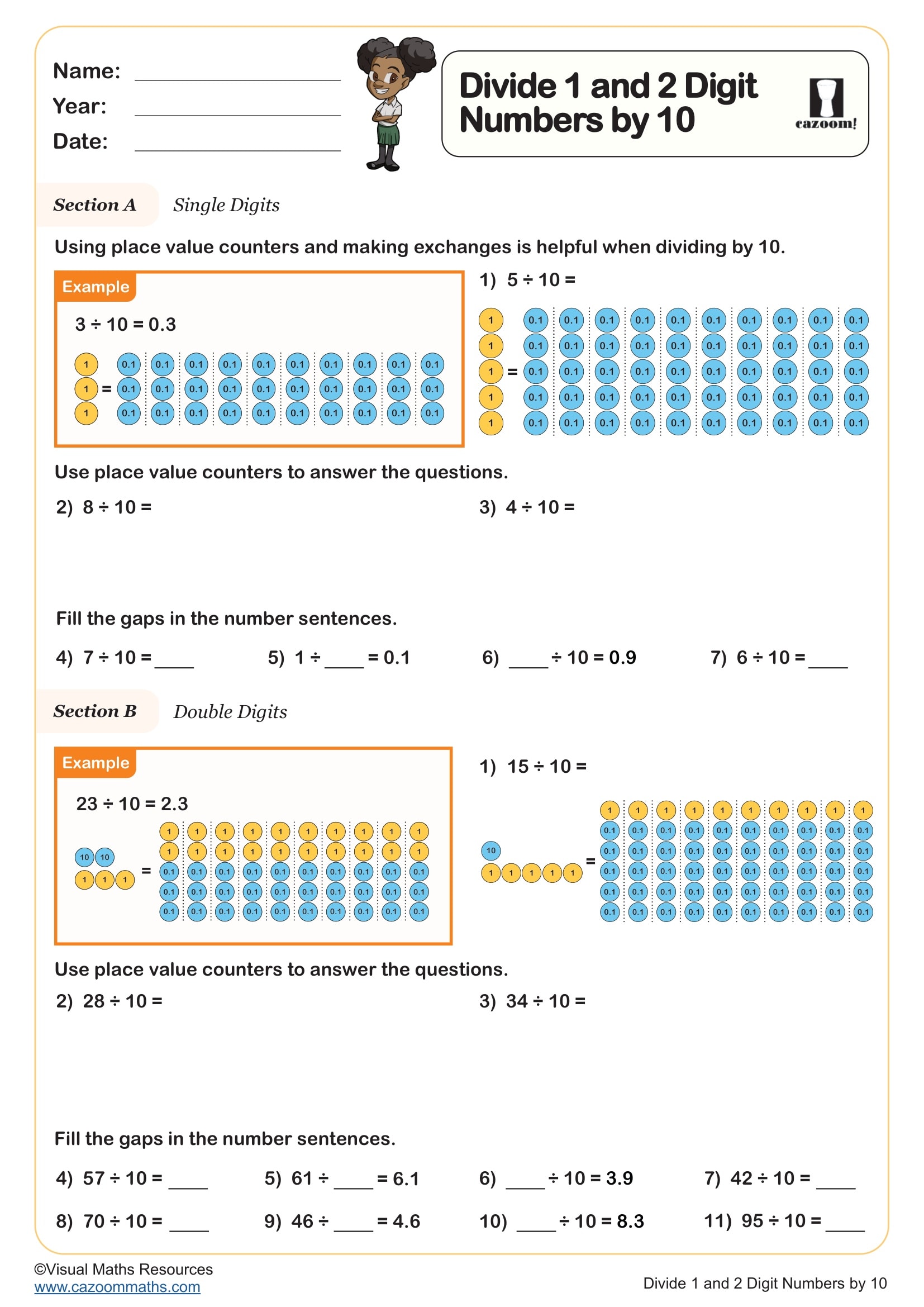
Divide 1 and 2 Digit Numbers by 10
Year groups: 4
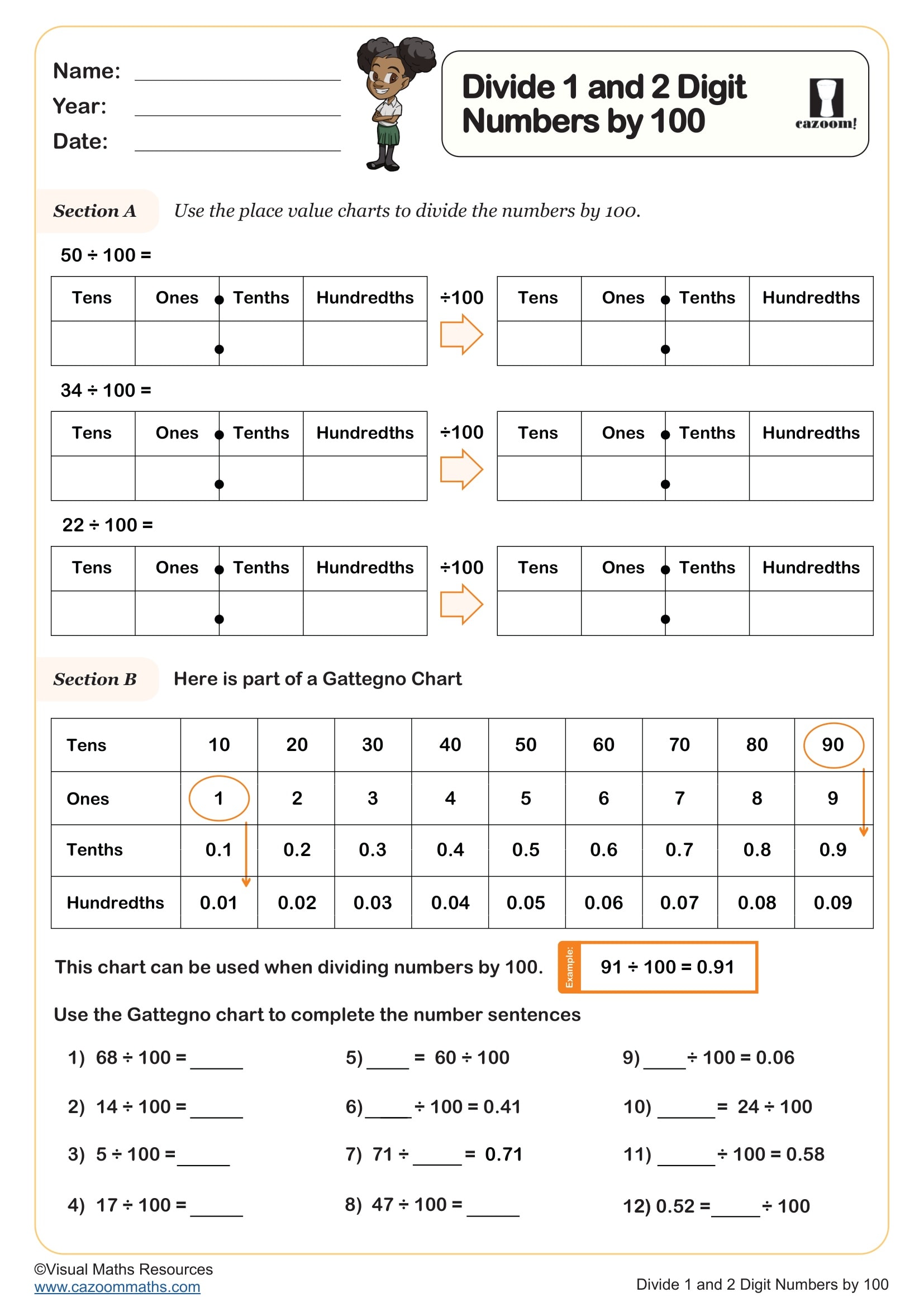
Divide 1 and 2 Digit Numbers by 100
Year groups: 4
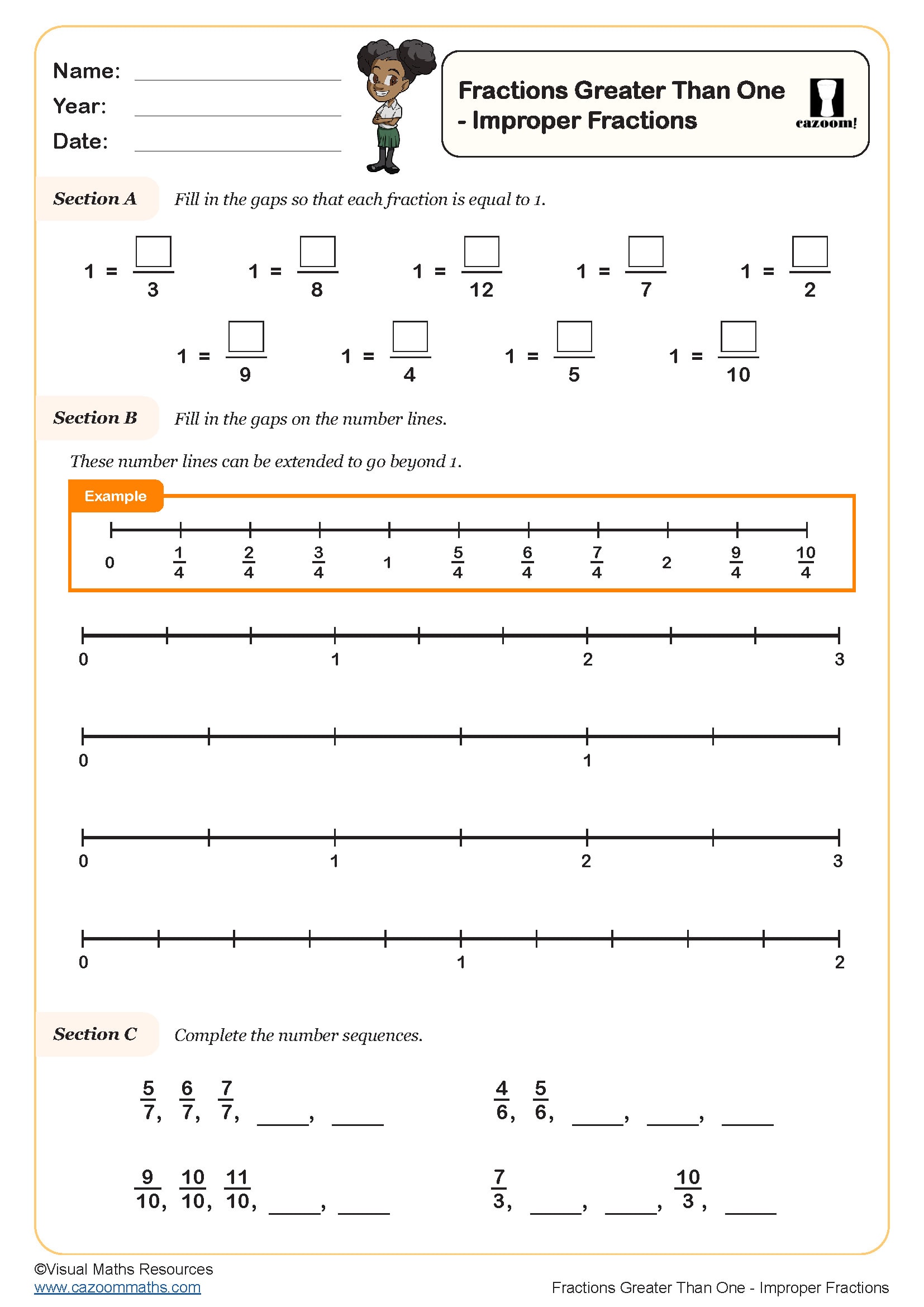
Fractions Greater Than One - Improper Fractions
Year groups: 4, 5
Fractions Greater Than One - Mixed Numbers
Year groups: 4, 5

Halving Odd Numbers by Halving One Less
Year groups: 4
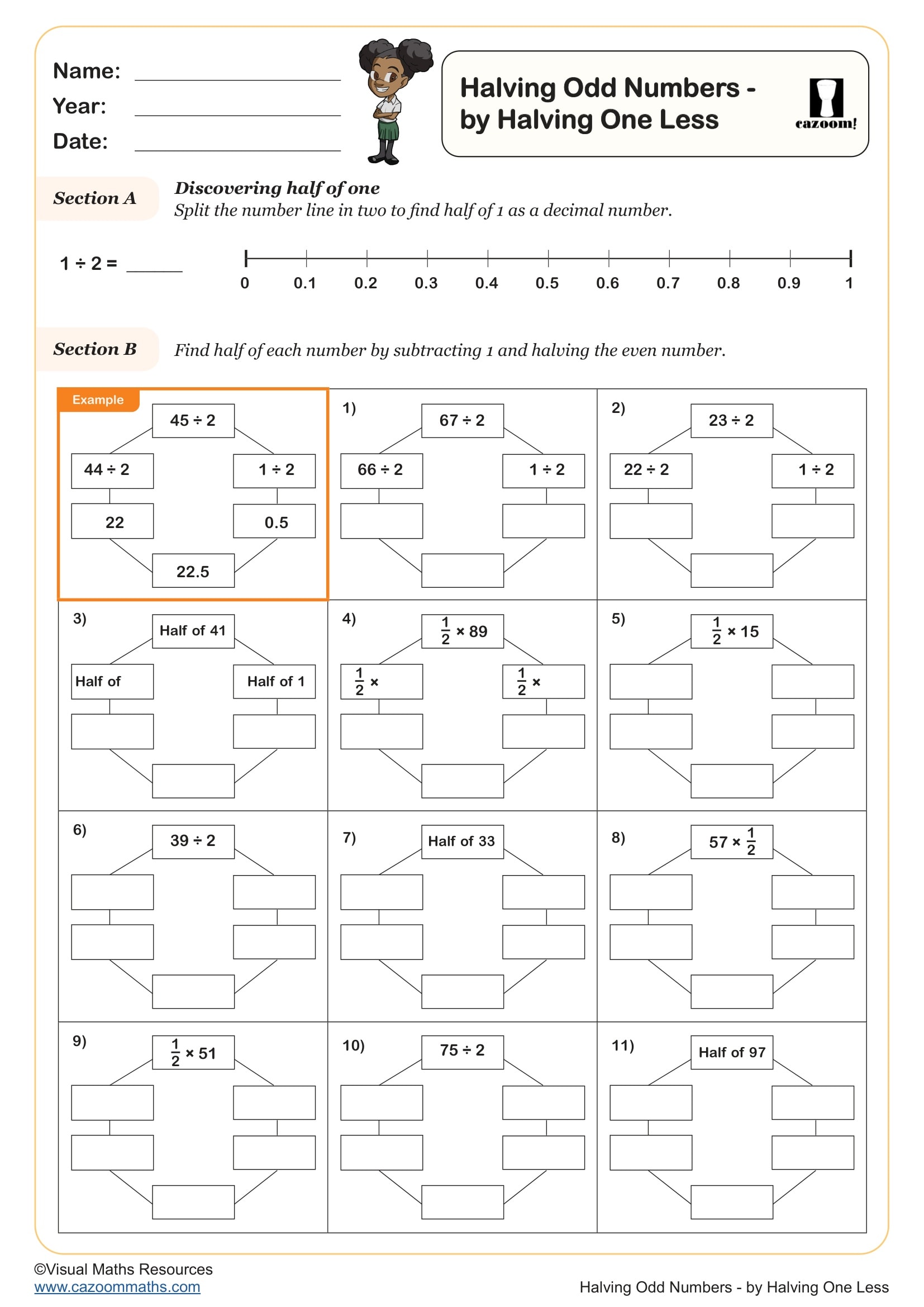
Halving Odd Numbers Partition Tens and Ones
Year groups: 4
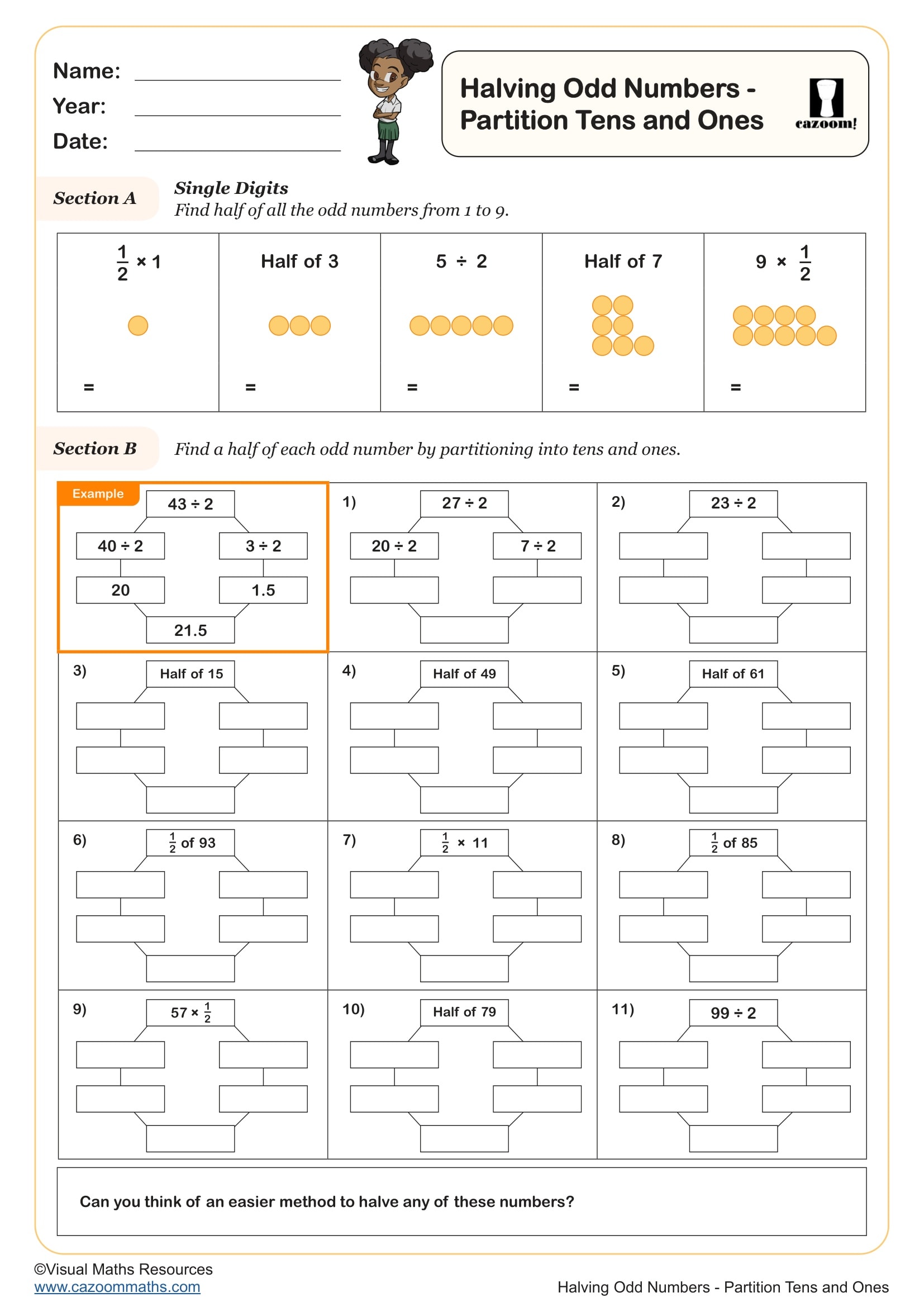
Making One Using Decimals and Fractions (A)
Year groups: 4
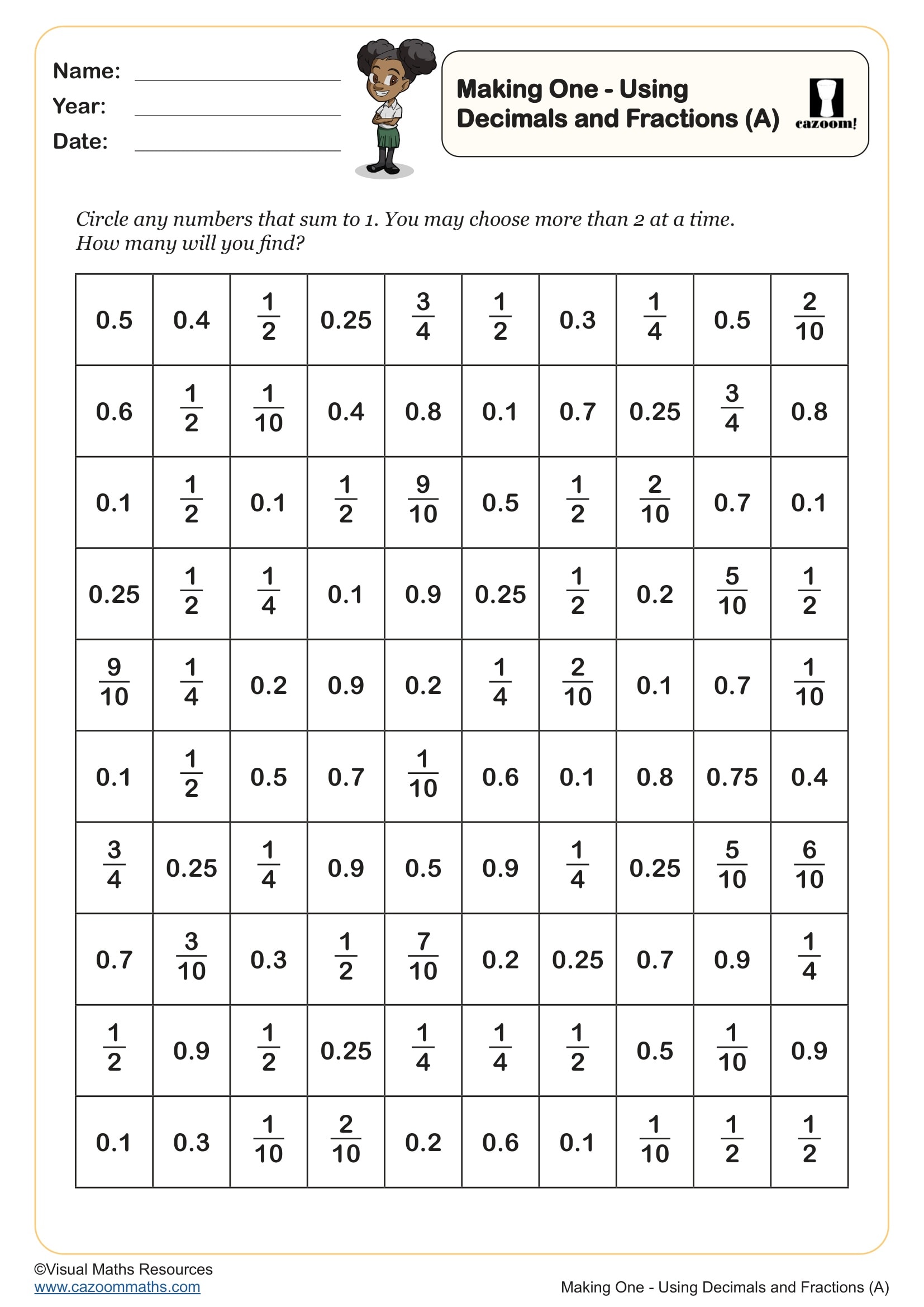
Making One Using Decimals and Fractions (B)
Year groups: 4
Partitioning Decimals - Tenths and Hundredths (A)
Year groups: 4
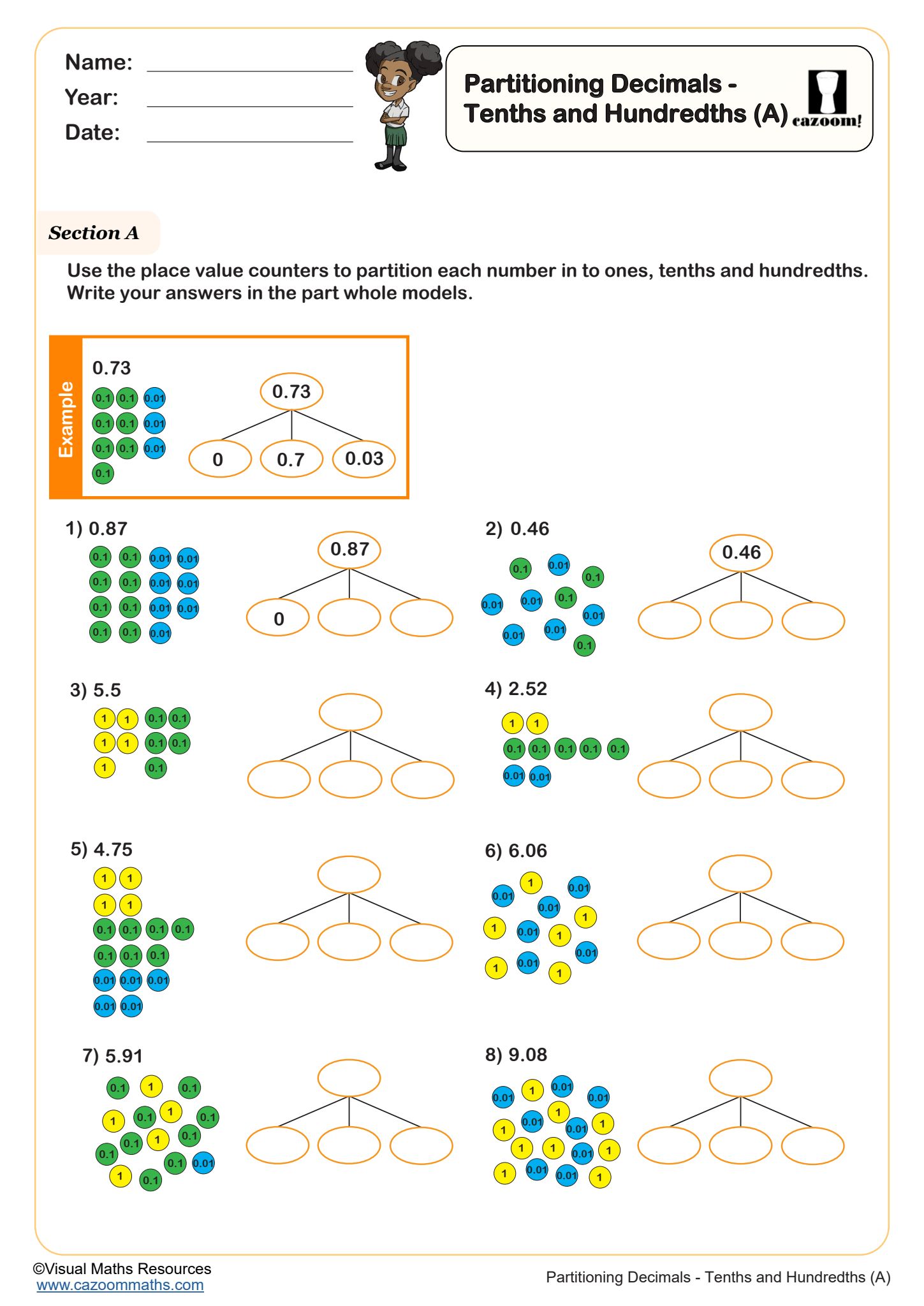
Partitioning Decimals - Tenths and Hundredths (B)
Year groups: 4
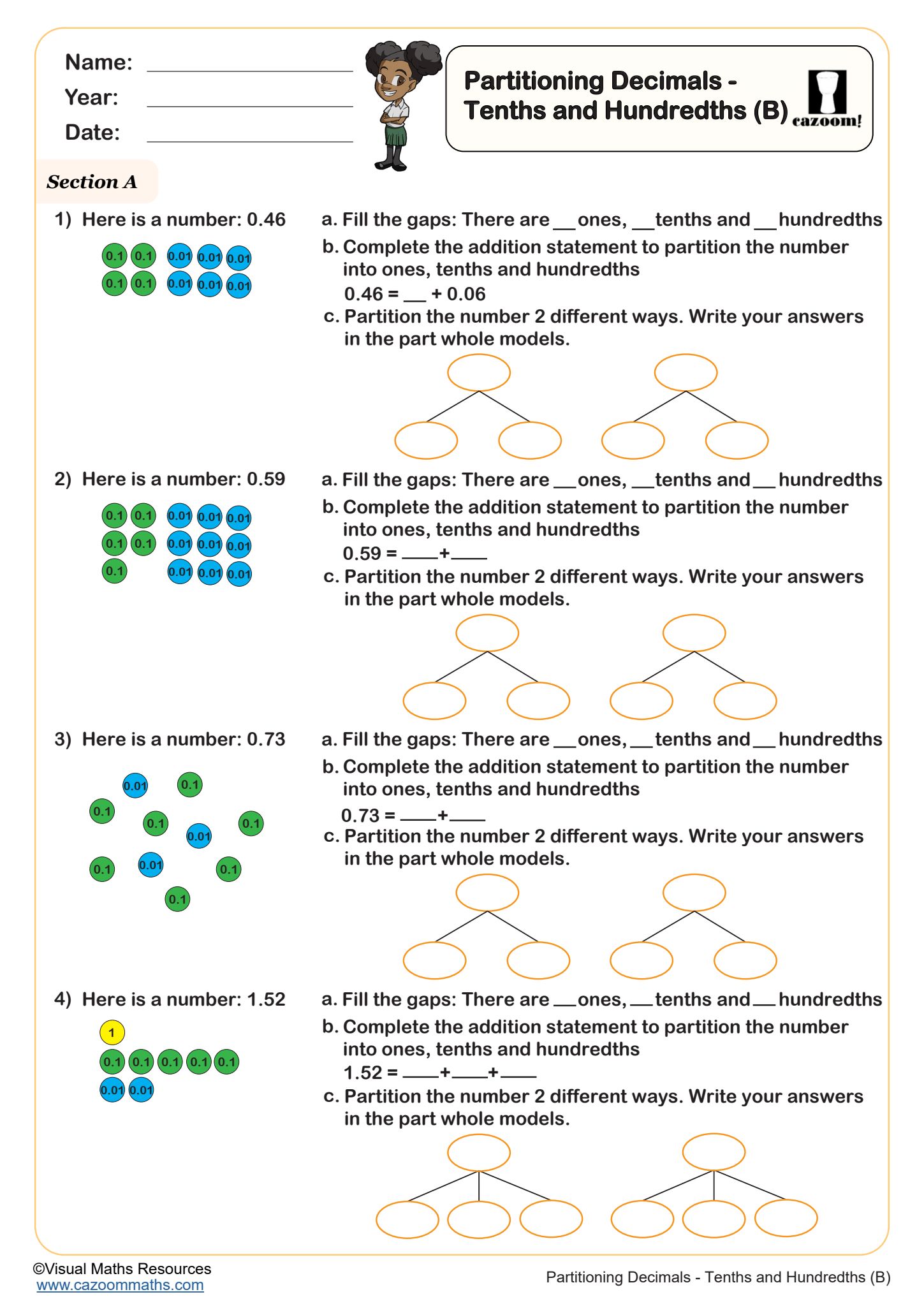
Partitioning Mixed Numbers
Year groups: 4, 5
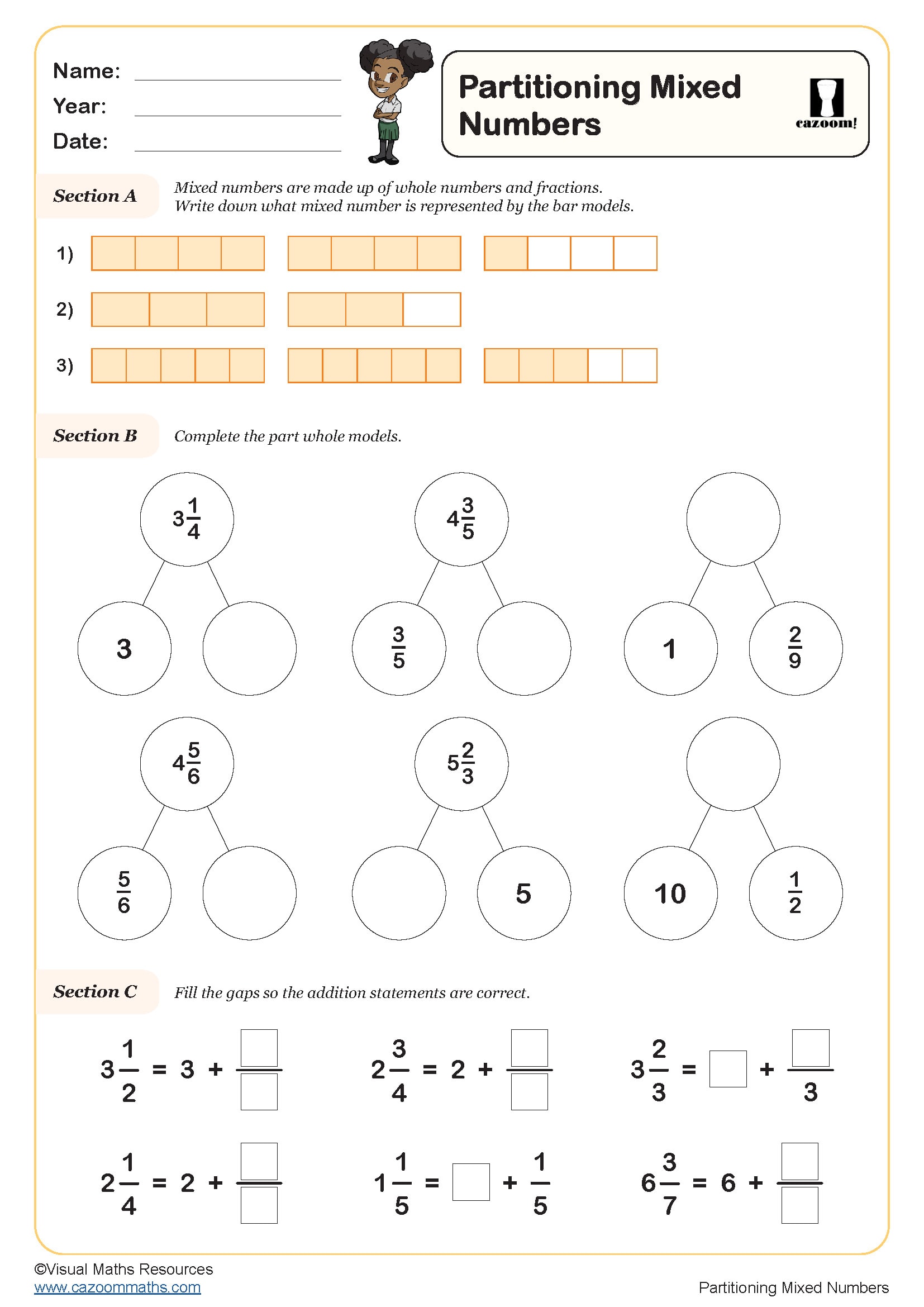
Solve Problems Involving Decimals
Year groups: 4
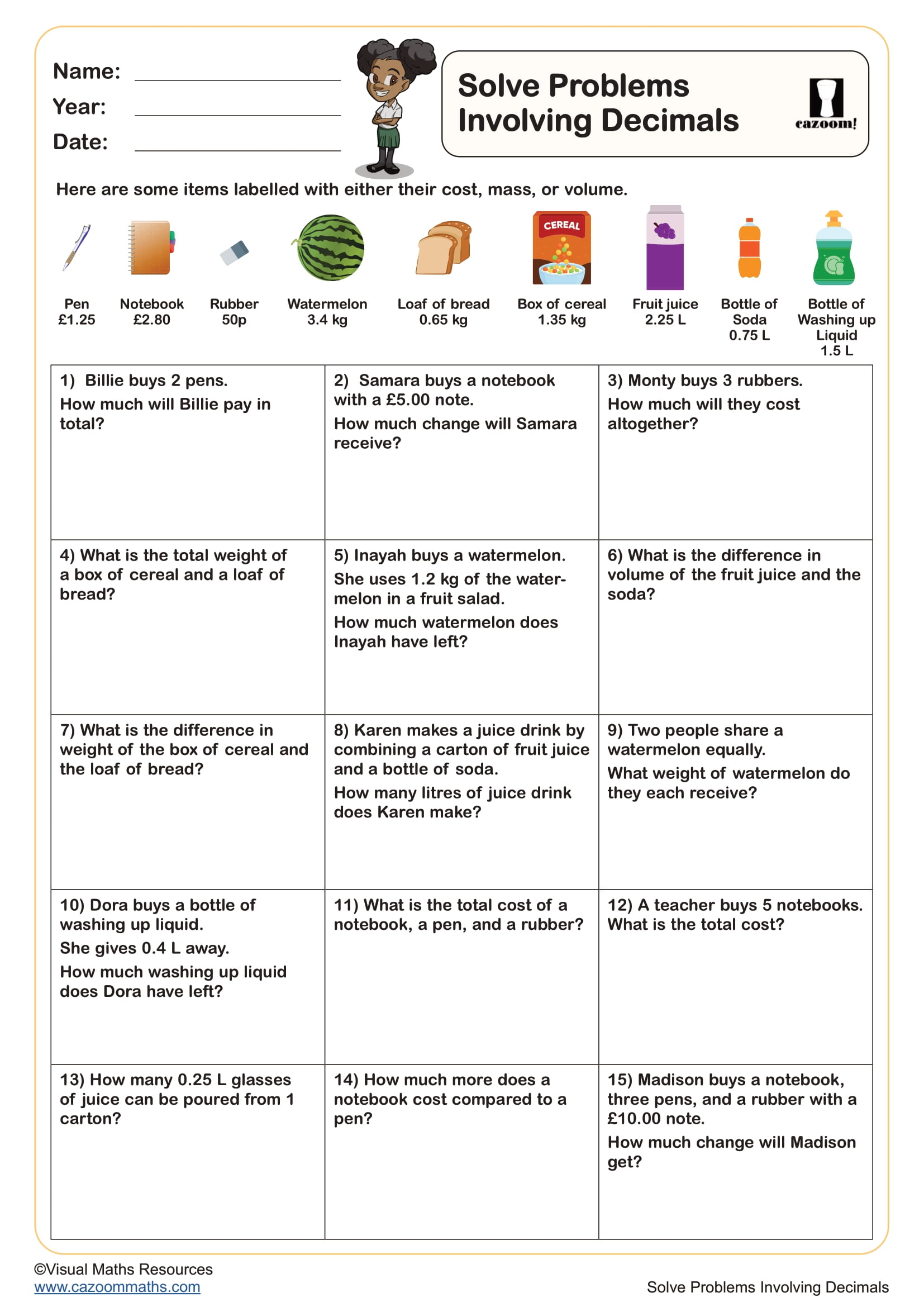
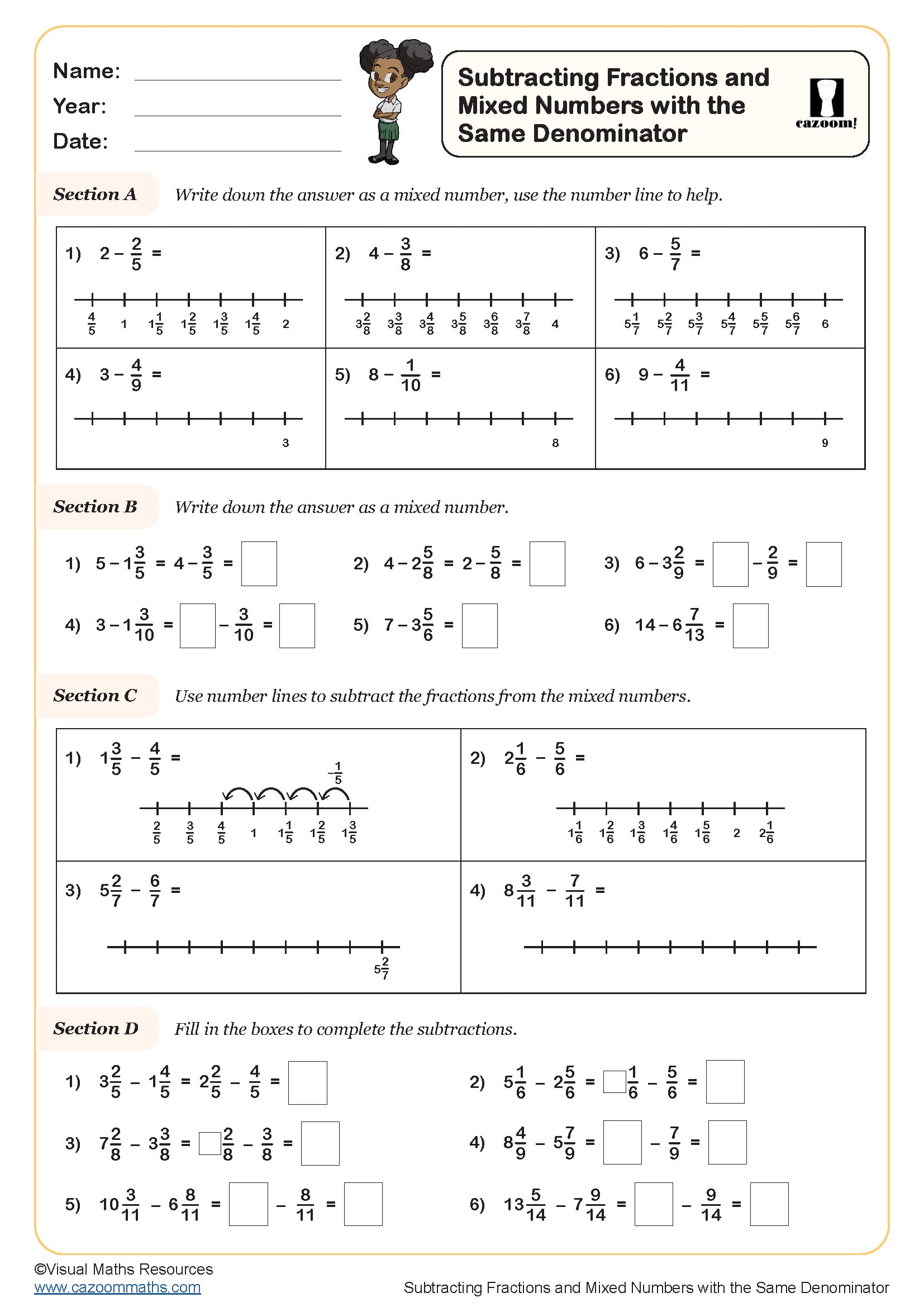
Subtracting Fractions and Mixed Numbers with the Same Denominator
Year groups: 4
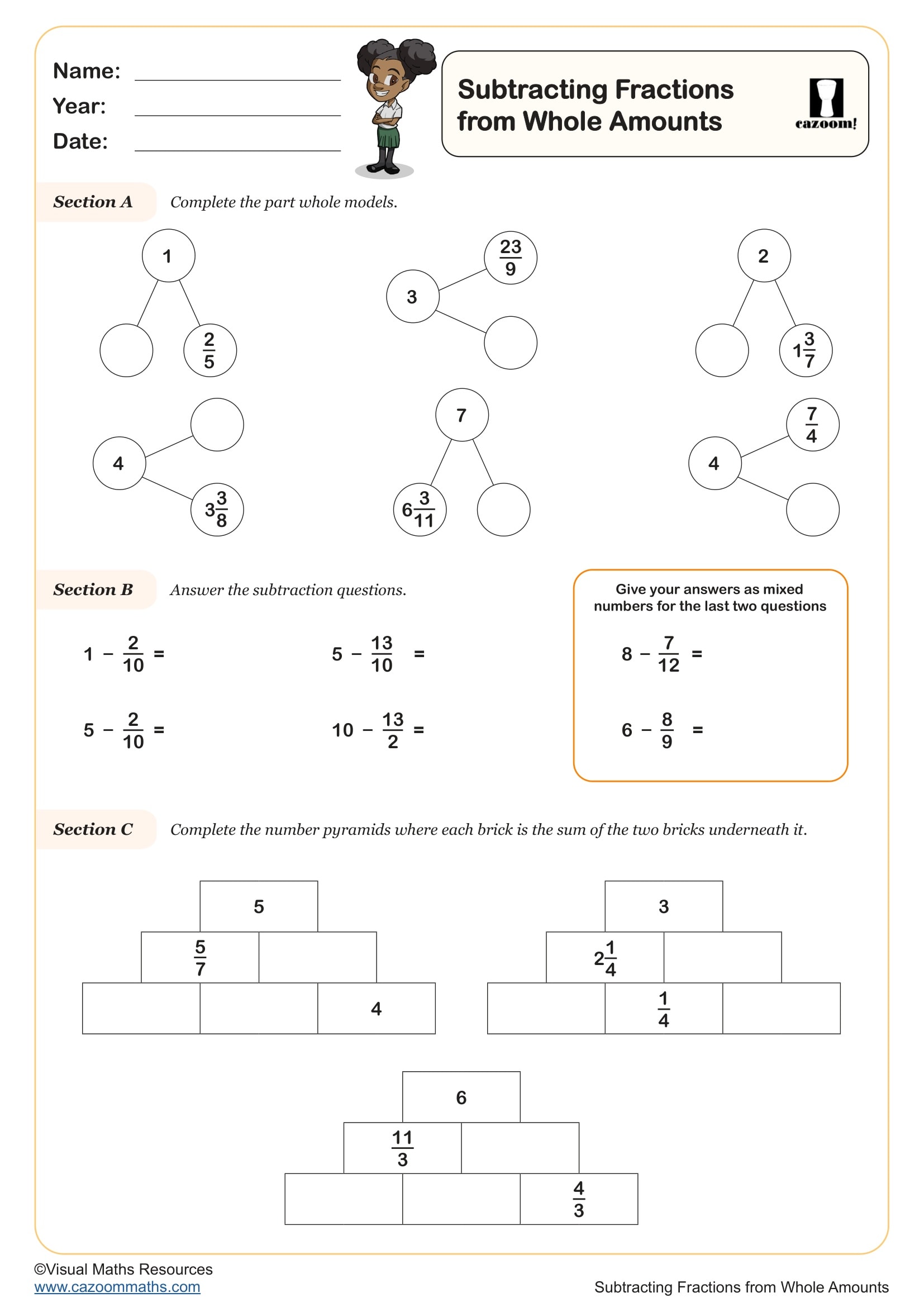
Subtracting Fractions from Whole Amounts
Year groups: 4, 5
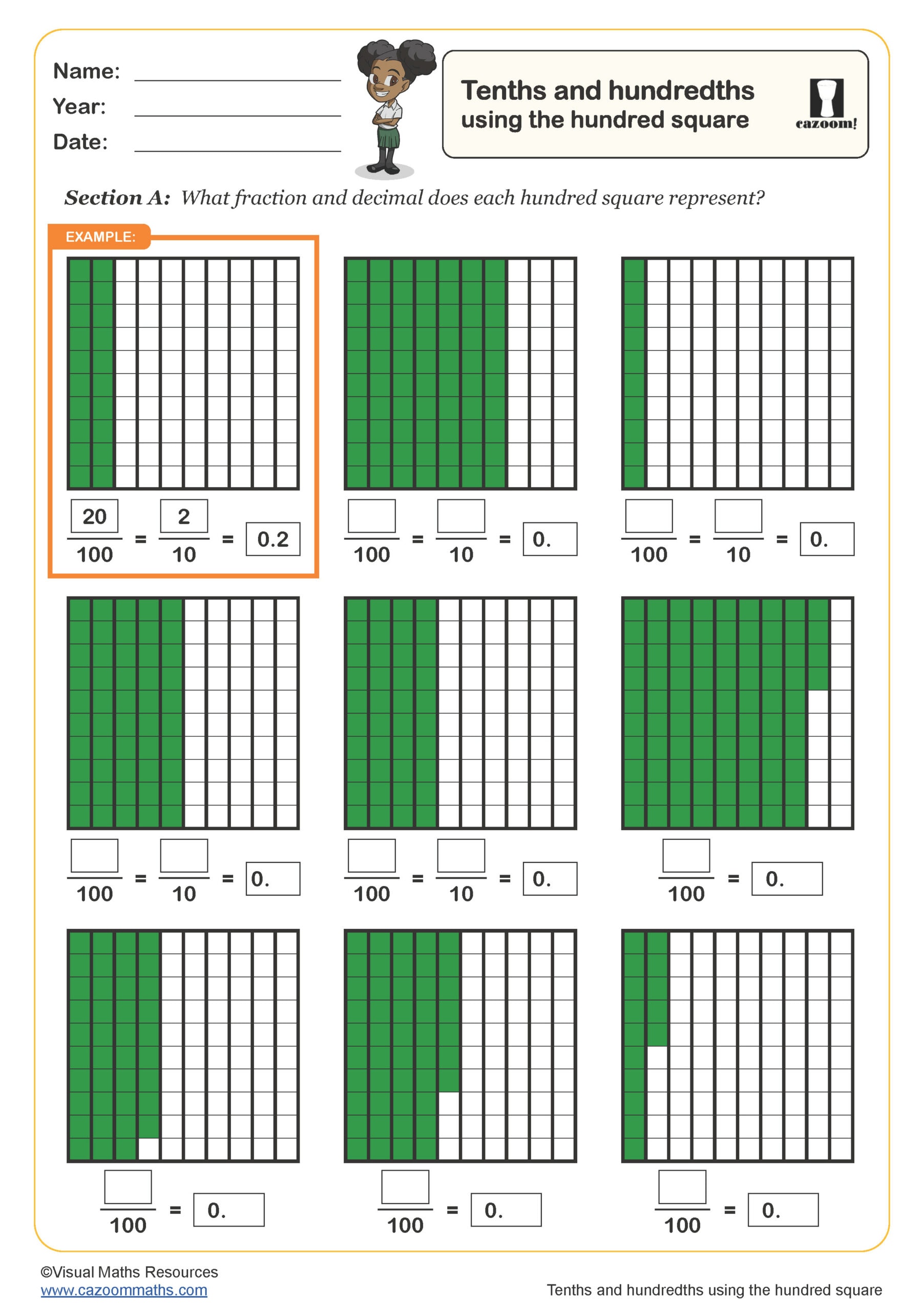
Tenths and Hundredths Using the Hundred Square
Year groups: 4
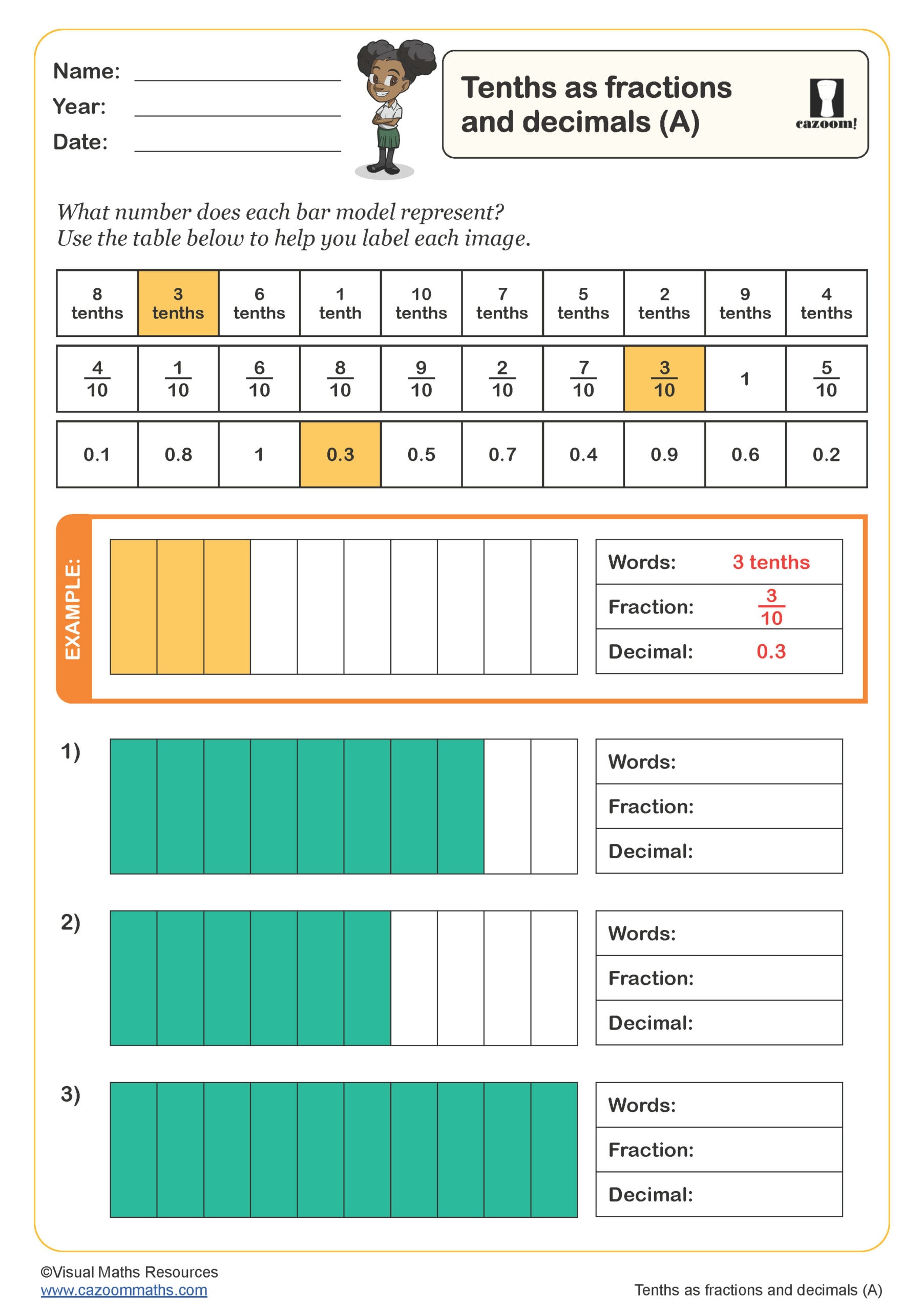
Tenths as Fractions and Decimals (A)
Year groups: 4
Tenths as Fractions and Decimals (B)
Year groups: 4

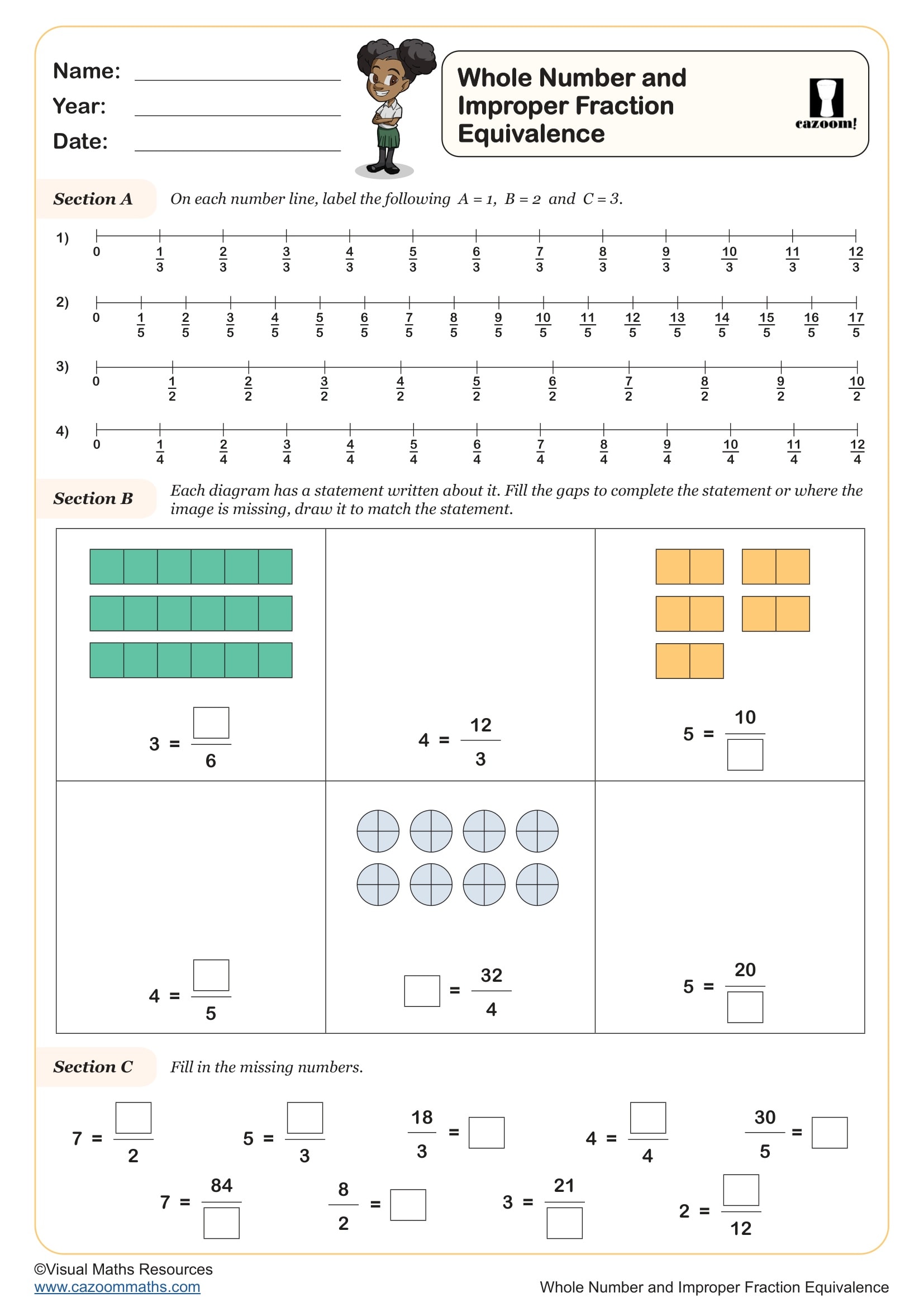
Whole Number and Improper Fraction Equivalence
Year groups: 4, 5
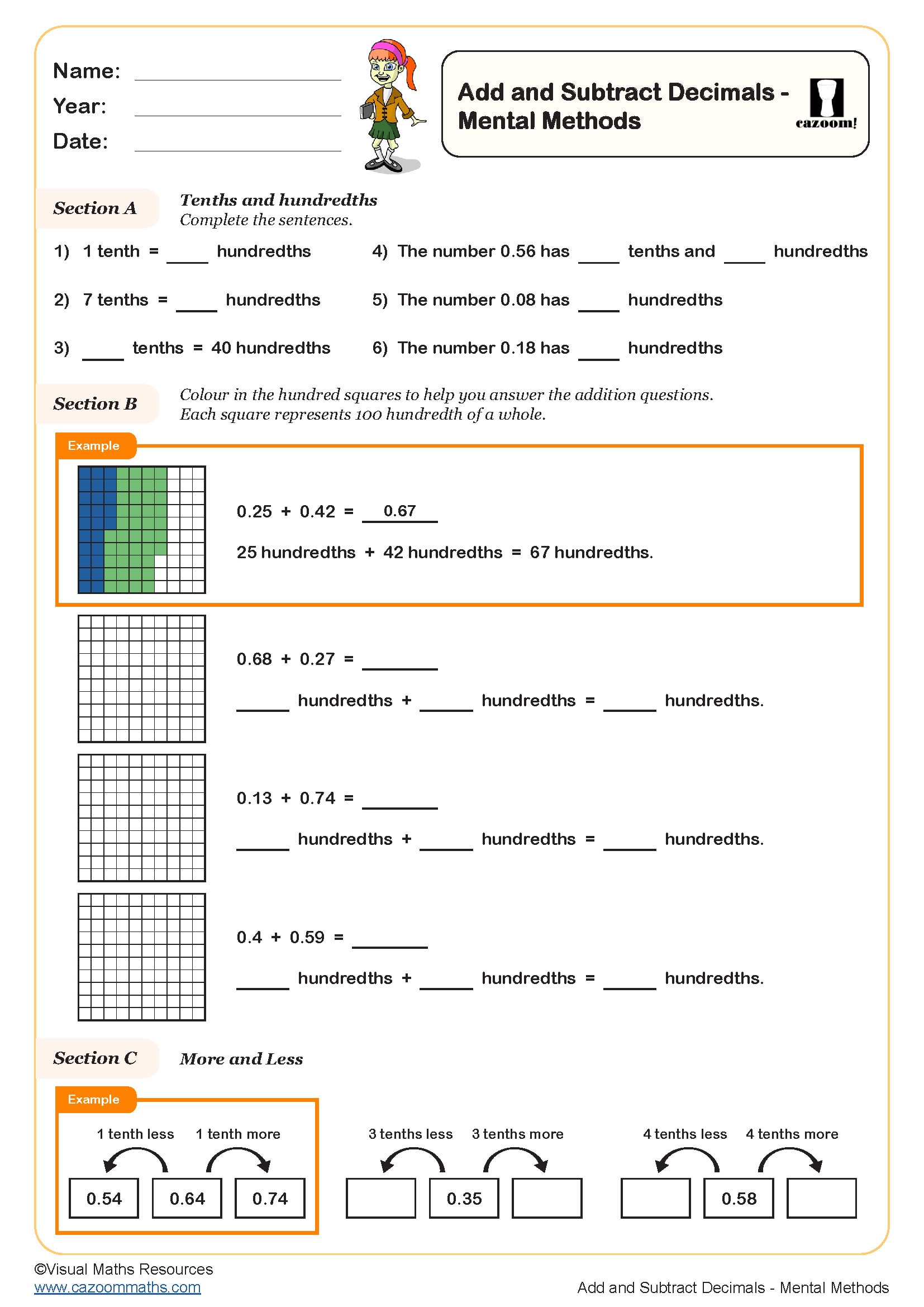
Add and Subtract Decimals - Mental Methods
Year groups: 5
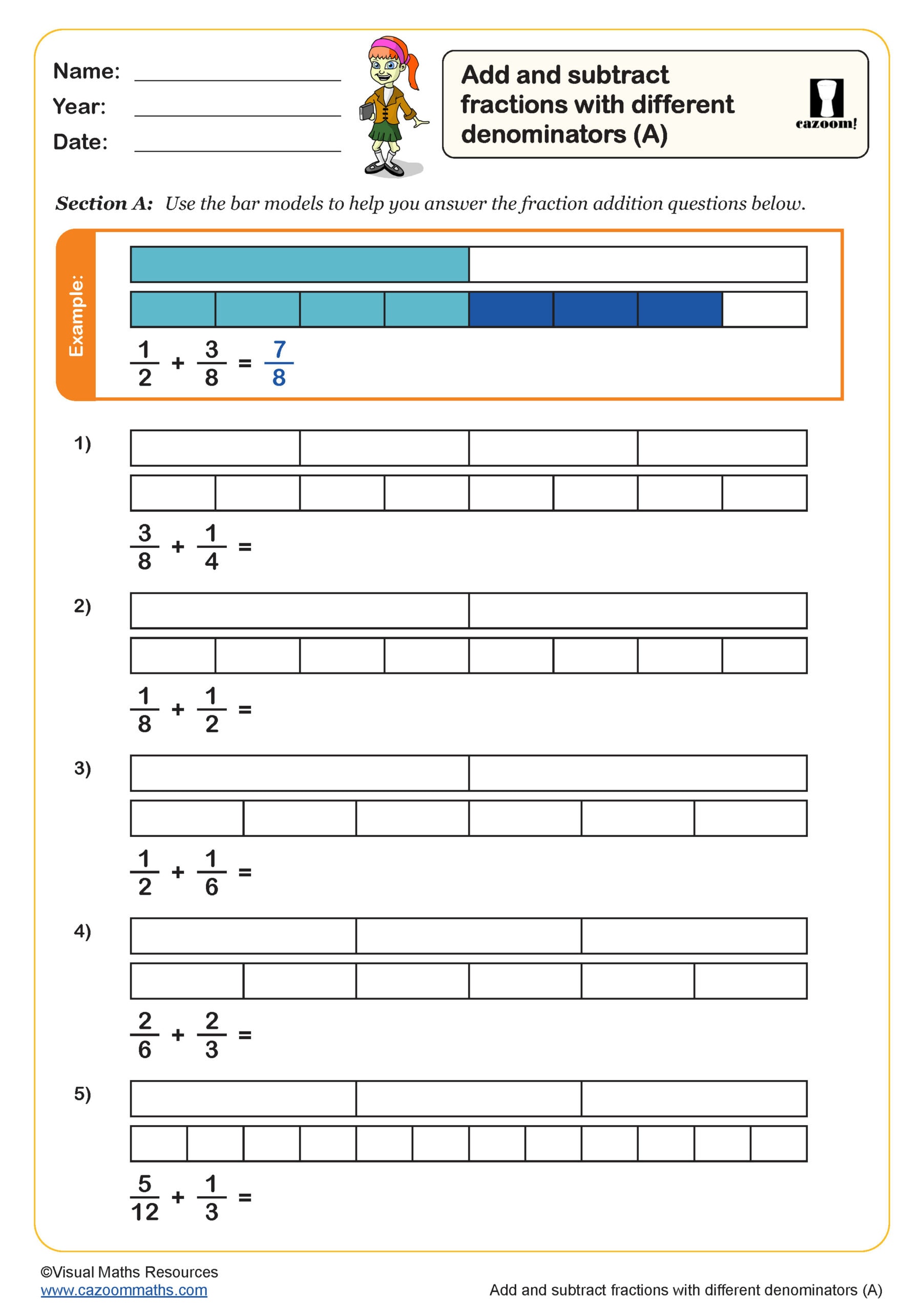
Add and Subtract Fractions with Different Denominators (A)
Year groups: 5
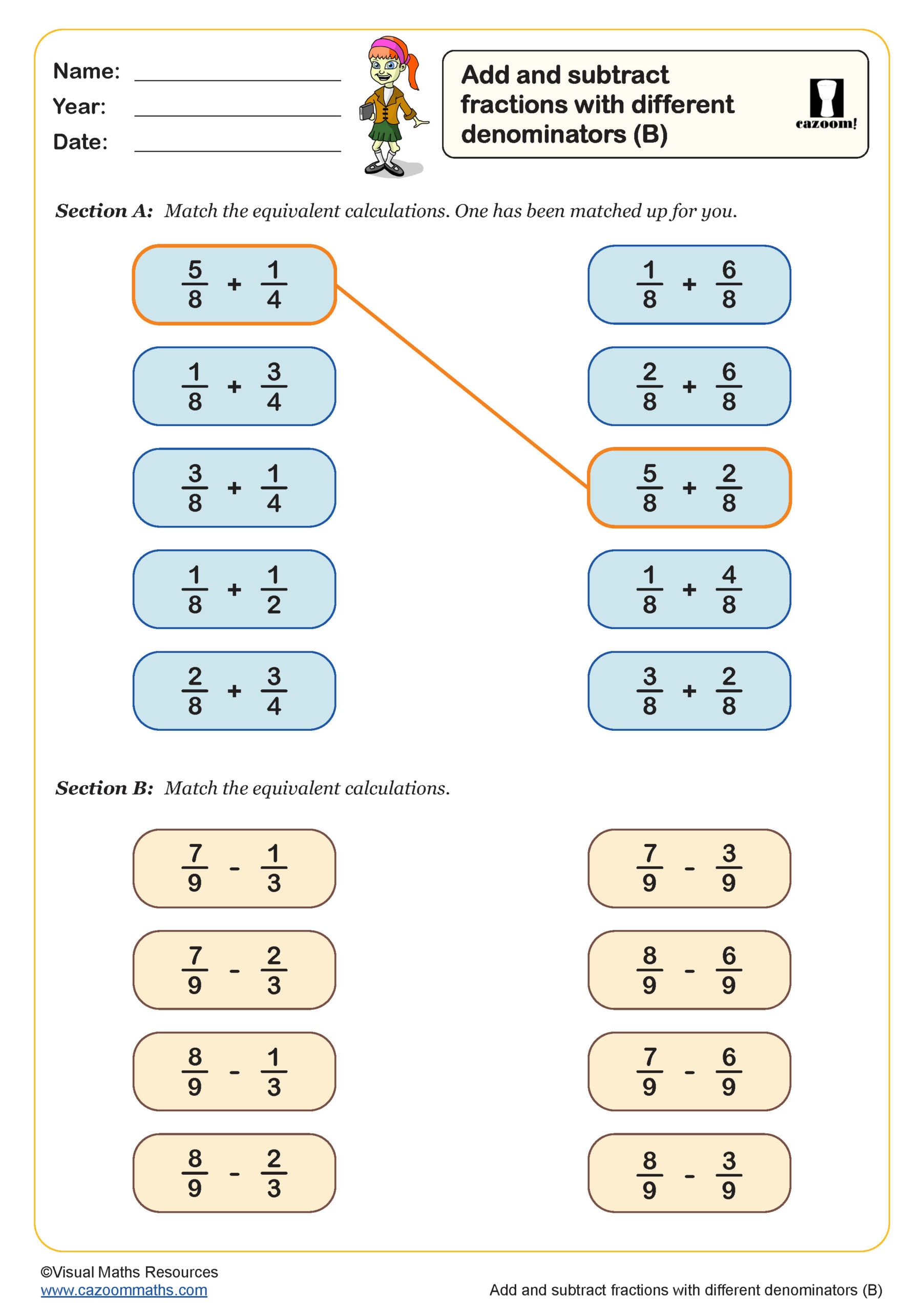
Add and Subtract Fractions with Different Denominators (B)
Year groups: 5
Adding and Subtracting Decimals
Year groups: 5

Colourful Equivalances (A)
Year groups: 5
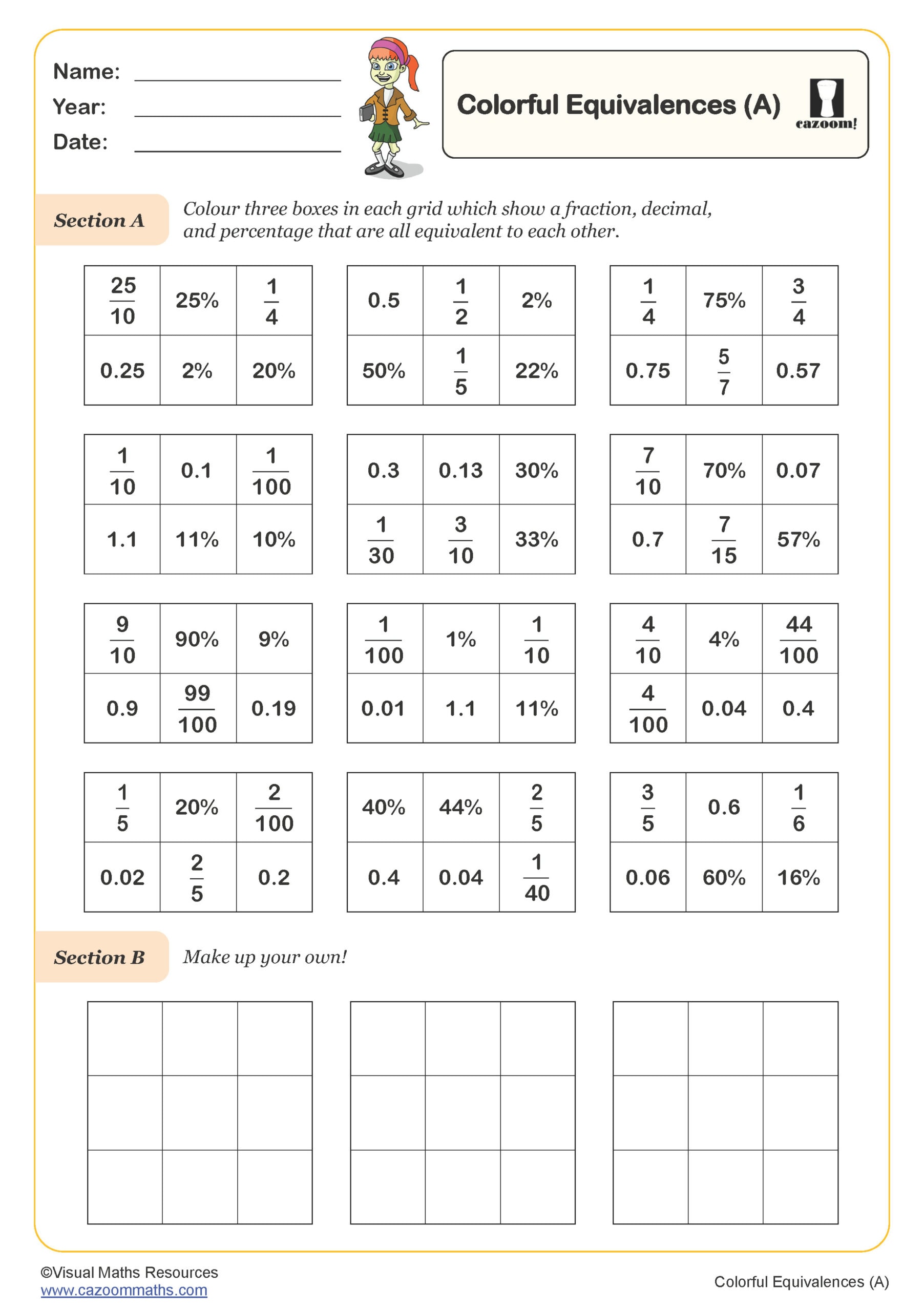
Column Addition - Decimals (A)
Year groups: 5
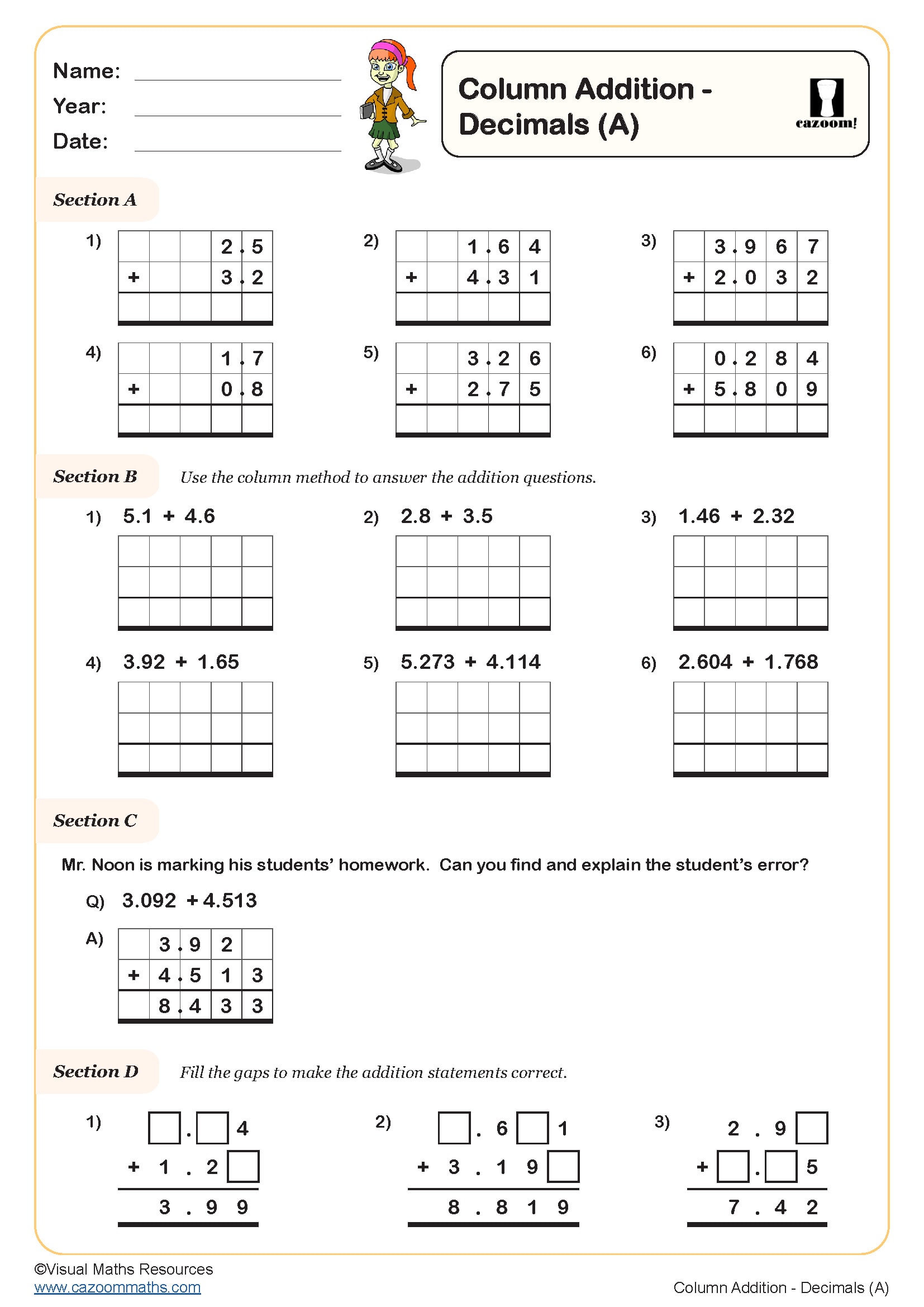
Column Addition - Decimals (B)
Year groups: 5, 6
Compare Fractions Less Than 1
Year groups: 5

Crack the Code - Decimals
Year groups: 5, 6
Decimals on Number Lines
Year groups: 5
Divide Decimals by Integers (B)
Year groups: 5, 6

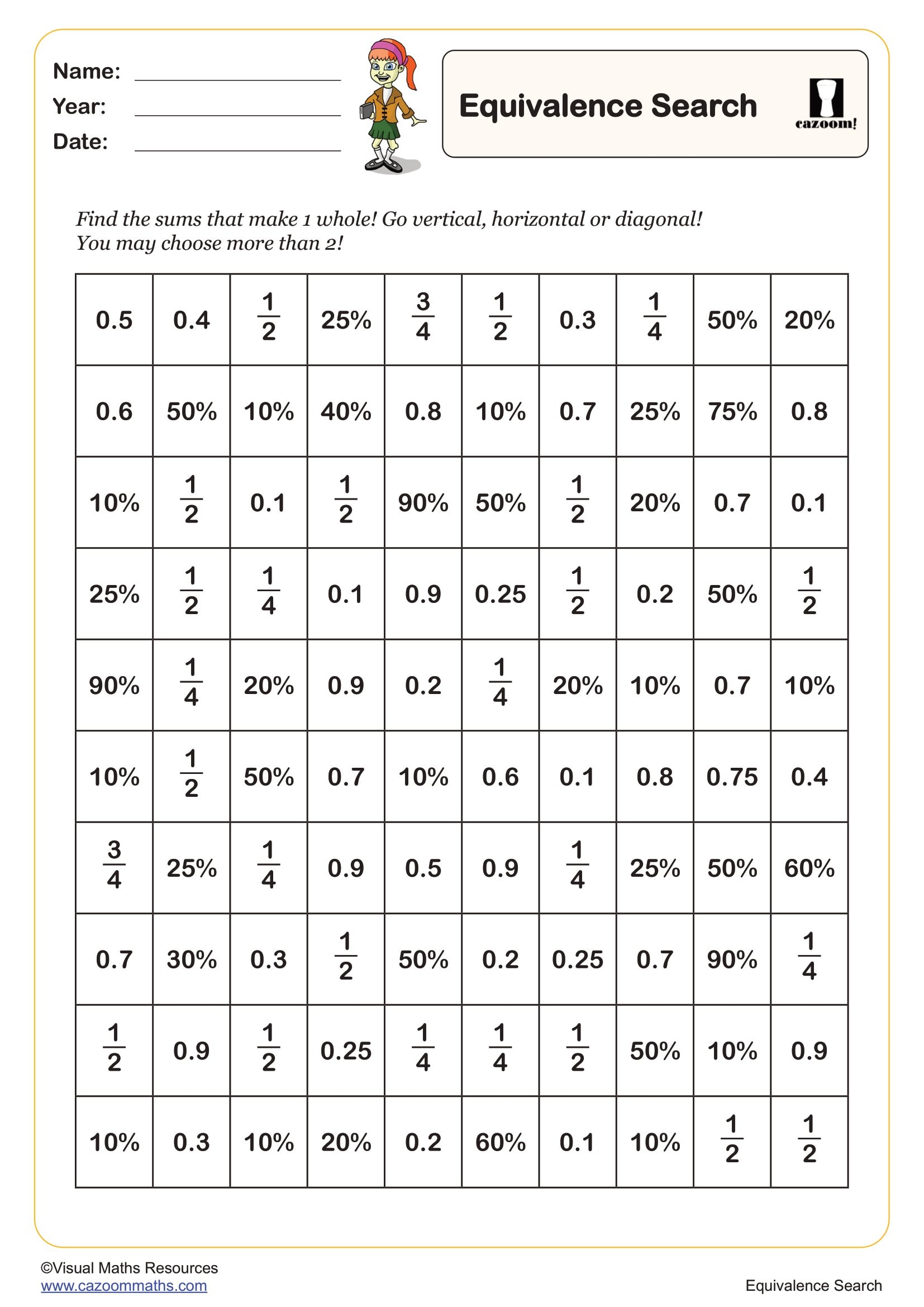
Equivalence Search
Year groups: 5
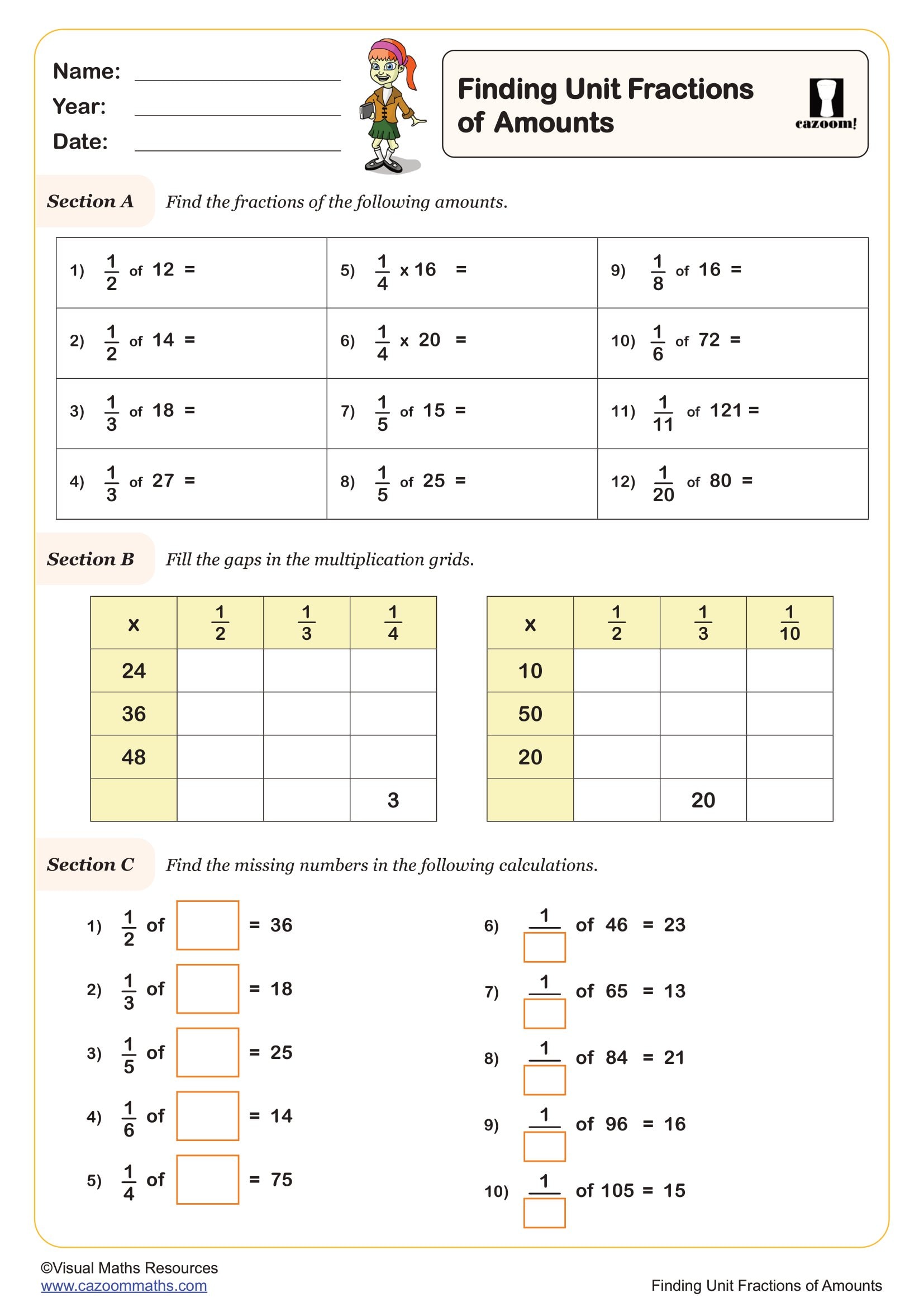
Finding Unit Fractions of Amounts
Year groups: 5
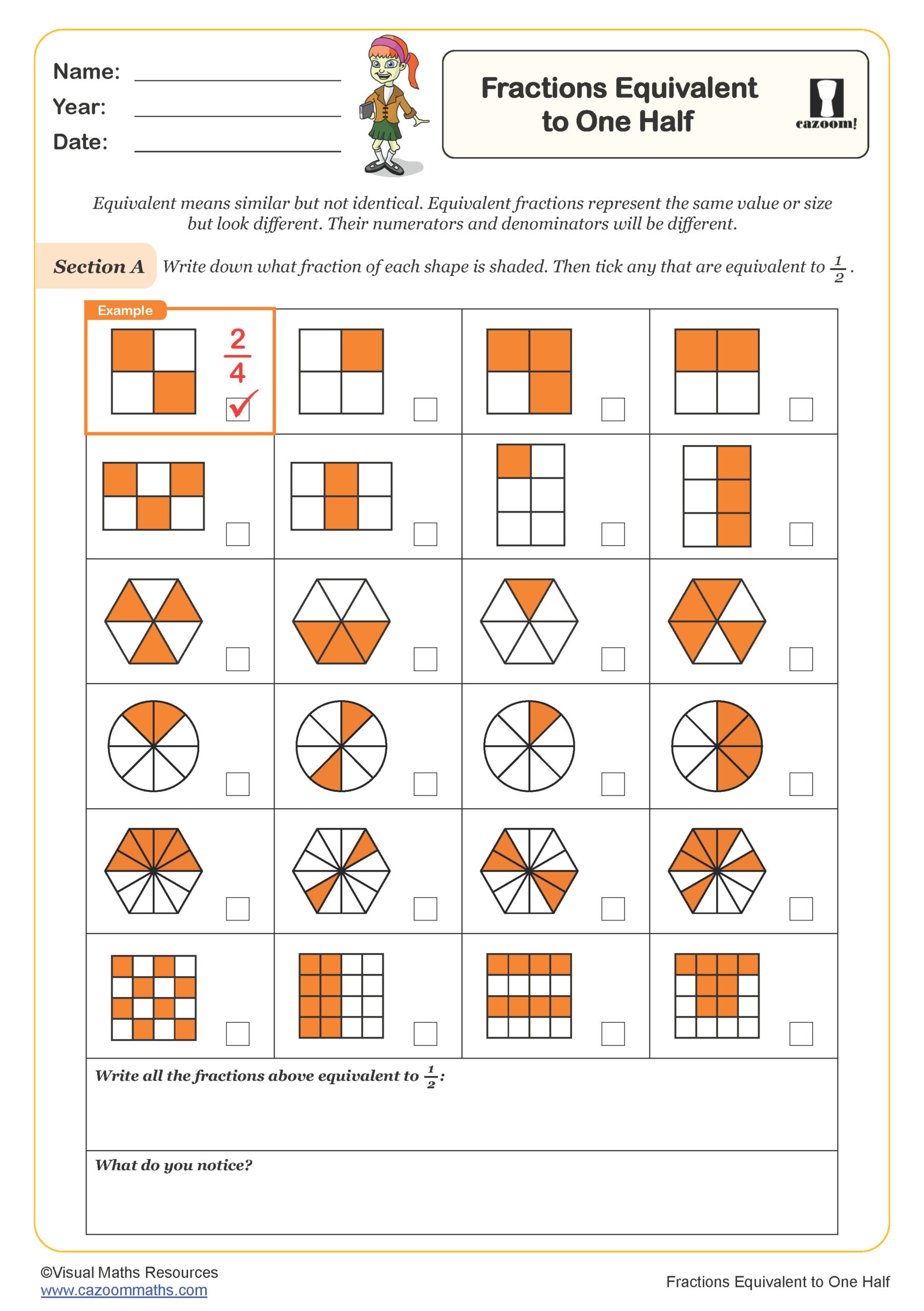
Fractions Equivalent to One Half
Year groups: 5
Fractions Equivalent to One Quarter
Year groups: 5
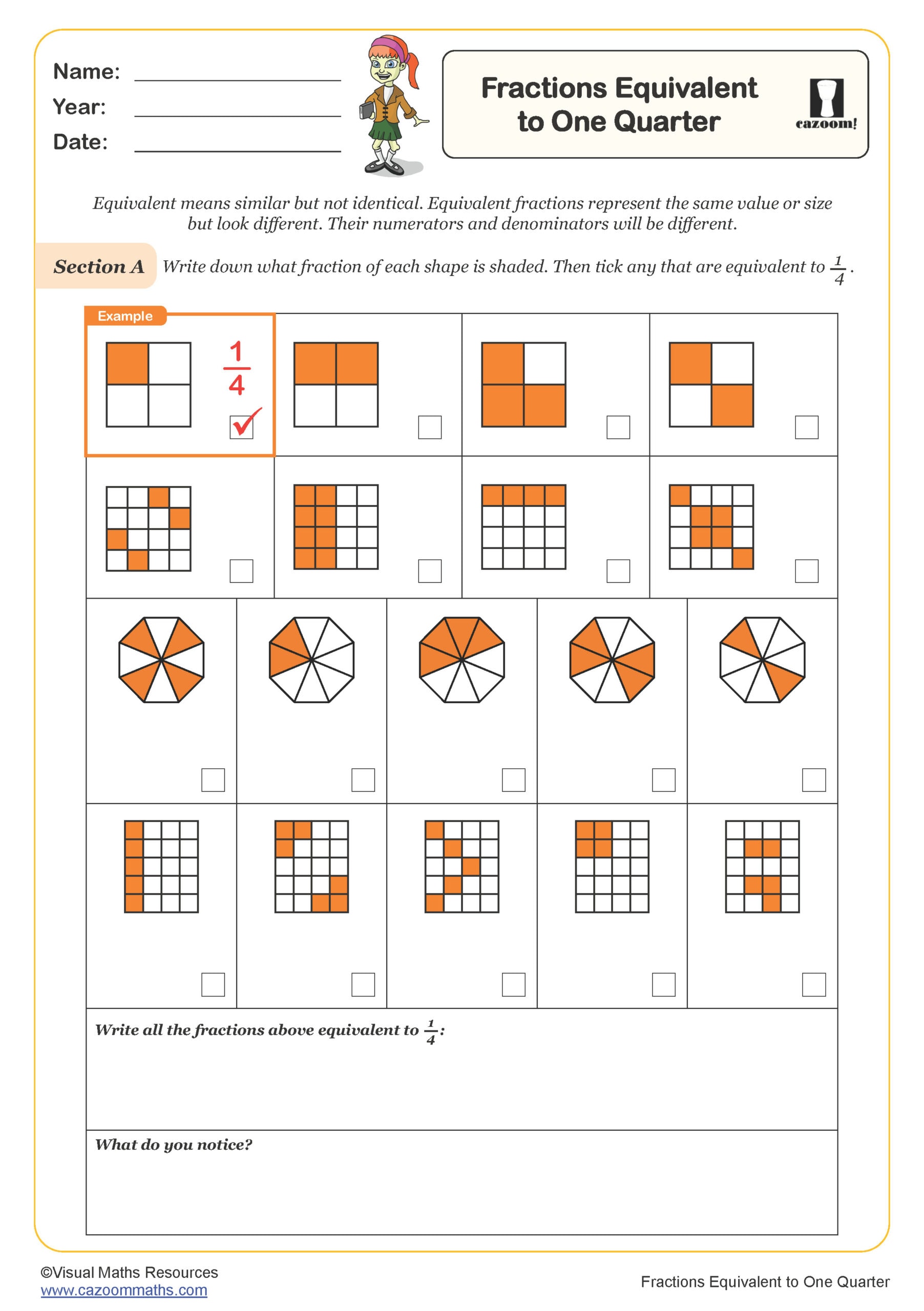
Fractions Equivalent to One Third
Year groups: 5
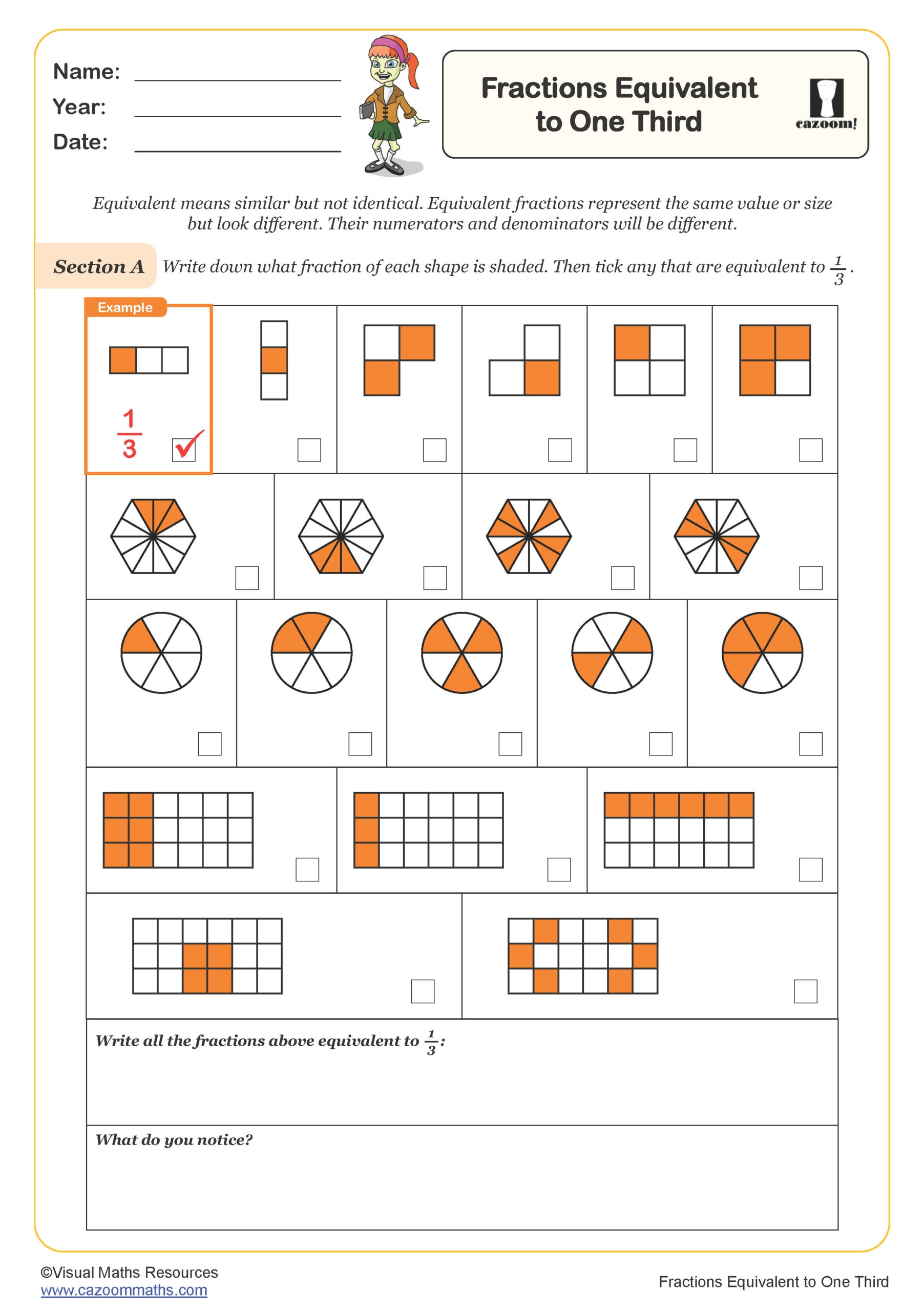
Fractions Greater Than One - Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions
Year groups: 5
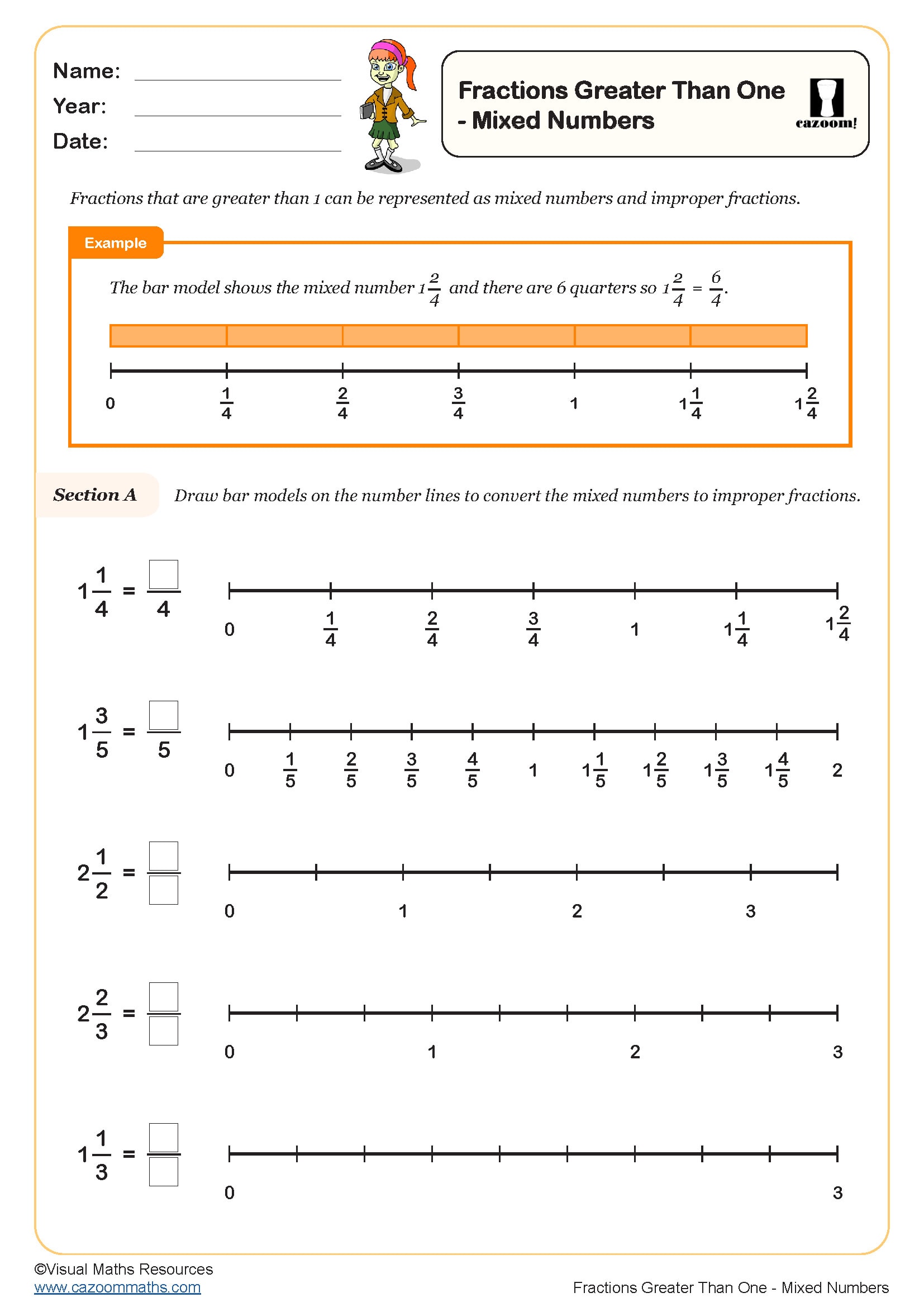
Fractions on Number Lines (A)
Year groups: 5, 6

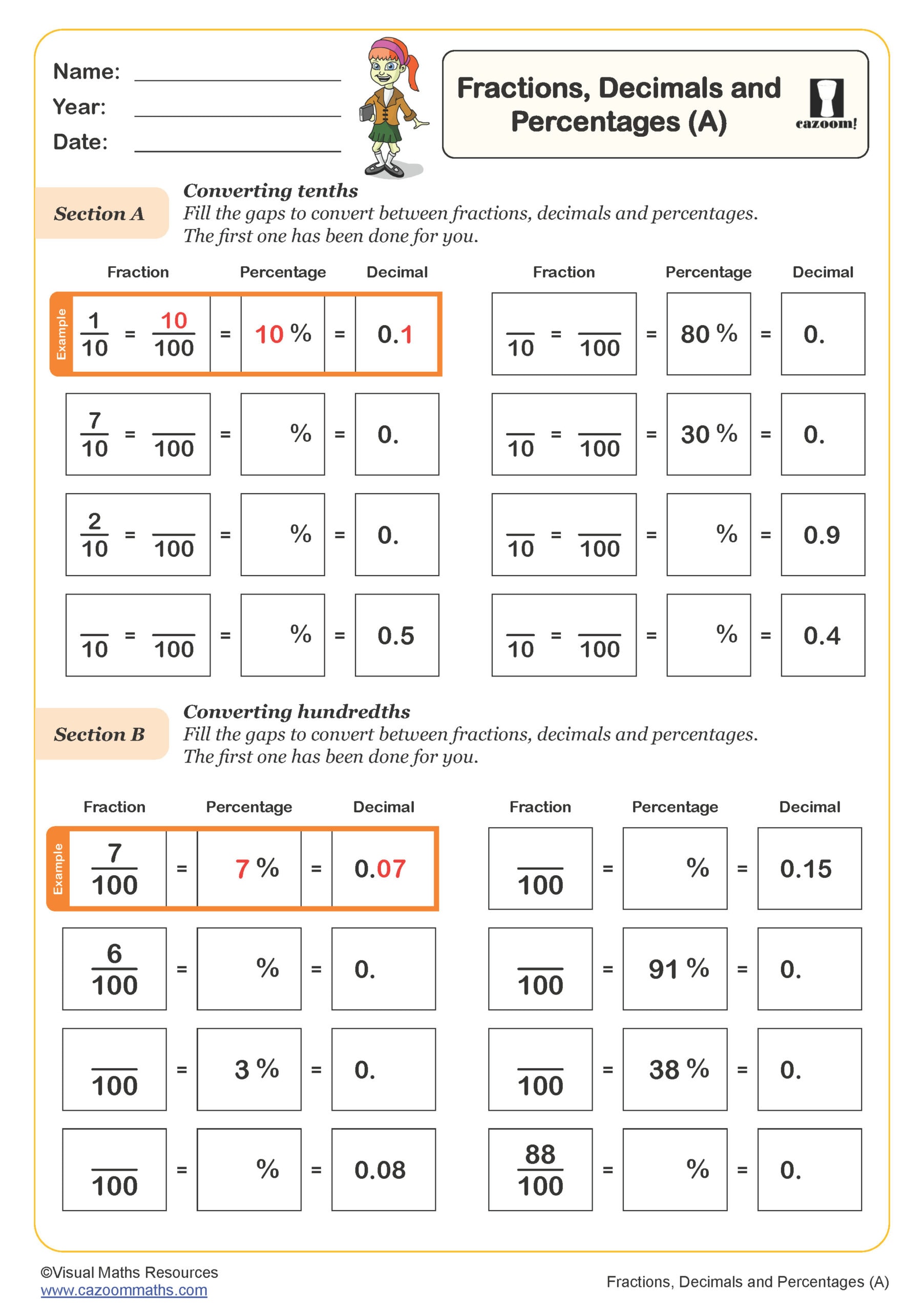
Fractions, Decimals and Percentages (A)
Year groups: 5
Making One
Year groups: 5
Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions (A)
Year groups: 5
Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions (B)
Year groups: 5
Ordering Decimals Maze
Year groups: 5
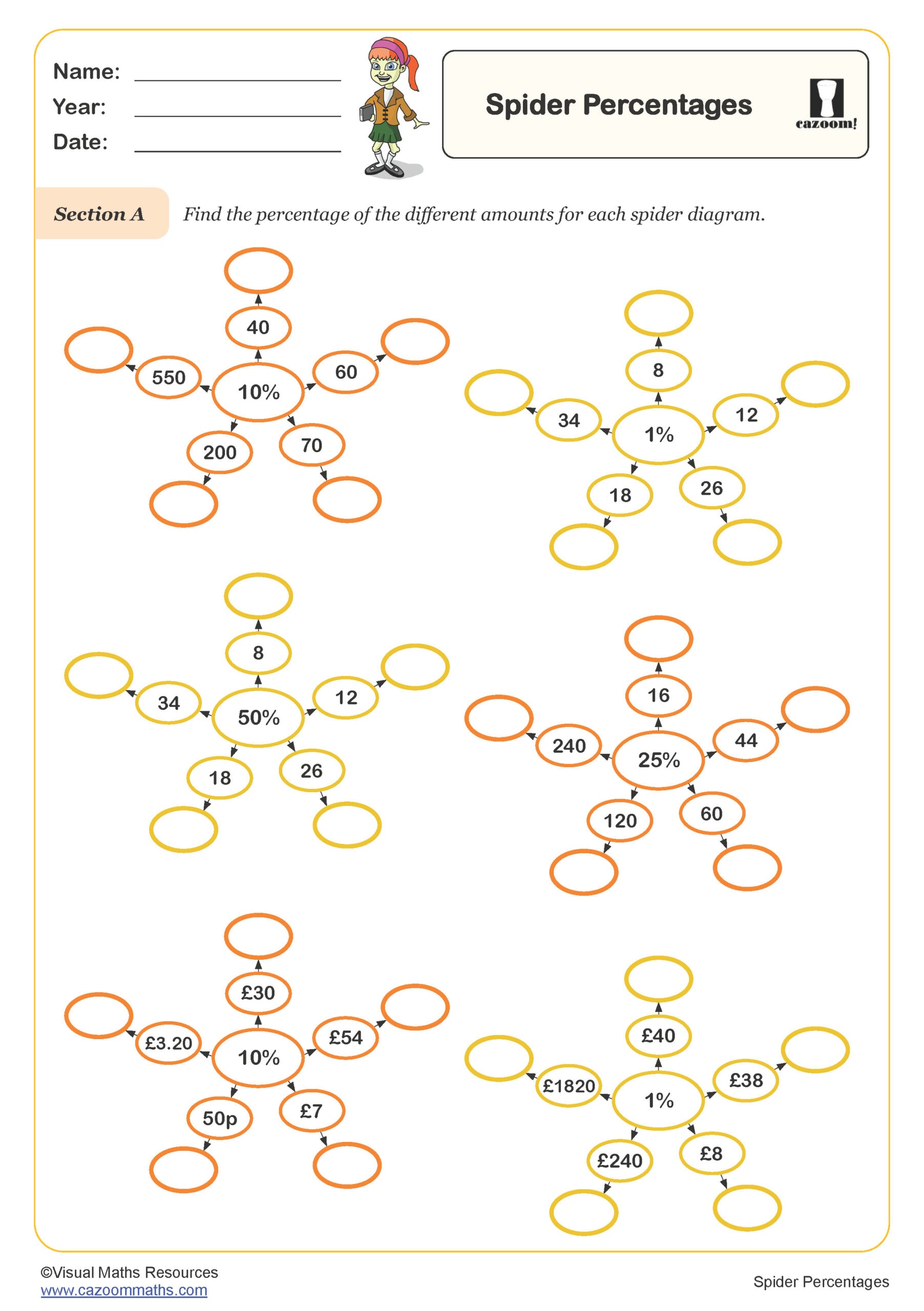
Spider Percentages
Year groups: 5
Using Number Lines to Add and Subtract Decimals Crossing One
Year groups: 5

Adding and Subtracting Fractions
Year groups: 6

Equivalent Fractions (A)
Year groups: 6
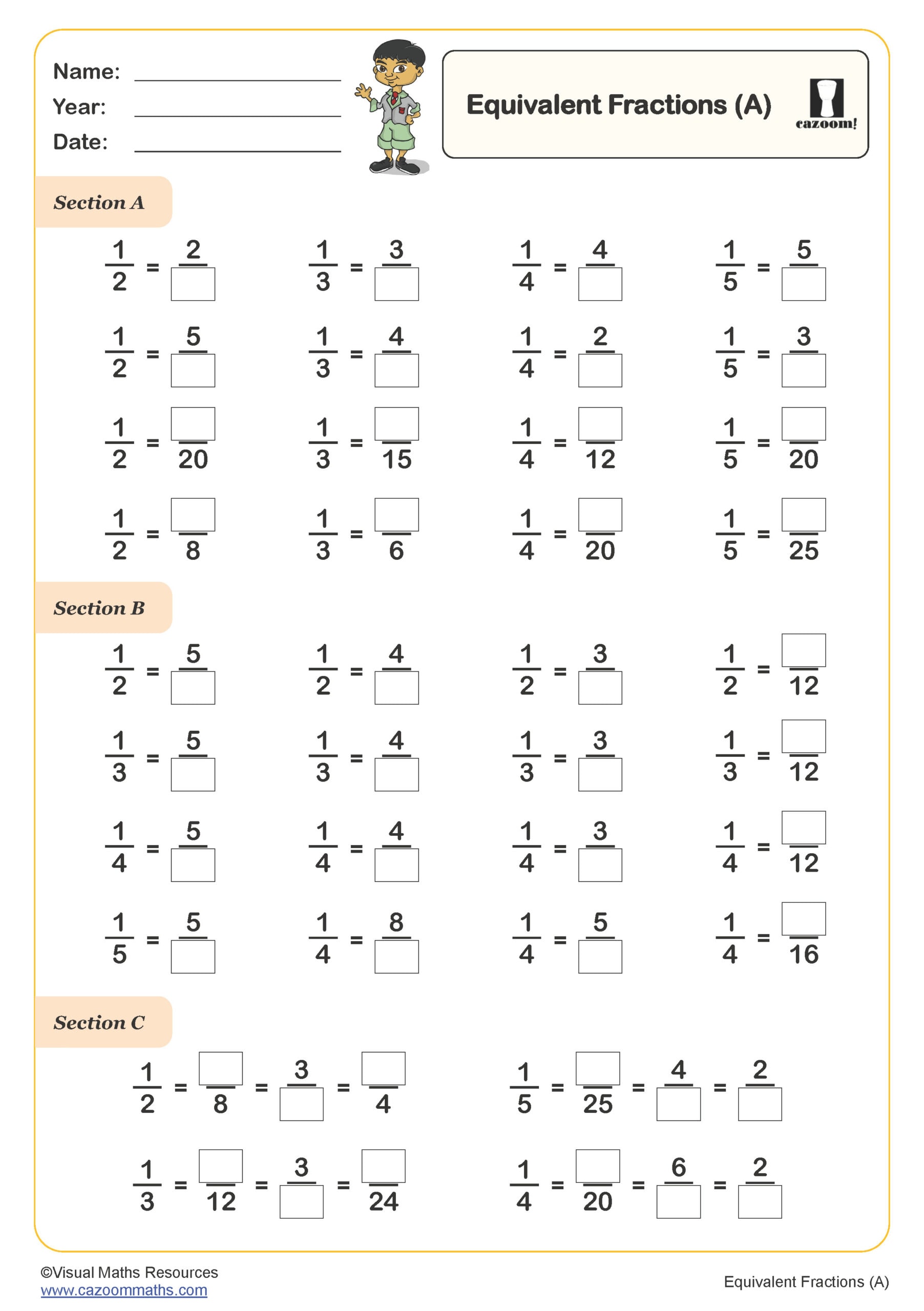
Equivalent Fractions (B)
Year groups: 6
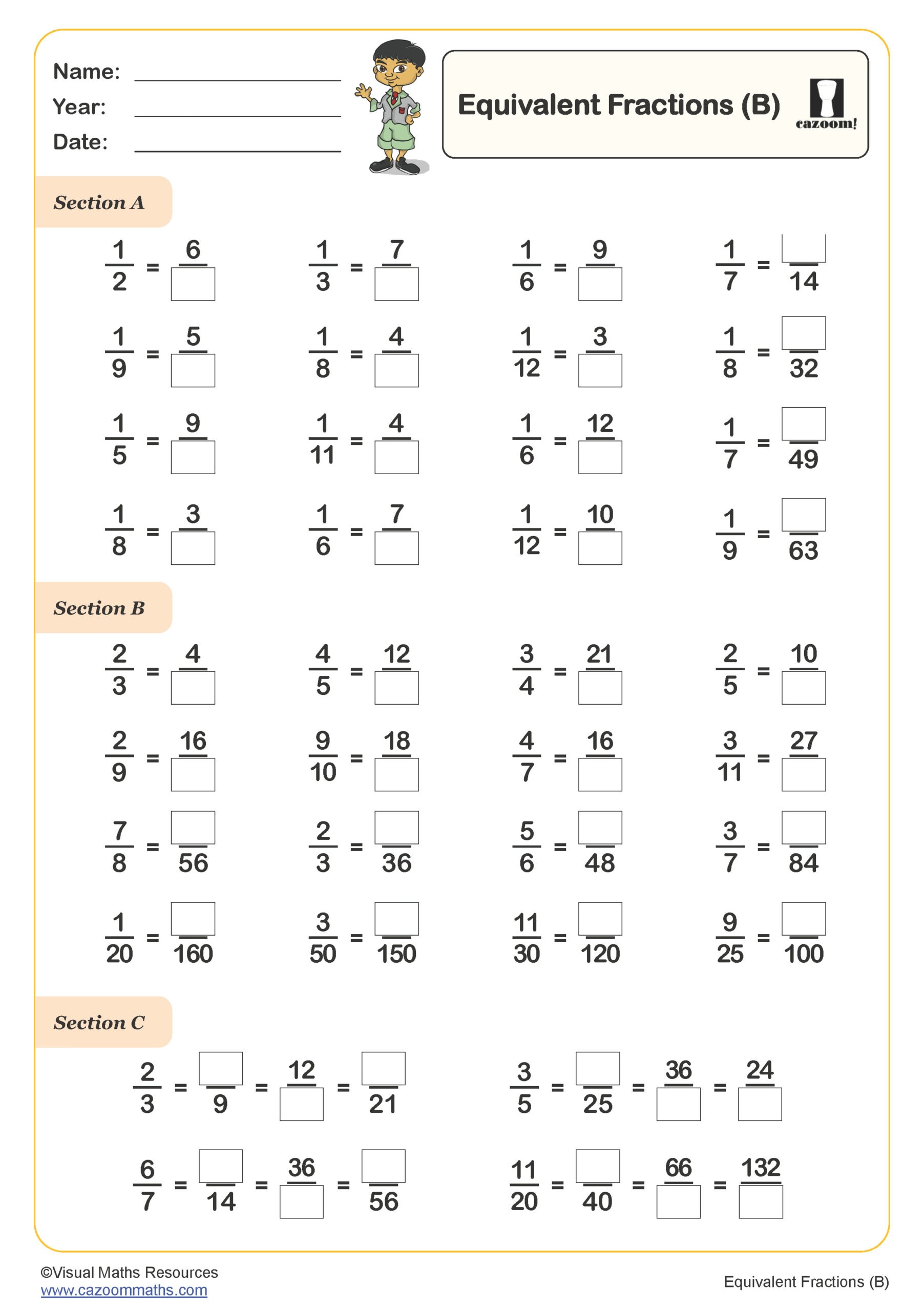
Equivalent Fractions (C)
Year groups: 6
Finding Fractions of Amounts
Year groups: 6
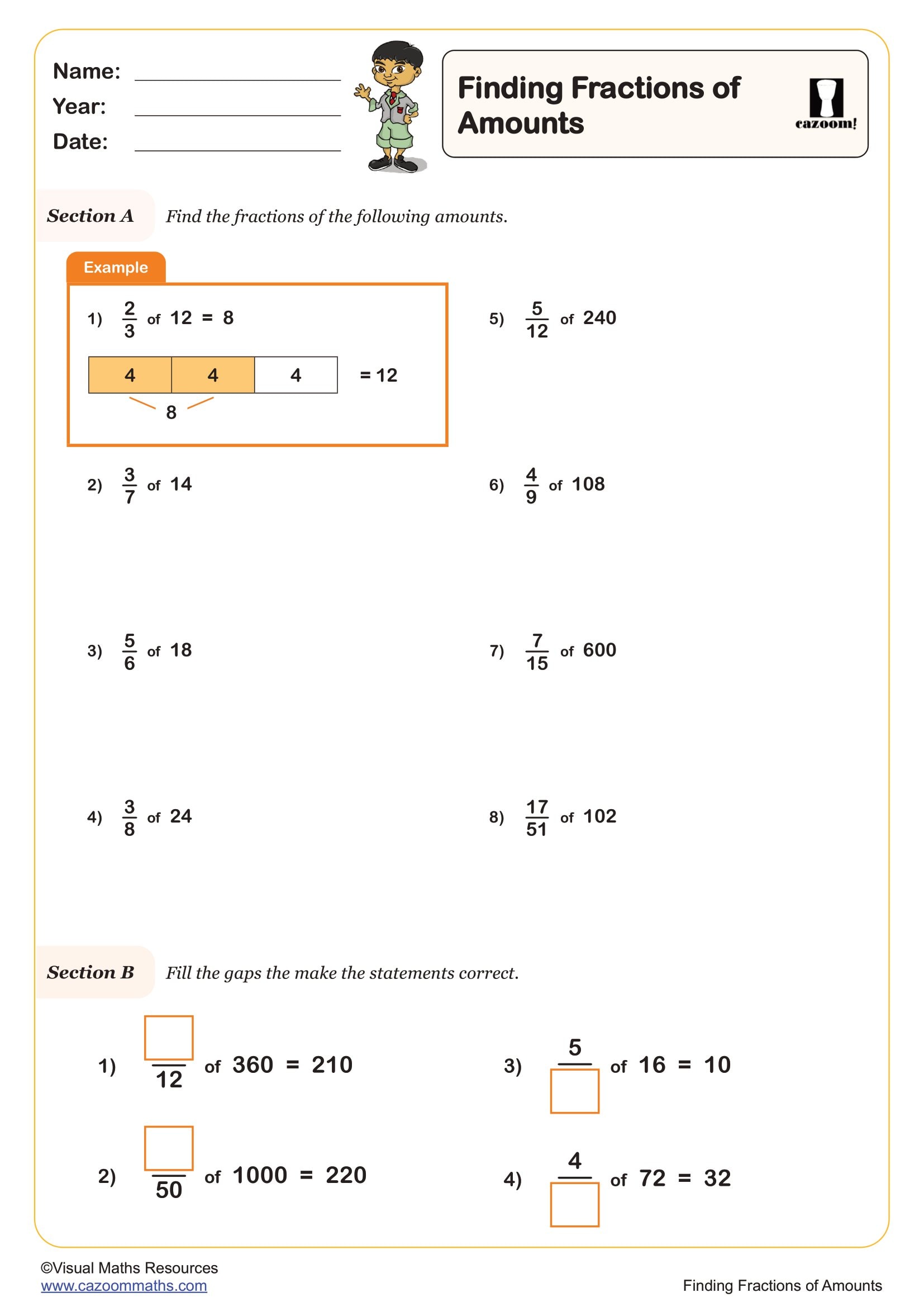
Finding the Whole
Year groups: 6
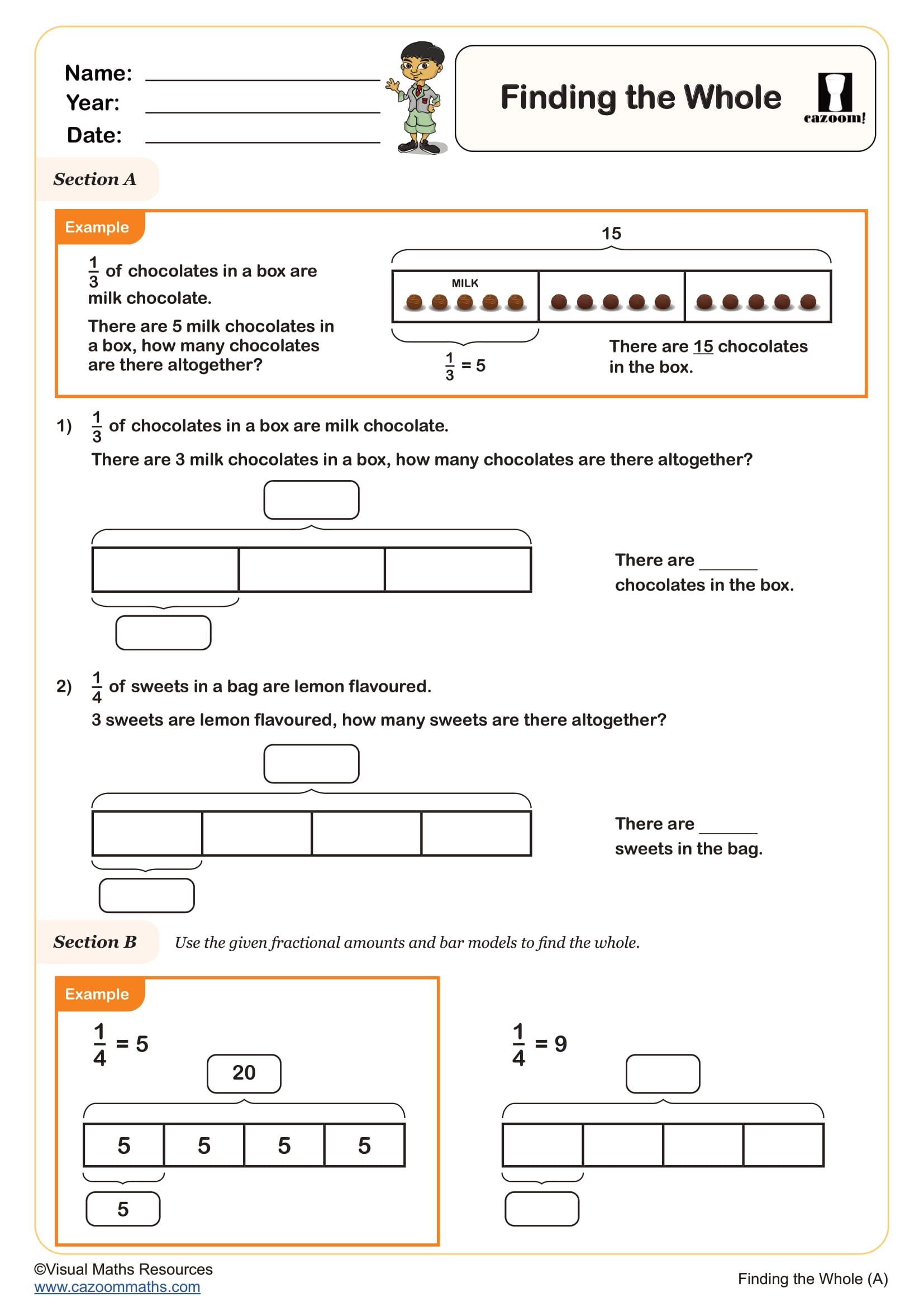
Fractions on Number Lines (B)
Year groups: 6
Introducing the Fraction Wall
Year groups: 6

Labelling a Number Line with Mixed Numbers
Year groups: 6
Mental Percentages
Year groups: 6
Multiply decimals by integers
Year groups: 6
Mutiplying Decimals (A)
Year groups: 6

Ordering Fractions
Year groups: 6
Ordering Fractions, Decimals and Percentages
Year groups: 6
Percentages of Amounts - Using a Bar Model (A)
Year groups: 6

Percentages of Amounts - Using a Bar Model (B)
Year groups: 6

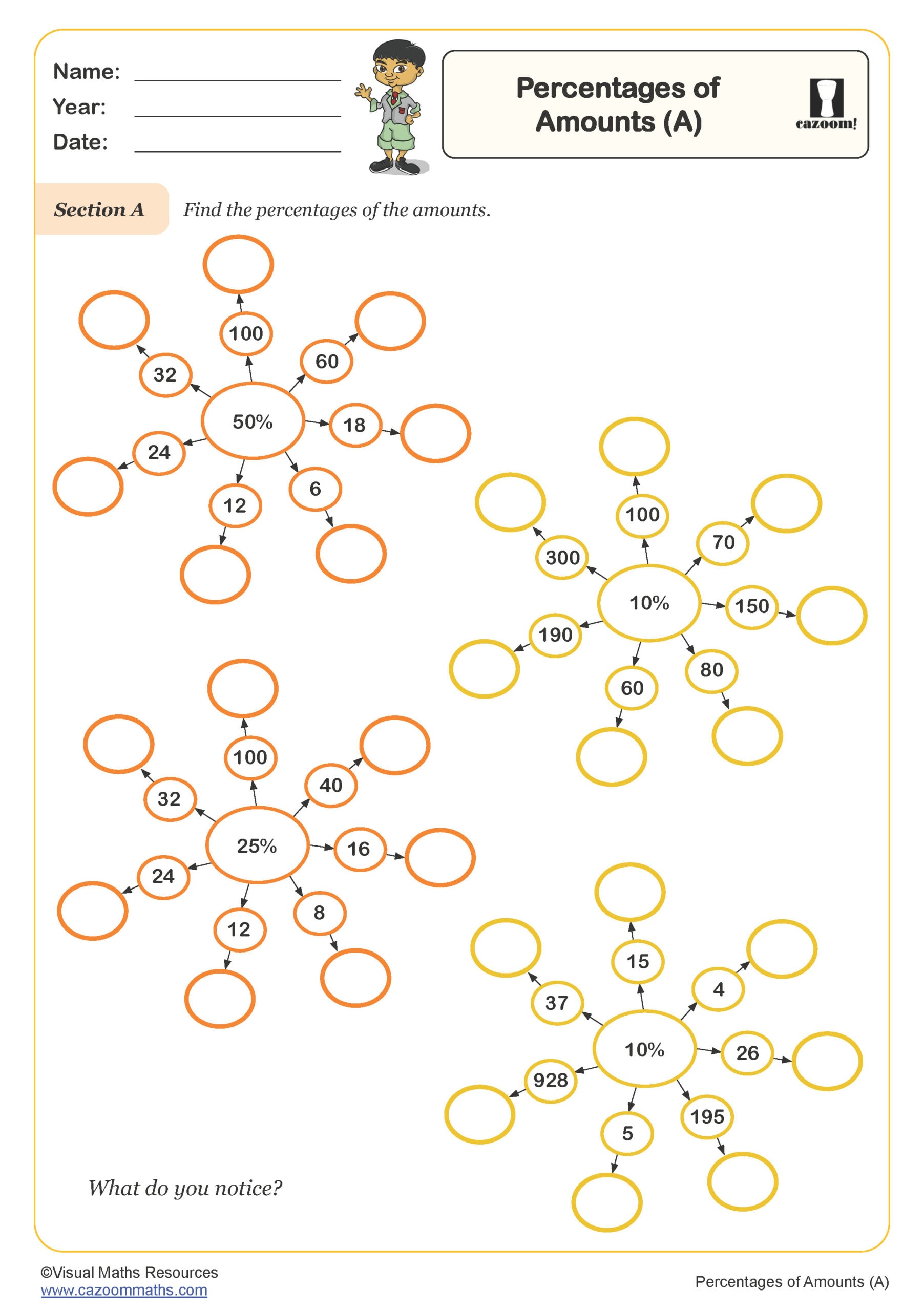
Percentages of Amounts (A)
Year groups: 6
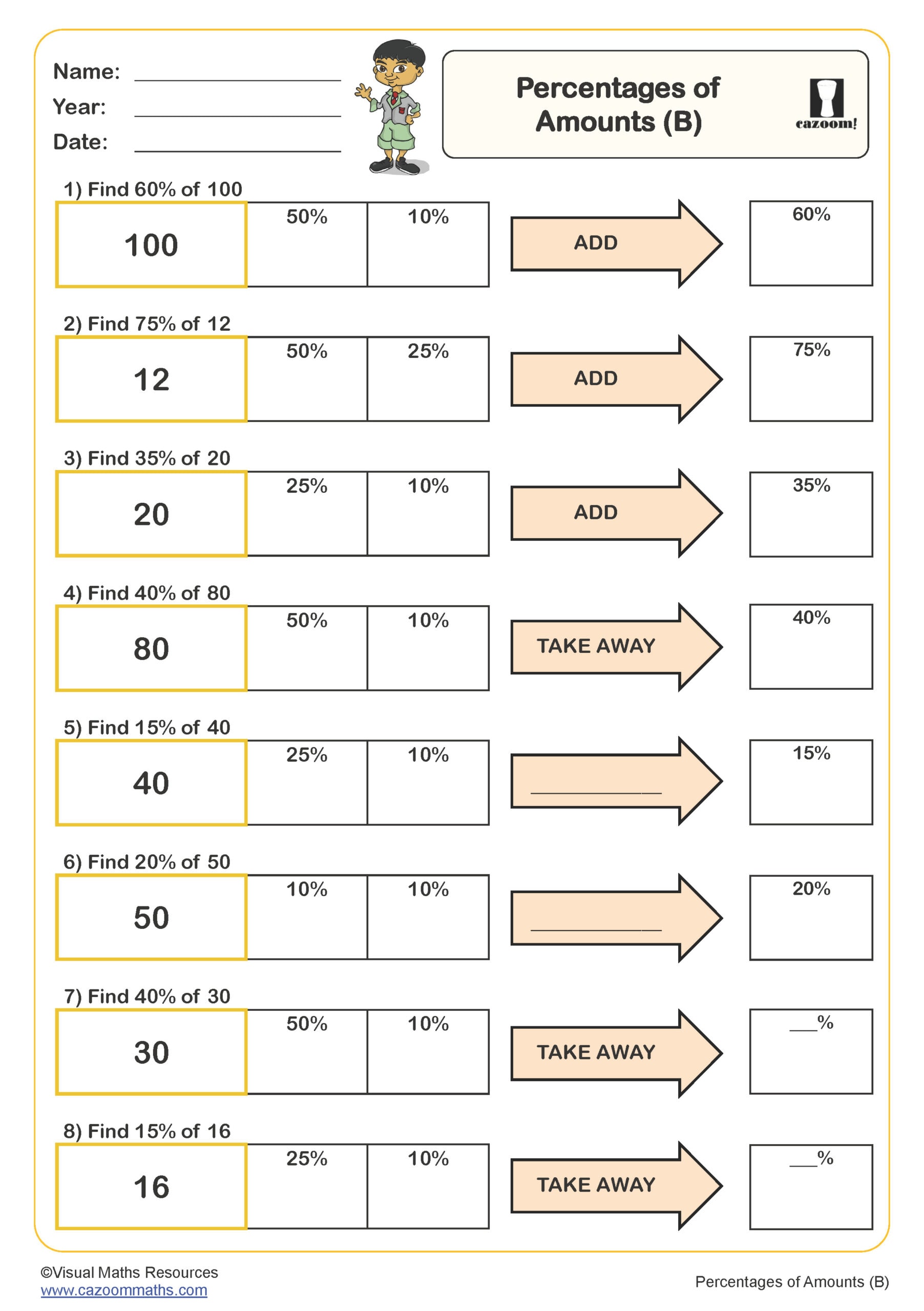
Percentages of Amounts (B)
Year groups: 6
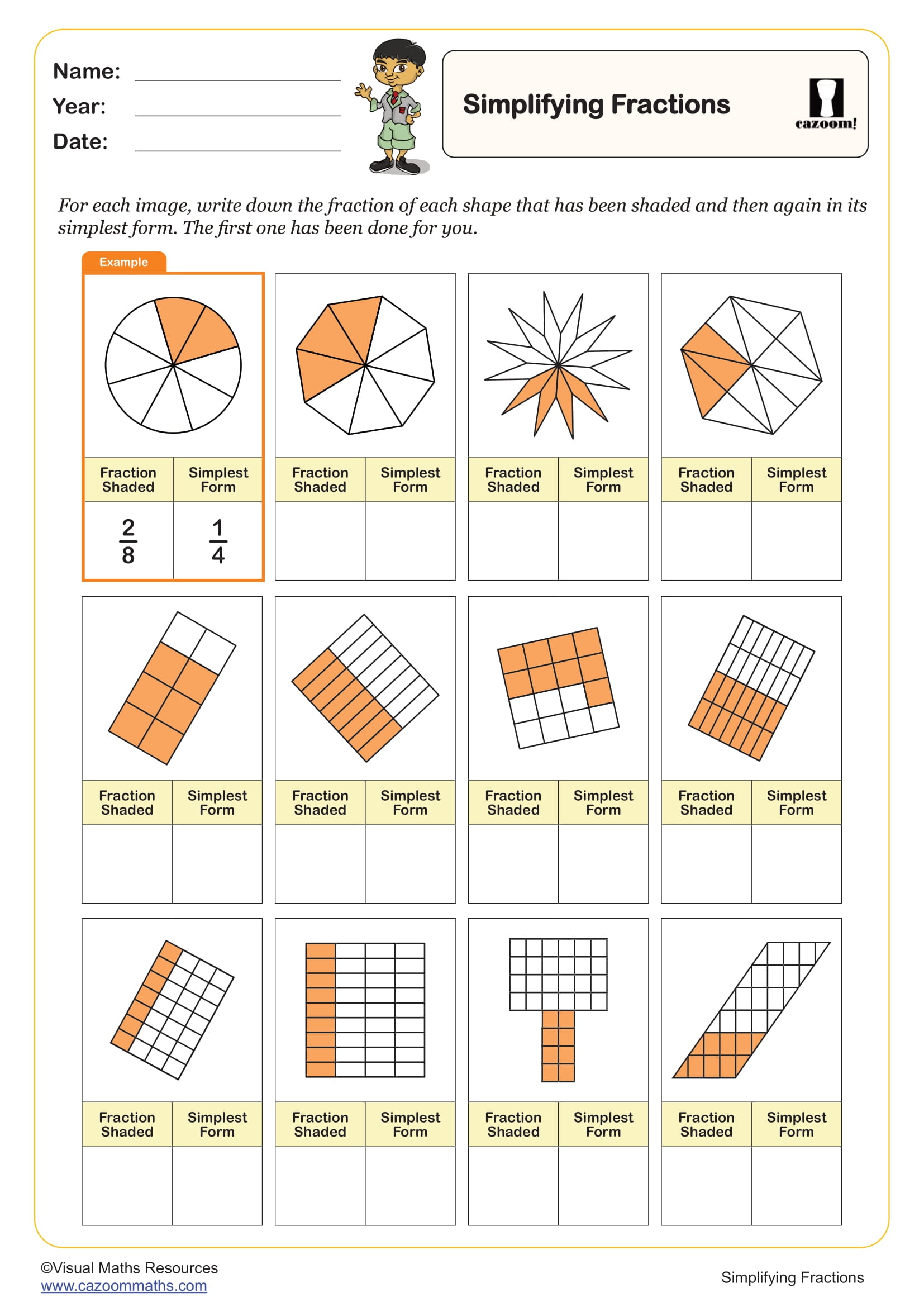
Simplifying Fractions
Year groups: 6
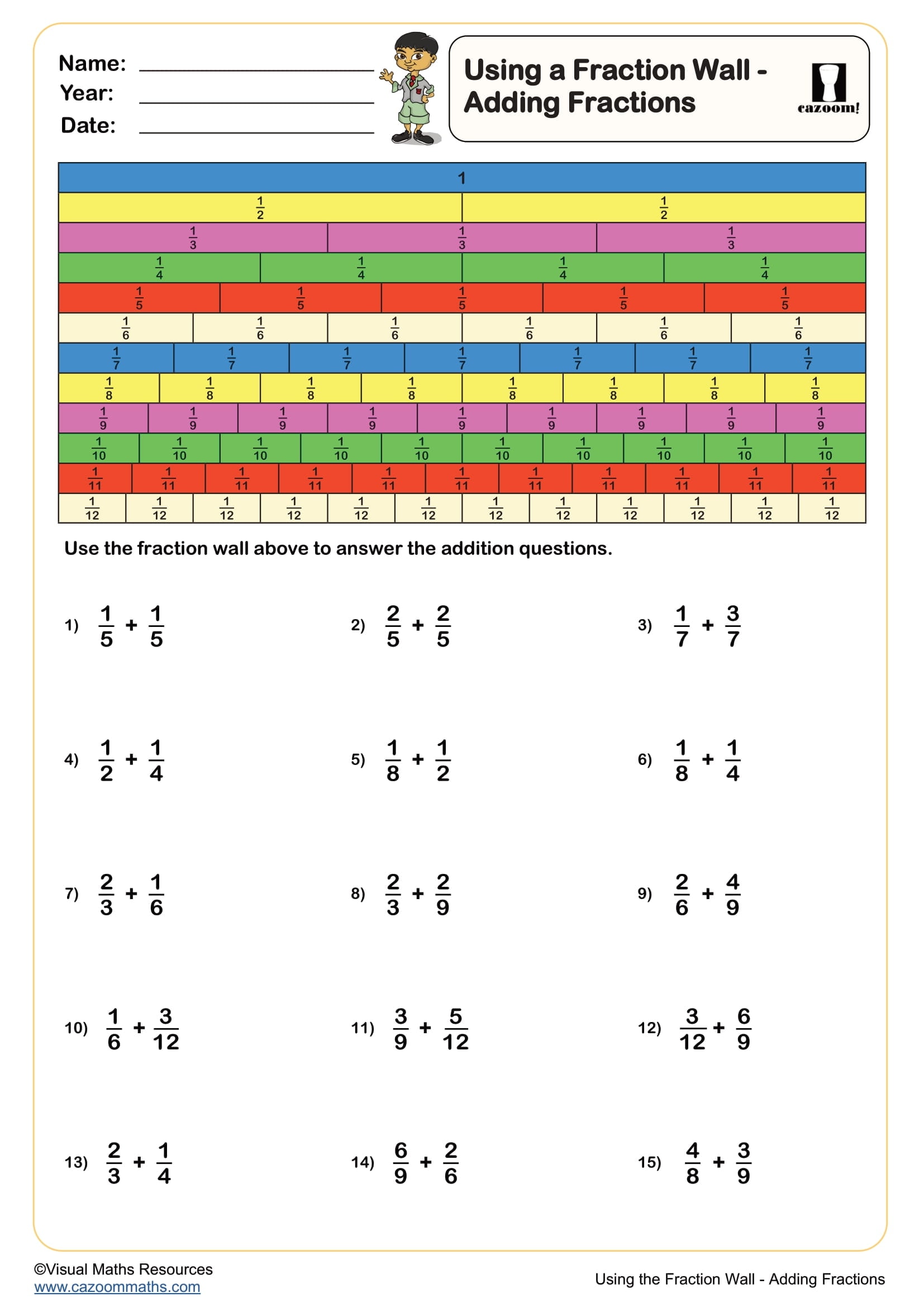
Using a Fraction Wall - Adding Fractions
Year groups: 6
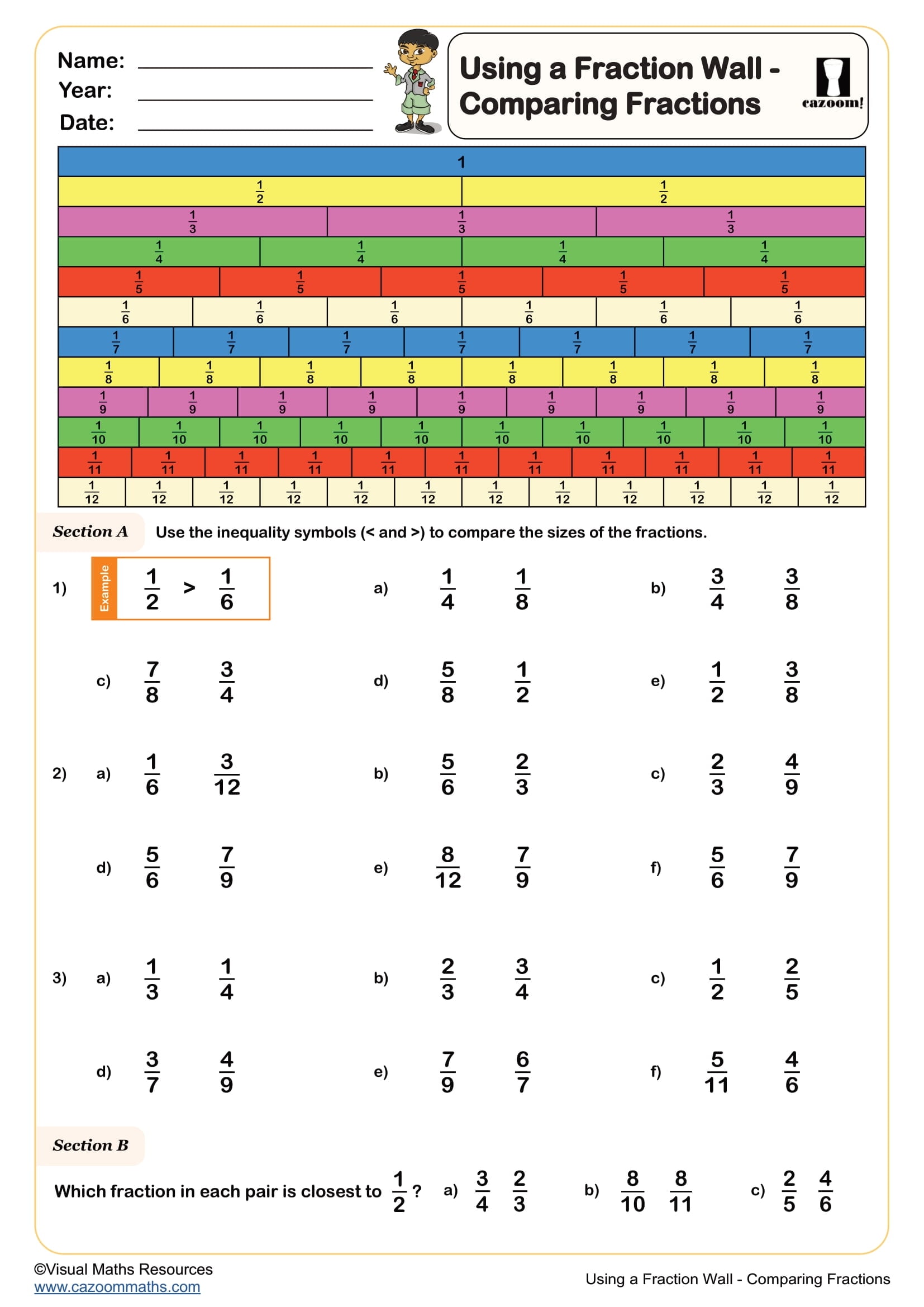
Using a Fraction Wall - Comparing Fractions
Year groups: 6
Using a Fraction Wall - Equivalent Fractions
Year groups: 6

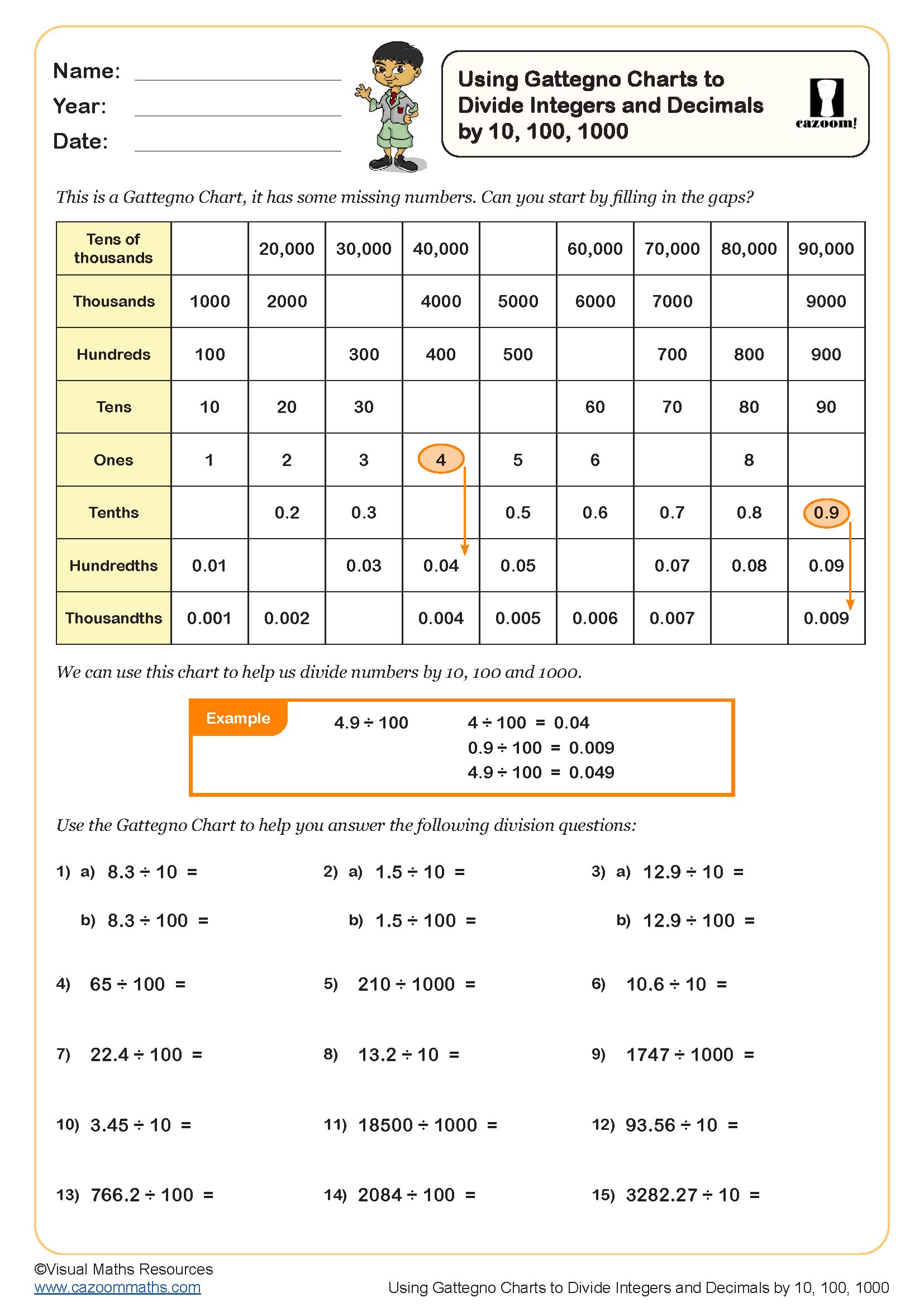
Using Gattegno Charts to Divide Integers and Decimals by 10, 100, 1000
Year groups: 6
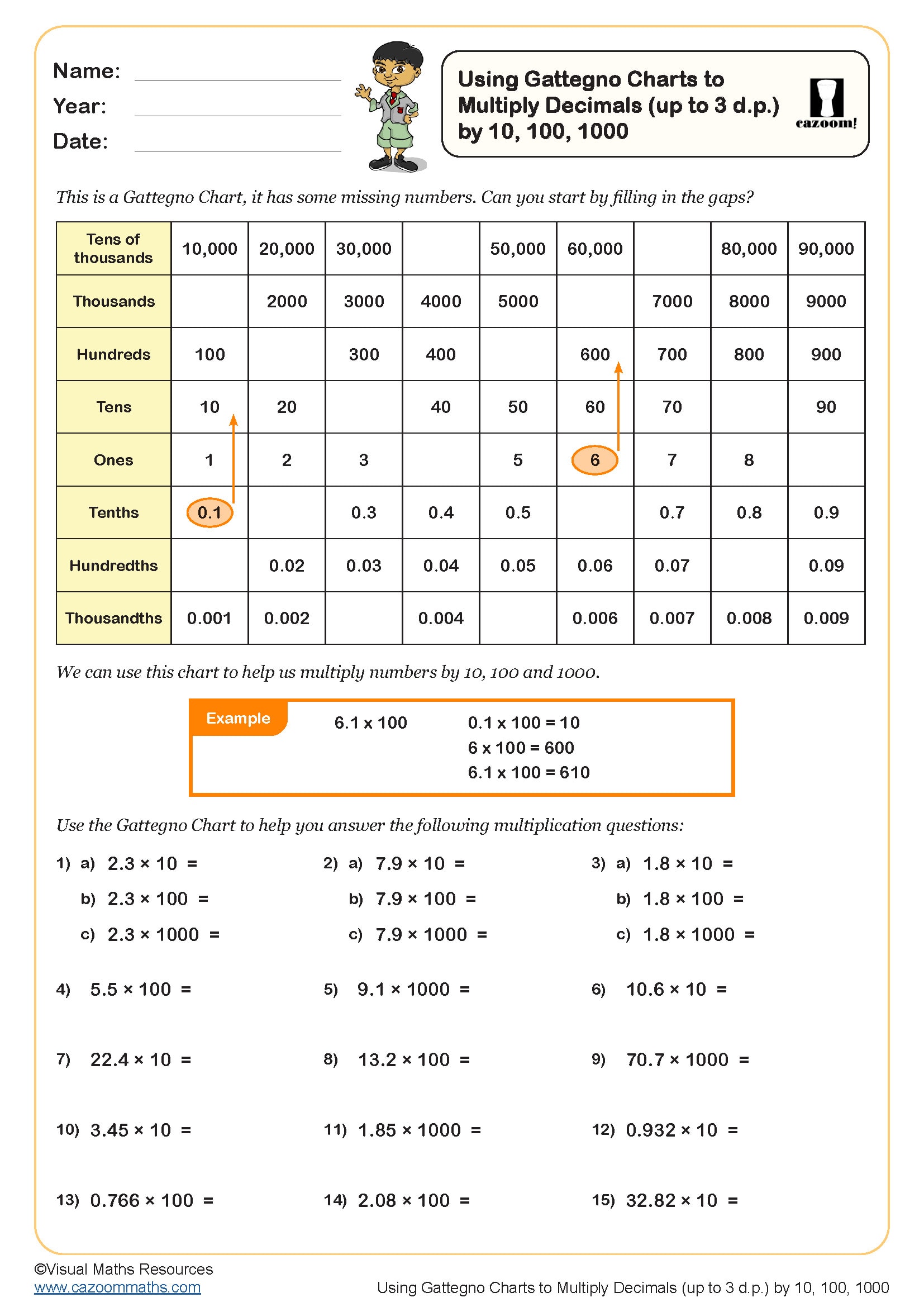
Using Gattegno Charts to Multiply Decimals ( up to 3 d.p.) by 10, 100, 1000
Year groups: 6
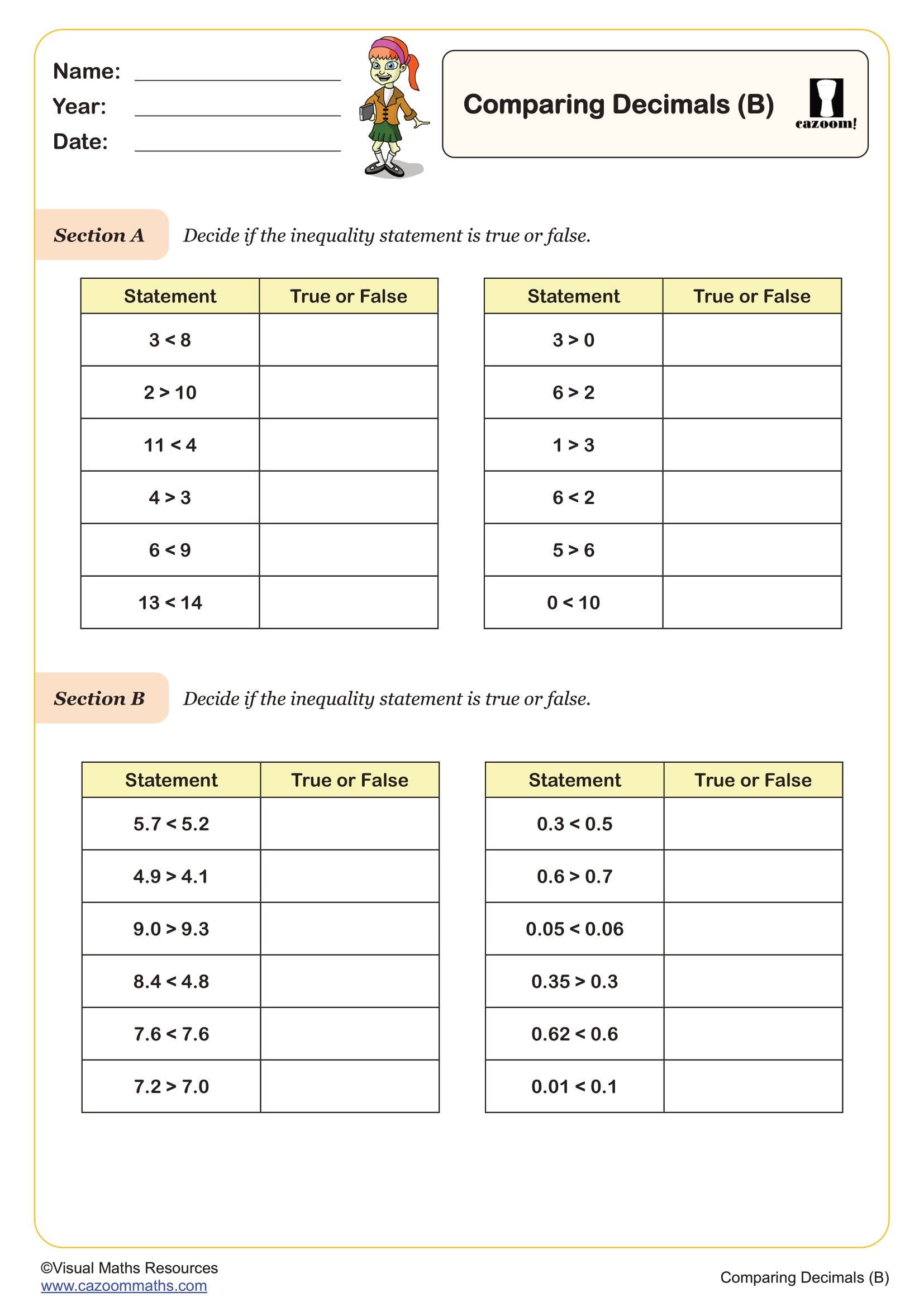
Comparing Decimals (B)
All worksheets are created by the team of experienced teachers at Cazoom Maths.
PRINTABLE PDF FRACTIONS, DECIMALS AND PERCENTAGES WORKSHEETS WITH ANSWERS
Check out and download our FDP Worksheet which will help your students learn about the basic mathematical equations related to Fractions, Decimals, and Percentages. Topics covered in these maths worksheets include the idea of half, and quarter, converting decimals, converting fractions. We also include worksheets on equivalent fractions, simplifying fractions, percentages fractions, finding fractions of a set of objects, adding and subtracting fractions, etc. These worksheets are created in easy-to-download PDF format, include answers, and are designed to help young learners develop problem-solving skills related to Fractions, Decimals, and Percentages. If you’re looking for resources on related topics like comparing fractions with the same denominators, ordering and comparing unit fractions, counting beyond 1 in decimal numbers, converting fluently between basic fractions, decimals and percentages, we also have those for you too! These worksheets are excellent resources for maths practice and will make the learning process fun and interesting!
What Are Fractions, Decimals, and Percentages?
Fractions, decimals, and percentages are different ways to represent parts of a whole in mathematics. A fraction, represented with a numerator above a denominator (like 1/2), denotes how many parts of a whole we have. Decimals, on the other hand, use a point to separate whole numbers from parts of a whole, such as 0.5, which is another way to represent half. Percentages use the percent symbol (%) and show parts per hundred; for instance, 50% means 50 out of 100, which is also equivalent to half. All three methods offer unique ways to describe quantities, and understanding their interrelation is a fundamental aspect of numeracy.
Understanding The Concepts of Fractions, Decimals, and Percentages
Fractions represent parts of a whole, split into equal segments. The top number, or numerator, indicates how many of these segments are being considered, while the bottom number, or denominator, tells us how many equal parts the whole is divided. For instance, in the fraction 3/4, the whole is divided into 4 equal parts and we are considering 3 of them.
Decimals provide another way to denote parts of a whole, using a system based on tens. The decimal point separates whole numbers from the fractional parts. Each place after the decimal represents tenths, hundredths, thousandths, and so on. For example, the decimal 0.25 means we have 25 out of 100 parts of a whole, or a quarter.
Percentages, literally meaning “per hundred”, offer a way to describe parts of a whole based on a scale of 100. When we say 50%, we mean 50 out of 100 parts or half of the whole. It’s a convenient way to compare and understand proportions, especially in contexts like finance and statistics, where relative values are key.
Use of Fractions, Decimals, and Percentages In Real Life
In our day-to-day lives, fractions, decimals, and percentages are the tools we use to make sense of the world around us. These three concepts allow us to measure, compare, and understand quantities. You’ve probably used these in various scenarios, such as a recipe or calculating discounts. We know that a slice of pizza can be one of the hardest things to measure when dividing it with someone else but somehow we manage it. And when it comes to money it is very important that we understand how much something costs or how much we’re saving. Just knowing them doesn’t mean much; actually understanding them will let you make informed decisions whether it be splitting up food or budgeting your expenses.